Ⅰ The first clear link between cyclin and MPF
advertisement

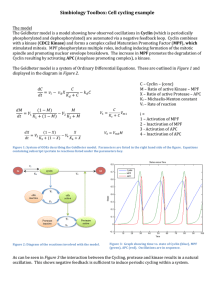
Ⅰ The first clear link between cyclin and MPF was demonstrated by Joan Ruderman and her colleagues at the Woods Hole Marine Biological Laboratore • .In these studies,an mRNA encoding cyclin A was transcribed in vitro from a cloned DNA fragment that contained the entire cyclin A coding sequence. • The identity of this mRNA was verified by translating it in vitro and finding that it encoded authentic clam cyclin A. .When the synthetic cyclin mRNA was injected into Xenopus oocytes,the cells underwent germinal vesicle breakdown and chromosome compaction over a time course not unlike that induced by progesterone treatment(Figure 5). • These results suggested that the rise in cyclin A,which occurs normally during meiosis and mitosis, has a direct role in promoting entry into M phase. • (The amount of cyclin A normally drops rapidly and must be resynthesized prior to the next division or the cells cannot reenter M phase.) But what is the relationship between cyclins and MPF? Ⅱ • One of the difficulties in answering this question was the use of different organisms. • (MPF had been studied primarily in amphibians,and cyclins in sea urchins and clams.) • Evidence indicated that frog oocytes contain a pool of inactive preMPF molecules,which are converted to active MPFs during meiosis Ⅰ. • Cyclin,on the other hand,is totally absent from clam oocytes but appears soon after fertilization. • Ruderman considered the possibility that cyclin A is an activator of MPF. Ⅲ • Meanwhile,another line of research was initiated to purify and characterize the substance responsible for MPF activity. • (In 1980,Michael Wu and John Gerhart of the University of California,Berkeley,accomplished a 20-to 30-fold purification of MPF by precipiating the protein in ammonium sulfate and subjecting the redissolved material to column chromatography.) • .In addition to stimulating oocyte maturation,injections of the partially purified MPF stimulated the incorporation of 32P into protins of the amphibian oocyte. • .When partially purified MPF perparations were incubated with [32P]ATP in vitro,proteins present within the sample became phosphorylated,suggesting that MPF induced maturation by acting as a protein kinase. Ⅳ • 1.MPF was finally purified in 1988 by a series of six successive chromatographic steps. • 2.MPF activity in these purified preparations was consistently associated with two polypeptides,one having a molecular mass of 32kDa and the other of 45 kDa. • 3.The purified MPF preparation possessed a high level of protein kinase activity,as determined by the incorporation of radioactivity from [32P]ATP into proteins. • 4.When the purified preparation was incubated in the presence of [32P]ATP,the 45-kDa polypeptide became labeled. Ⅴ • .By the end of the 1980s,the efforts to uncover the role of cyclins and MPF had begun to merge with another line of research that had been conducted on fission yeast by Paul Nurse and his colleagues at the University of Oxford. • .It had been shown that yeast produced a protein kinase with a molecular weight of 34kDa whose activity was required for these cells to enter M phase . •The yeast protein was called p34cdc2 or simply cdc2. • The first evidence of a link between cdc and MPF came as the result of a collaboration between yeast and amphibian research groups. Antibodies formed against cdc2 from fission yeast were shown to react specifically with the 32-kDa component of MPF isolated from Xenopus eggs. •These findings indicate that this component of MPF is a homologue of the 34-kDa yeast kinase and,therefore,that the machinery controlling the cell cycle in yeast and vertebrates contains evolutionarily conserved components. Ⅵ • A similar study using antibodies against yeast cdc2 showed that the homologous protein in vertebrates does not fluctuate during the cell cycle. • .This supports the proposal that the 32kDa protein kinase in vertebrate cells depends on another protein. .In all of these cases,it was shown that the active MPF present in M-phase animal cells is a complex consisting of two types of subunits:(1)a 32-kDa subunit that contains the protein kinase active site and is homologous to the yeast cdc2 protein kinase,and (2) a larger subunit (45 kDa) indentified as a cyclin whose presence is required for kinase activity. The studies described in this Experimental Pathway provided a unified view of the regulation of the cell cycle in all eukaryotic organisms. . Thanks!!