Section 1.4
advertisement

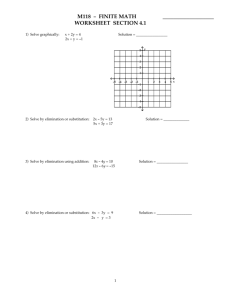
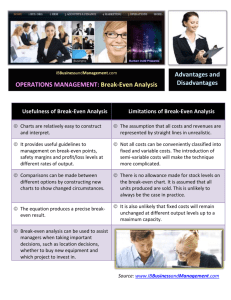
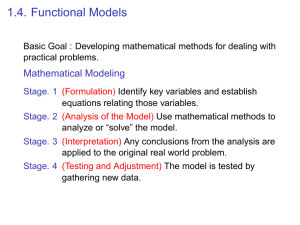
Section 1.4 Intersection of Straight Lines Intersection Point of Two Lines Given the two lines L1 : y m1 x b1 L2 : y m2 x b2 m1 ,m2, b1, and b2 are constants Find a point (x, y) that satisfies both equations. L1 L2 Solve the system consisting of y m1 x b1 and y m2 x b2 Ex. Find the intersection point of the following pairs of lines: y 4x 7 y 2 x 17 4x 7 2x 17 6 x 24 x4 Notice both are in Slope-Intercept Form Substitute in for y Solve for x y 4x 7 4(4) 7 9 Find y Intersection point: (4, 9) Break-Even Analysis The break-even level of operation is the level of production that results in no profit and no loss. Profit = Revenue – Cost = 0 Revenue = Cost break-even point Dollars Revenue profit loss Cost Units Ex. A shirt producer has a fixed monthly cost of $3600. If each shirt has a cost of $3 and sells for $12 find the break-even point. If x is the number of shirts produced and sold Cost: C(x) = 3x + 3600 Revenue: R(x) = 12x R( x) C ( x) 12 x 3x 3600 x 400 R (400) 4800 At 400 units the break-even revenue is $4800 Market Equilibrium Market Equilibrium occurs when the quantity produced is equal to the quantity demanded. price supply curve demand curve x units Equilibrium Point Ex. The maker of a plastic container has determined that the demand for its product is 400 units if the unit price is $3 and 900 units if the unit price is $2.50. The manufacturer will not supply any containers for less than $1 but for each $0.30 increase in unit price above the $1, the manufacturer will market an additional 200 units. Both the supply and demand functions are linear. Let p be the price in dollars, x be in units of 100 and find: a. The demand function b. The supply function c. The equilibrium price and quantity a. The demand function 3 2.5 x, p : 4,3 and 9, 2.5 ; m 4 9 0.1 p 3 0.1 x 4 p 0.1x 3.4 b. The supply function 1 1.3 x, p : 0,1 and 2,1.3 ; m 0.15 02 p 0.15 x 1 c. The equilibrium price and quantity Solve p 0.1x 3.4 and p 0.15 x 1 simultaneously. 0.1x 3.4 0.15x 1 0.25x 2.4 x 9.6 p 0.15(9.6) 1 2.44 The equilibrium quantity is 960 units at a price of $2.44 per unit.