Types of Business - Glen Innes High School
advertisement

Types of Business
Lesson 5
BUSINESS CLASSIFICATIONS
• Business organisations can be classified in a number of
different ways. The key classifications include:
1. Size: often in terms of the number of people the
business employs.
2. Work Type: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
and quinary.
3. Industry Sector: mining, manufacturing, agricultural,
construction, financial.
4. Legal Structure (Business Ownership): sole trader,
partnership, company.
SIZE OF BUSINESS
ENTERPRISES
Small Business Enterprises
• Usually sole trader and partnerships.
• Common in the following areas: farming, retailing and
building, professions such as medicine, dentistry, law and
accounting.
• Non-manufacturing firms such as retail outlets, which
employ less than 20 employees.
• Manufacturing firms - less than 100 employees.
• Independently owned and managed.
• Small share of the market
• Financed by the owner.
• About 96% of businesses in Australia are small, and employ
about half of the workforce.
Medium Business Enterprises
• Usually public companies.
• One with 20 to 200 employees.
• Mainly in personal services and
manufacturing.
Large Business Enterprises
•
•
•
•
Often public companies.
One that employs more than 200 people.
Found in the public sector, eg Telstra
In the private sector - two largest private enterprise
companies are Coles-Myer and BHP.
• ‘Big Business’ – that small number of companies that
employ the other half of the workforce.
• Multinationals – based here, but operating overseas.
• Transnationals – internationally based and owned.
WORK TYPE
Primary Sector
• Provides the raw materials on which other
economic activity depends
• Involves the exploitation of raw materials (coal
mining, drilling for oil), the growth of food and
textile crops, forestry, fishing and quarrying.
Some of these resources are renewable, some
are non-renewable
• Involves low value added industries - has an
environmental consequence, particular during
resource exhaustion
Secondary Sector
• Manufacturing - "Manufacturing has always been
a necessary human activity ever since the first
fashioning of a plough or spear from the branch
of a tree" - Adam Smith.
• Adds more value by processing or both
processing and combining raw materials.
• Capital or basic industries produce equipment for
other industries.
• Assembly industries ('screw-driver industries')
• Consumer industries produce goods for direct
sale to consumers.
Tertiary Sector
• Service sector: produces no physical 'product'
• Historically the largest single group has been
servants and slaves - today includes fast food
operatives and geriatric health care.
• Not necessarily highly paid - One of major
examples is Tourism.
Quaternary Sector
• Originally Sub-set of tertiary sector - Reliance
on high-skill labour.
• Includes wholesaling and advertising.
Information production and management.
Quinary Sector
• Not widely used.
• Splits paid and unpaid domestic and
accommodation labour from the Quaternary
category.
• Initiated by Barry Jones (‘Sleepers Wake!’ an
Australian icon).
SUMMARY OF BUSINESS
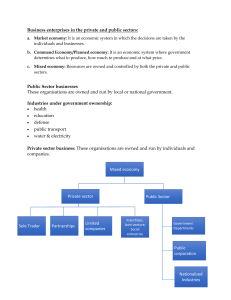
ENTERPRISES IN AUSTRALIA
• So a business enterprise is a “single legal entity or unit
operating to satisfy the wants of consumers.”
• A business enterprise may be:
A private enterprise owned by one or more people.
More than 90% of business enterprises are privately
owned.
More than 95% of these are small businesses
employing fewer than 20 people, eg sole traders,
partnerships, companies and co-operatives.
• A public enterprise owned and controlled by
government appointees
• There are approximately 5 000 government
owned business enterprises.
• Dominate three sectors:
o public administration and defence
o communication and electricity
o gas and water.
• Provide community health, education and
welfare services and transport and construction.
• Employ more than one-quarter of our working
population..
• A foreign owned enterprise.
• Produce half the output of mining industry
and more than a third of manufacturing.
• A business operating in Australia is regarded
as foreign-owned if 25% of its voting shares
are controlled by overseas interests and no
equal or larger single shareholdings are held
by an Australian.
Question!
• Business Ownership: Private Sector - Which
form of ownership is best?
• Refer to handout on ownership.