White-box testing
advertisement

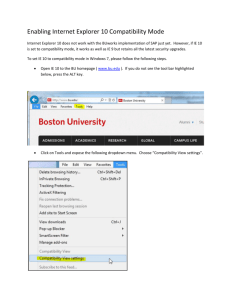
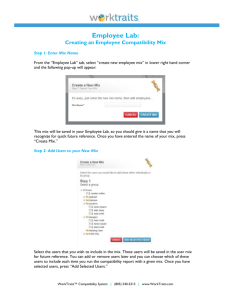
WHITE BOX TESTING K.KARTHIKEYAN How do you test a system? 2 WHITE BOX • White-box testing (also known as clear box testing, glass box testing, transparent box testing, and structural testing) is a method of testing software that tests internal structures or workings of an application, as opposed to its functionality (i.e. black-box testing). In white-box testing an internal perspective of the system, as well as programming skills, are used to design test cases. • White-box testing can be applied at the unit, integration and system levels of the software testing process White box testing Test data Tests Derives Component code Test outputs White box testing technique • White-box test design techniques include the following code coverage criteria: 1. Control flow testing 2. Data flow testing 3. Branch testing 4. Statement coverage 5. Decision coverage 6. Modified condition/decision coverage 7. Prime path testing 8. Path testing BASIC PROCEDURE • White-box testing's basic procedures involves the tester having a deep level of understanding of the source code being tested. • The programmer must have a deep understanding of the application to know what kinds of test cases to create so that every visible path is exercised for testing. • Once the source code is understood then the source code can be analyzed for test cases to be created. These are the three basic steps that white-box testing takes in order to create test cases: • Input involves different types of requirements, functional specifications, detailed designing of documents, proper source code, security specifications. This is the preparation stage of white-box testing to layout all of the basic information. Cont.. • Processing involves performing risk analysis to guide whole testing process, proper test plan, execute test cases and communicate results. • This is the phase of building test cases to make sure they thoroughly test the application the given results are recorded accordingly. • Output involves preparing final report that encompasses all of the above preparations and results. Advantages • Provides traceability of tests from the source, allowing future changes to the software to be easily captured in changes to the tests. • White box tests are easy to automate. • White box testing give clear, engineering-based, rules for when to stop testing. Disadvantages • The tests focus on the software as it exists, and missing functionality may not be discovered. • White-box testing requires a programmer with a high-level of knowledge due to the complexity of the level of testing that needs to be done. • Expensive as one has to spend both time and money to perform white box testing. Compatibility testing • Compatibility testing, part of software non-functional tests, is testing conducted on the application to evaluate the application'scompatibility with the computing environment. • Computing capacity of Hardware Platform (IBM 360, HP 9000, etc.).. • Bandwidth handling capacity of networking hardware • Compatibility of peripherals (Printer, DVD drive, etc.) • Operating systems (Linux, Windows, Mac etc.) • Database (Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, etc.) • Other System Software (Web server, networking/ messaging tool, etc.) • Browser compatibility (Chrome, Firefox, Netscape, Internet Explorer, Safari, etc.) Testing Life Cycle Project Initiation Summary Reports System Study Analysis Test Plan Regression Test Design Test Cases Report Defects Execute Test Cases ( manual /automated ) Testing Levels • Unit testing • Integration testing • System testing UNIT TESTING Tests each module individually. Follows a white box testing (Logic of the program). Done by developers. INTEGRATION TESTING Once all the modules have been unit tested, integration testing is performed. It is systematic testing. Produce tests to identify errors associated with interfacing. Types: Big Bang Integration testing Top Down Integration testing Bottom Up Integration testing Mixed Integration testing SYSTEM TESTING The system as a whole is tested to uncover requirement errors. Verifies that all system elements work properly and that overall system function and performance has been achieved. Types: Alpha Testing Beta Testing Acceptance Testing Performance Testing Alpha Testing It is carried out by the test team within the developing organization . Beta Testing It is performed by a selected group of friendly customers. Acceptance Testing It is performed by the customer to determine whether to accept or reject the delivery of the system. Performance Testing It is carried out to check whether the system meets the nonfunctional requirements identified in the SRS document. Types of Performance Testing: Stress Testing Volume Testing Configuration Testing Compatibility Testing Regression Testing Recovery Testing Maintenance Testing Documentation Testing Usability Testing THANK U