File - Tech Electronics
advertisement

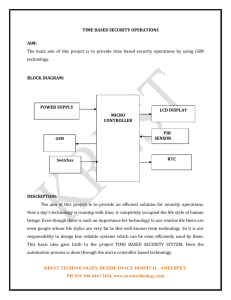
LPG Gas Detector and alerting using GSM Module Abstract: LPG gas detection projects main idea is to implement security system for detecting leakage of gas in closed environment. In this project gas leakage is identified by using sensors which works only in closed environment. In present situation there are many cases related to gas leakage which cause innocent people lives and property damage. Implementing this application can be useful for companies, houses, which can save lives of people. The presence of dangerous LPG leakage in the cars, service station or in the storage tank environment can be detected using the Ideal Gas Sensor. This unit can be easily integrated into a unit that can sound an alarm or give a visual suggestion of the LPG concentration. The sensor has both admirable sensitivity and rapid response time. This sensor can also be used to sense other gases like iso-butane, propane, LNG and even cigarette smoke. The output of the sensor goes LOW as soon as the LPG sensor senses any gas leakage from the storage. This is detected by the microcontroller and the LED & buzzer is turned ON. After the delay of few milliseconds, the exhaust fan is also turned ON for throwing the gas out and it continues sending message as ‘GAS LEAKAGE’ to a mobile number which is pre-defined. Block Diagram : Switch MQ6 Power, clock LCD Display Reset Gas Sensor Signal conditi on AVR-controller Relay driver RS 232 INTERFACE Theft Sensor Reset GSM Modem Alarm exhaust fan Relay Relay Block Diagram : 1. Gas sensor : MQ-6 Gives analog output as per concentration of combustible gas in air. Used in gas leakage detecting equipments for detecting of LPG, iso-butane, propane, LNG combustible gases. The sensor does not get trigger with the noise of alcohol, cooking fumes and cigarette smoke. 2. Theft Sensor 3. SCHEMATICS - TACTILE BUMP SENSOR CIRCUIT 4. 5. Tactile Bump Sensors are great for collision detection, but the circuit itself also works fine for user buttons and switches as well. There are many designs possible for bump switches, often depending on the design and goals of the robot itself. But the circuit remains the same. They usually implement a mechanical button to short the circuit, pulling the signal line high or low. An example is the microswitch with a lever attached to increase its range, as shown above. 6. There are several versions below, depending on how you plan to use the circuit and your available switches. For the resistor use a very high value, such as 40kohms. 7. Tactile Bump Sensor Circuits Voltage goes high with contact Voltage goes with contact low More efficient switch for 3 lead switches (use for microswitches) Introduction : LPG gas is supplied in pressurized steel cylinders. As this gas is heavier than air, when it leaks from a cylinder it flows along floor and tends to settle in low spots such as a basement. This can cause fire or suffocation if not dealt with. Here is a circuit that detects the leakage of LPG gas and alerts the user through audio-visual indications. This LPG Gas Sensor (MQ6), ideal sensor for use to detect the presence of a dangerous Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and it has high sensitivity to propane, butane, isobutene, natural gas. The sensor can also be used to detect combustible gases, especially methane. This circuit can detect leakages in your Home, car or in a service station, storage tank environment. This unit can be easily implemented to industrial level by upgrading its ranges. This project is designed to detect the LPG from 200parts per million (PPM) to 10,000 PPM. Whenever there is LPG concentration of 1000 ppm (parts per million) in the area, the OUT pin of the sensor module goes high. This LPG Gas Sensor can be used to make wireless Gas leak detector in home security system .The LPG Gas Sensor Module is designed to enable LPG detection interface to AVR-controller without inbuilt ADC Channels. By providing a GSM modem we can receive “SMS ALERTS” also.. CONTROLLER-AVR-AT-MEGA328 FEATURES The AVR-ATMEGA328, CMOS FLASH-based 8-bit microcontroller is upward compatible with theATmega48A ,ATmega48PA ,ATmega88A ,ATmega88PA ,ATmega168A ,ATmega168PA ,ATmega328 ,ATmega328P devices. It features 200 ns instruction execution, 256 bytes of EEPROM data memory, self programming, an ICD, 2 Comparators, 8 channels of 8 bit Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter, 2 capture/compare/PWM functions, a synchronous serial port that can be configured as either 3-wire SPI or 2-wire I2C bus, a USART, and a Parallel Slave Port. High Performance RISC CPU Only 35 single word instructions to learn All single cycle instructions except for program branches which are two-cycle Operating speed: DC 20 MHz clock input, DC 200 ns instruction cycle Up to 8K x 14 words of FLASH Program Memory Up to 368 x 8 bytes of Data Memory (RAM) Pin out compatible to the ATmega48A,ATmega48PA,ATmega88A, Pin out compatible to the ATmega88PA,ATmega168A,ATmega168PA Interrupt capability (up to 12 sources) Eight level deep hardware stack Direct, Indirect and Relative Addressing modes Processor read access to program memory Special Microcontroller Features Power up Timer (PWRT) and oscillator Start up Timer (OST) Watchdog Timer (WDT) with its own on chip RCoscillator for reliable operation Programmable code protection Power saving SLEEP mode Selectable oscillator options In Circuit Serial Programmingvia twoPins Peripheral Features Timer0: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit prescaler Timer1: 16-bit timer/counter with prescaler can be incremented during Sleep via external crystal/clock Timer2: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit period register, prescaler and postscaler Two Capture, Compare, PWM modules 16-bit Capture input; max resolution 12.5 ns 16-bit Compare; max resolution 200 ns PWM max resolution is 10-bit Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) with SPI (Master mode) and I2C (Slave) 8-bit, up to 8-channel Analog-to-Digital converter Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (USART/SCI) Parallel Slave Port (PSP), 8-bits wide with external RD, WR and CS controls (28/44-pin Only) Brown-out detection circuitry for Brown-Out Reset Analog Comparator module 2 analog comparators Programmable on-chip voltage reference module Programmable input multiplexing from device inputs and internal VREF Comparator outputs are externally accessible CMOS Technology Low power, high speed CMOS FLASH technology Fully static design Wide operating voltage range: 2.0V to 5.5V High Sink/Source Current: 25 mA Industrial temperature range Low power consumption < 2 mA typical @ 5V, 4 MHz, A typical @ 3V, 32 kHz < 1 μA typical standby current Following are the major blocks of AVR Microcontroller. Program Memory (FLASH) It is used for storing a written program. Since memory made in FLASH technology can be programmed and cleared more than once, it makes this microcontroller suitable for device development. EEPROM It is usually used for storing important data that must not be lost if power supply suddenly stops. For instance, one such data is an assigned temperature in temperature regulators. If during a loss of power supply this data was lost, we would have to make the adjustment once again upon return of supply. Thus our device looses on self-reliance. RAM Data memory used by a program during its execution. In RAM are stored all inter-results or temporary data during run-time. FREE RUN TIMER It is an 8-bit register inside a microcontroller that works independently of the program. On every fourth clock of the oscillator it increments its value until it reaches the maximum (255), and then it starts counting over again from zero. As we know the exact timing between each two increments of the timer contents, timer can be used for measuring time which is very useful with some devices. LCD DISPLAY DISPLAY: Various display device such as seven segment display. LCD display, etc can be interfaced with microcontroller to read the output directly. In our project we use a two line LCD display with 16 characters each. LCD Liquid crystal Display (LCD) displays temperature of the measured element, which is calculated by the microcontroller. CMOS technology makes the device ideal for application in hand held, portable and other battery instruction with low power consumption. GENERAL SPECIFICATION: Drive method: 1/16 duty cycle Display size: 16 character * 2 lines Character structure: 5*8 dots. Display data RAM: 80 characters (80*8 bits) Character generate ROM: 192 characters Character generate RAM: 8 characters (64*8 bits) Both display data and character generator RAMs can be read from MPU. Internal automatic reset circuit at power ON. Built in oscillator circuit. Net Media 2x16 Serial LCD Display Module POWER SUPPLY There are many types of power supply. Most are designed to convert high voltage AC mains electricity to a suitable low voltage supply for electronic circuits and other devices. A power supply can by broken down into a series of blocks, each of which performs a particular function. For example a 5V regulated supply: Each of the blocks is described in more detail below: Transformer - steps down high voltage AC mains to low voltage AC. Rectifier - converts AC to DC, but the DC output is varying. Smoothing - smoothes the DC from varying greatly to a small ripple. Regulator - eliminates ripple by setting DC output to a fixed voltage. Power supplies made from these blocks are described below with a circuit diagram and a graph of their output: Transformer Transformer Transformer Transformer only + Rectifier + Rectifier + Smoothing + Rectifier + Smoothing + Regulator Transformer only The low voltage AC output is suitable for lamps, heaters and special AC motors. It is not suitable for electronic circuits unless they include a rectifier and a smoothing capacitor. Transformer + Rectifier The varying DC output is suitable for lamps, heaters and standard motors. It is not suitable for electronic circuits unless they include a smoothing capacitor. Transformer + Rectifier + Smoothing The smooth DC output has a small ripple. It is suitable for most electronic circuits. Transformer + Rectifier + Smoothing + Regulator # The regulated DC output is very smooth with no ripple. It is suitable for all electronic circuits. The fig. above shows the circuit diagram of the power supply unit. This block mainly consists of a two regulating IC 7805 and a bridge rectified and it provides a regulated supply approximately 5V.The transformer used in this circuit has secondary rating of 7.5V. The main function of the transformer is to step down the AC voltage available from the main. The main connections are given to its primary winding through a switch connected to a phase line. The transformer provides a 7.5V AC output at its secondary terminals and the maximum current that can be drawn form the transformer is 1 Amp which is well above the required level for the circuit.The bridge rectified the AC voltage available from the secondary of the transformer, i.e. the bridge rectifier convert the AC power available into DC power but this DC voltage available is not constant. It is a unidirectional voltage with varying amplitude. #To regulate the voltage from the bridge rectifier, capacitors are connected. Capacitors C1 filter the output voltage of the rectifier but their output is not regulated and hence 7805 is connected which is specially designed for this purpose.Although voltage regulators can be designed using op-amps, it is quicker and easier to use IC voltage regulator. Further more, IC voltage regulators are available with features such as programmable output current/ voltage boosting, internal short circuit current limiting, thermal shut down and floating operation for high voltage applications. The 78 XX series consists of three terminals viz, input, output & ground. This is a group of fixed positive voltage regulator to give and output voltage ranging form 5V to 24V. These IC’s are designed as fixed voltage regulators and with adequate heat sinking, can delivery output current in excess of 1 Amp although these devices do not require external components and such components can be used to obtain adjustable voltage and current limiting. In addition, the difference between the input and output voltages (V in Vo) called the dropout voltage must be typically 2V even from a power supply filter. #Capacitors C2, C3, C4, and C5 are small filters which are used for extra filtering.LED1& LED2 are used for Power ON indicator for IC1 and IC2, current-limiting resistors R2&R4, which prevents the LED’s from getting heated and thus damaged. What is a GSM Modem? A GSM modem is a specialized type of modem which accepts a SIM card, and operates over a subscription to a mobile operator, just like a mobile phone. From the mobile operator perspective, a GSM modem looks just like a mobile phone. When a GSM modem is connected to a computer, this allows the computer to use the GSM modem to communicate over the mobile network. While these GSM modems are most frequently used to provide mobile internet connectivity, many of them can also be used for sending and receiving SMS and MMS messages. A GSM modem can be a dedicated modem device with a serial, USB or Bluetooth connection, or it can be a mobile phone that provides GSM modem capabilities. For the purpose of this document, the term GSM modem is used as a generic term to refer to any modem that supports one or more of the protocols in the GSM evolutionary family, including the 2.5G technologies GPRS and EDGE, as well as the 3G technologies WCDMA, UMTS, HSDPA and HSUPA. TECHNICAL DETAILS GSM is a cellular network, which means that mobile phones connect to it by searching for cells in the immediate vicinity. There are five different cell sizes in a GSM network—macro, micro, Pico, femto and umbrella cells. The coverage area of each cell varies according to the implementation environment. Macro cells can be regarded as cells where the base station antenna is installed on a mast or a building above average roof top level. Micro cells are cells whose antenna height is under average roof top level; they are typically used in urban areas. Pico cells are small cells whose coverage diameter is a few dozen meters; they are mainly used indoors. Femto cells are cells designed for use in residential or small business environments and connect to the service provider’s network via a broadband internet connection. Umbrella cells are used to cover shadowed regions of smaller cells and fill in gaps in coverage between those cells. GSM CARRIER FREQUENCIES GSM networks operate in a number of different carrier frequency ranges (separated into GSM frequency ranges for 2G and UMTS frequency bands for 3G), with most 2G GSM networks operating in the 900 MHz or 1800 MHz bands. Where these bands were already allocated, the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz bands were used instead (for example in Canada and the United States). In rare cases the 400 and 450 MHz frequency bands are assigned in some countries because they were previously used for first-generation systems. Most 3G networks in Europe operate in the 2100 MHz frequency band. Regardless of the frequency selected by an operator, it is divided into timeslots for individual phones to use. This allows eight full-rate or sixteen half-rate speech channels per radio frequency. These eight radio timeslots (or eight burst periods) are grouped into a TDMA frame. Half rate channels use alternate frames in the same timeslot. The channel data rate for all 8 channels is 270.833 Kbit/s, and the frame duration is 4.615 ms. The transmission power in the handset is limited to a maximum of 2 watts in GSM850/900 and 1 watt in GSM1800/1900. NETWORK STRUCTURE The structure of a GSM network The network is structured into a number of discrete sections: The Base Station Subsystem (the base stations and their controllers). the Network and Switching Subsystem (the part of the network most similar to a fixed network). This is sometimes also just called the core network. The GPRS Core Network (the optional part which allows packet based Internet connections). The Operations support system (OSS) for maintenance of the network. SUBSCRIBER IDENTITY MODULE One of the key features of GSM is the Subscriber Identity Module, commonly known as a SIM card. The SIM is a detachable smart card containing the user's subscription information and phone book. This allows the user to retain his or her information after switching handsets. Alternatively, the user can also change operators while retaining the handset simply by changing the SIM. Some operators will block this by allowing the phone to use only a single SIM, or only a SIM issued by them; this practice is known as SIM locking. Project Members #Nikhil Patil #Gaurav Patil #Pritesh Patil G.H.RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT, JALGAON