Geometric Book
advertisement

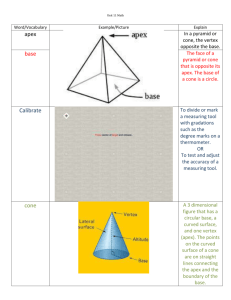
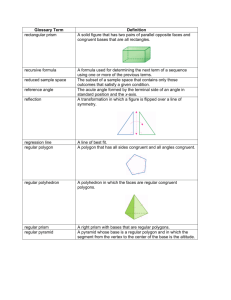
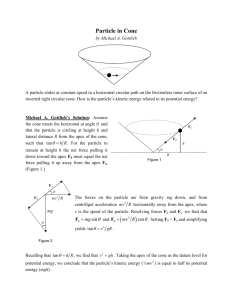
A triangle for which all interior angles are acute. The distance from the apex of a cone to the base. Formally, the shortest line segment betw een the apex of a cone and the (possibly extended) base. Altitude also refers to the length of this segment In plane geometry or so lid geometry, the bottom of a figure. If the top is parallel to the bottom (as in a trapezoid or prism), both the top and bottom are called bases. Point B is between points A and C if it is on the line segment conn ecting A and C. A box shape in three dimensional figure. Formally, a polyhedron f or which all faces are re ctangles. A three dimensional fig ure with a single base tapering to an apex. The base can be any simple closed curve. Often the word cone ref ers to a right circular cone. A regular polyhedron for which all faces are sq uares. Note: It is one of the five platonic solids. A threedimensional geometric figure with parallel congruent base s. The bases can be shaped like any closed plane figure (not necessarily a circle) and must be oriented identically. A geometric figure made up of two right circular cones placed a pex to apex as shown below. Typically a double cone is considered to extend infinitely far in both directions, especially when working with conic sections and degenerat e conic sections. A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides that are congruent. Note that the diagonals of a kite are perpendicular. A polygon with eight sides. Two distinct co planar lines th at do not intersect. Note: Parallel lines have the same slope. A polygon with five sides. A solid with parallel congruent ba ses which are both polygons. The bases must be oriented identically. The lateral faces of a prism are all parallelogra ms or rectan gles. A polyhedron with a polygonal b ase and later al faces that taper to an apex. A pyramid with a triangular base is called a tetrahedron. A part of a line starting at a particular poin t and extending infini tely in one direction. A transformation in which a geometric figure is reflected across a line, creating a mirror image. That line is called the axis of reflection. Identical in shape, although not necessarily the same size. A three dimensional solid consisting of all points equidistant from a given point. A rectangle with all four sides of equal length. Formally, a square is a quadrilateral with four congruent sides and four congruent angles (all 90°).