Section 1.4 Notes MATH 141-501
advertisement

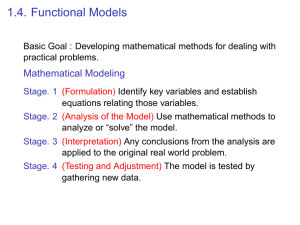
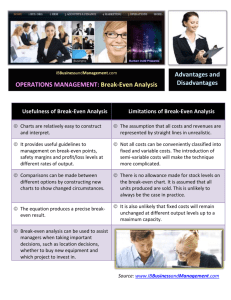
Section 1.4 Notes MATH 141-501 In many business-related problems, it is important to find where two lines intersect. i.e. when does ? (Break-Even point) when does ? (Market equilibrium) First, we look at the mathematical process involved. Skill: Given the equations of two straight lines, determine where they intersect. Example: Find the intersection point of the straight lines that have equations y= and y= 1 . Applications Break-Even Analysis If a business has linear cost and revenue functions, the break-even point is 1. the level of production at which 2. the point (x0 , y0 ) where x0 is called the break-even and y0 is called the break-even . 2 Example (Break-Even Level and Analysis) A manufacturer of mattresses has monthly fixed costs of $12000. It costs $80 to manufacture each mattress, and each mattress is sold for $120. How many mattresses will the manufacturer need to make and sell to break even? What will be the manufacturer’s profit be if 3000 mattresses are made and sold? How many mattresses should the manufacturer make in order to make a monthly profit of $5000? 3 Example (Decision Analysis) Maria has to choose between two jobs. The first, as a technical writer, will pay $ The other job, as an editor, will pay $ an hour. an hour. She can do the technical writing job from home. If she works as an editor, she will want to put her dogs in pet day care at an hourly rate of $ . She will also have to spend $ each week in additional expenses if she takes the editor job (gasoline, parking expenses, car maintenance, etc.) • If Maria plans to work 30 hours a week, which job makes more sense financially? • How many hours would Maria need to work for the editor job to be better financially? 4 Market Equilibrium In a totally free market (one with tually reach a level so that ), price will even- This condition is called It corresponds to the point where the tersect. and the • Quantity at this level is called • Price at this level is called 5 i Example (Market Equilibrium) CheapCheapPhone is a cell phone manufacturer which specializes in extremely cheap phones. When the unit price is $14, the quantity demanded for CheapCheapPhone’s cell phones is 2500. When the unit price is $11, the quantity demanded is known to be 10000.The supply equation is known to be p = , where p = price (in dollars) and x = demand (in cell phones). Assume the demand equation is linear. • Find the demand equation. • Find the market equilibrium. • Find the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. 6