140123 – Cell Reg Lecture - Scheid Signalling Lab @ York University
advertisement

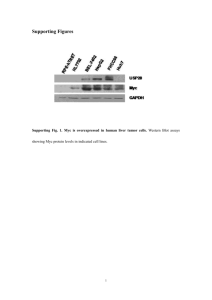
CDCA7 A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION January 23rd, 2014 Tim Gabor | Dr. Michael Scheid| York University LECTURE KEY WORDS - Cell cycle Transcription factors Phosphorylation Heterodimerization Immunohistochemistry Immunprecipitation Growth factors Apoptosis Colony formation Nuclear localization Consensus sequences Motifs CDCA7 | A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION • Cell cycle control is the endgame of cellular regulation - critical balance between proliferation and apoptosis CANCER CDCA7 | A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION • Cell cycle control is the endgame of cellular regulation - critical balance between proliferation and apoptosis CANCER • Modes: -phosphorylation, -subcellular localization - heterodimerization CDCA7 | WHAT IS KNOWN • Myc and E2F target gene with peak expression at G1-S • Novel member of cell division cycle-associated gene family • Frequently overexpressed in human tumors • JPO2 binds Myc and promotes Myc dependent transformation • JPO2 and CDCA7 share cysteine rich C-term which may bind DNA • Not known if CDCA7 interacts with Myc MYC | JUST THE FACTS • Discovered in Burkitt’s lymphoma patients • Member of bHLH-LZ family of transcription factors • Requires heterodimerization with Max to transactivate • Regulates the expression of ~10-15% of genes • Role in development, cell division, cell growth, metabolism, angiogenesis • Early response gene induced by growth factors, levels peak at G0-G1 • Driving force of cell cycle and malignant transformation • Active in 70% of human cancers • ~100,000 cancer deaths per year in the US due to changes in Myc Growth Factors Receptor Tyrosine Kinase P P P P PIP3 PIP2 PI3K PDK1 P P AKT CDCA7 P P 14-3-3 TOR rictor 14-3-3 P 14-3-3 Cytoplasm AKT P 14-3-3 14-3-3 AKT CDCA7 P 14-3-3 P CDCA7 Myc Myc Transcription Pro-apoptotic Genes ? Nucleus CDCA7 | A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION • Cell cycle control is the endgame of cellular regulation - critical balance between proliferation and apoptosis CANCER • Modes: -phosphorylation -subcellular localization -heterodimerization CDCA7 | CONSERVATION AKT consensus site CDCA7 T163 >90% conserved human monkey dog mouse chicken frog zebrafish 24 49 69 78 112 190 R X R X X T/S F/L R P R R R T F 261 363 AKT kinase 0.005% 1 371 T163 humCDCA7 zinc finger 261 361 CDCA7 IS PHOSPHORYLATED AT T163 • Many ways to prove phosphorylation • Custom made antibody against phospho-T163 Radioactivity and mutational analysis T163A T163A + CIP CDCA7 Vector CDCA7+ CIP WT Phosphotase a-FLAG T163A a-P-T163 Vector CDCA7 IS PHOSPHORYLATED AT T163 0 5 15 45 120 360 PDGF (min) a-P-T163 a-FLAG Treatments w/ growth factors Merge 1.0 T= 0’ 2.2 3.6 4.7 T= 20’ 4.0 3.9 Ratio P-T163/ Total CDCA7 T= 30’ Immunohistochemistry T= 40’ T= 50’ T= 60’ CDCA7 IS PHOSPHORYLATED AT T163 BY AKT Inhibitors Vector CDCA7 Akt inh VIII IP: a-FLAG Blot: a-P-T163 IP: a-FLAG Blot: a-FLAG CDCA7 | A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION • Cell cycle control is the endgame of cellular regulation - critical balance between proliferation and apoptosis CANCER • Modes: -phosphorylation -subcellular localization -heterodimerization CDCA7 | CONSERVATION >90% conserved human monkey dog mouse chicken frog zebrafish 24 49 69 78 112 1 190 261 363 371 T163 humCDCA7 NLS? zinc finger NLS? 261 157-186 RRPRRRTFPGVASRRNPERRARPLTRSRSR How do we test for a nuclear localization signal? Isolate region in question and test its ability to target an innocuous protein to the nucleus 361 WHERE IS CDCA7 FOUND? a-Flag CDCA7 T163A CDCA7 DAPI CDCA7 CONTAINS AN NLS • Passive diffusion into nucleus <45 KDa SV40 SV40 KE 157-188 R171E R171/176E 157-188 CDCA7 157-167 CDCA7 R176E 167-188 CDCA7 157-188 (T163A) R176/184E R184E 157-RRPRRRTFPGVASRRNPERRARPLTRSRSRIL-188 PHOSPHORYLATION ALTERS LOCALIZATION a-CDCA7 Unstimulated PDGF PDGF + LY Nuclei Merge CDCA7 | A CASE STUDY IN CELLULAR REGULATION • Cell cycle control is the endgame of cellular regulation - critical balance between proliferation and apoptosis CANCER • Modes: -phosphorylation -subcellular localization -heterodimerization CDCA7 | CONSERVATION >90% conserved human monkey dog mouse chicken frog zebrafish 24 49 69 78 112 1 190 261 363 371 T163 humCDCA7 NLS? zinc finger NLS? 261 157-186 361 RRPRRRTFPGVASRRNPERRARPLTRSRSR 14-3-3 consensus binding site R-[S/F/Y]-X-pS/T -X cdcA7 T163 Mekk2 T283 R G R R R K T T F F -P P P 14-3-3 | JUST THE FACTS • Large family of highly conserved, small, acidic polypeptides of 28-33 kDa • Seven different isoforms in humans, 14-3-3σ directly implicated in cancer • Binds to protein ligands at defined phospho-serine/threonine motif RSXpS/TXP • Over 200 known ligands • 14-3-3 regulates process relevant to cancer biology: cell-cycle progression, apoptosis and mitogenic signaling 14-3-3 | MODES OF INFLUENCE • 14-3-3 exists as a dimer and offers two binding sites for phospho-S/T motifs • Can function as adaptor protein for: a) two proteins that would otherwise not associate b) one protein with two 14-3-3 motifs = high affinity Adapted from Hermeking, 2005 • Affects change by: • Alteration of enzymatic activity – maintains RAF1 in inactive state • Alteration of DNA-binding activity – increases p53 DNA-binding after DNA damage • Sequestration - BAD, FKHRL1, HDAC5 and CDC25C are localized to cytoplasm • Altering protein-protein interactions - reduced affinity of CDC25A to CDC2 • Adaptor protein functions – bridging of RAF1 to BCR CDCA7 BINDS14-3-3 AND IS PHOSPHO DEPENDENT P165A X pT X P T163A F164A - R R161A R162A - R158A P159A R160A Vector Wildtype 14-3-3 consensus site S/F/Y Western blots Blot: a-FLAG a-P-T163 a-14-3-3 14-3-3 ALTERS CDCA7 LOCALIZATION a-Flag DAPI CDCA7 T163A CDCA7 R161A CDCA7 R161A/ T163A CDCA7 Is 14-3-3 masking the NLS within the T163 region? CDCA7 | WHAT IS KNOWN • Myc and E2F target gene with peak expression at G1-S • Novel member of cell division cycle-associated gene family • Frequently overexpressed in human tumors • JPO2 binds Myc and promotes Myc dependent transformation • JPO2 and CDCA7 share cysteine rich C-term which may bind DNA • Not known if CDCA7 interacts with Myc CDCA7 BINDS THE TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR MYC D(170-370) CDCA7 D(153-370) CDCA7 D(230-370) CDCA7 D(260-370) CDCA7 T163A CDCA7 D(112-137) CDCA7 D(1-146) CDCA7 D(1-172) CDCA7 D(1-202) CDCA7 D(1-234) CDCA7 WT CDCA7 Co-immunoprecipitation CDCA7 WT T163A D(112-137) D(1-146) His-Myc Pulldown Blot: a-FLAG D(1-172) D(1-202) D(1-234) D(260-370) D(230-370) D(170-370) D(153-370) Input Blot: a-FLAG + + + + + + + - SO HOW DOES CDCA7 AFFECT PHENOTYPE? APOPTOSIS PROLIFERATION 14-3-3/CDCA7 BINDING INFLUENCE MYC-INDUCED TRANSFORMATION Colony formation assay 14-3-3/CDCA7 BINDING INFLUENCE MYC-INDUCED APOPTOSIS Rat1 Trypan blue exclusion Myc-Rat1 Sh1-Myc-Rat1 Growth Factors Receptor Tyrosine Kinase P P P P PIP3 PIP2 PI3K PDK1 P P AKT CDCA7 P P 14-3-3 TOR rictor 14-3-3 P 14-3-3 Cytoplasm AKT P 14-3-3 14-3-3 AKT CDCA7 P 14-3-3 P CDCA7 Myc Myc Transcription Pro-apoptotic Genes ? Nucleus SUMMARY • CDCA7 is a novel target of AKT required for Myc-dependent apoptosis • Phosphorylation of T163 inhibits CDCA7/Myc apoptosis by: • Promoting 14-3-3 binding • Disruption of Myc binding • Shuttling to the cytoplasm • Potential for medical intervention in Myc tumors where AKT is dysregulated