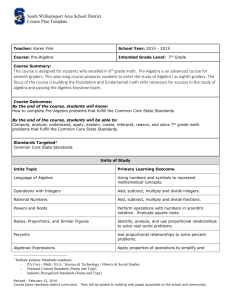
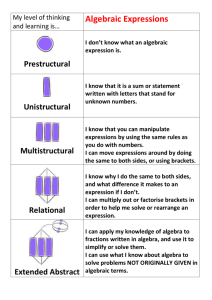
ALGEBRA - Pascack Valley Regional School District
advertisement

PREPARING FOR THE COMMON CORE STANDARDS: CCSS ALGEBRA PRESENTED SUMMER 2011 BY JUDITH T. BRENDEL, NJPSA/FEA SUPERVISOR OF MATHEMATICS & ART PASCACK VALLEY REGIONAL H.S. DISTRICT BE PRO-ACTIVE PREPARE FOR THE CHANGE • Timeline: implementation & assessment • What’s different? • Transition Phase - Today’s Reality: Pre-Algebra LAST YEAR (gr. 7 - 8) vs CCSS Algebra THIS YEAR (gr. 8 – 9) • Mathematical Practices • Plan: Curriculum, Pacing, Assessments • Resources: Textbook alignment +++ TIMELINE Curriculum Assessments 2011-12 K-2 CCSI 2012-13 3-12 3-5, HS New NJASK, HSPASAT (transition) NJASK, HSPA, 2012-13 NJASK, HSPA, 2013-14 HS 6-8 CCSI New NJASK, HSPASAT 3-5 CCSI 2014K?-Alg. NEW* 2013-14 6-8 CCSI NJASK, HSPA • from • Algebra-EOC test to quarterly benchmarks for all students ASSESSMENT Measure standards that are rigorous, globally competitive, and consistent across the states. New Jersey’s choice The assessment consortium PARCC (Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers) New assessments will replace current state NCLB tests in 2014-2015. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN TO YOU? TRANSITION YEAR(S) CONTENT • CCSS Skills not mastered in PreAlgebra • Grade-8: NJASK8 standards not in CCSS • Grade-9: HSPA/SAT content not in CCSS PROCESS • Conceptual understanding of content • Applying skills in real-world situations • New vocabulary OLD EXPECTATIONS Find ‘F’ when ‘S’ = 81 VERMONT: F = 4 ( S – 65 ) + 10 (The speeding fine in Vermont is $4 for every mile per hour over the 65 mph limit plus $10 handling fee.) CONNECTICUT: F = 10 (S-55) + 40 What is the fine for driving 72 mph? (Maximum speeding fine in Ct. is $350) NEW EXPECTATIONS 1. Describe the speeding fine in words. 2. In Connecticut at what speed does it no longer matter? 3. At 80 mph how much better off would you be in VT than in CT? 4. Use a graph to show this difference. TRANSITION PHASE: “Mathematics Grade-8” (pre-algebra) FOCUS: 3 CRITICAL AREAS p.521- Formulate and reason about expressions & equations 2- Grasp the concept of function and using functions to describe relationships 3- Analyze 2 and 3-dimensional space/figures (distance, angle, similarity, congruence; understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem.) TRANSITION PHASE: 5 DOMAINS Mathematics Grade-8 Overview (p.53)(pre-algebra) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The Number System Expressions and Equations Functions Geometry Statistics and Probability EXPRESSIONS Price plus 6% sales tax p + .06p or p(1.06) Perimeter: L L+w+L+w L+L+w+w 2(L) + 2(w) 2(L + w) W W L CREATE EQUATIONS CREATE * REPRESENT * REARRANGE 1. Create equations in 2 or more variables to represent relationships: A line going through (2,5) (-3,8) 2. Create an inequality: The car and insurance payments cannot exceed 8% of her income. 3. Rearrange Ohm’s law: V = IR to highlight resistance R REASON WITH EQUATIONS Explain each step in solving a simple equation. 8x + 2(x-6) = 16 – 3(x-2) 1. 8x + 2x – 12 = 16 – 3x +6 2. 10x - 12 = 22 – 3x 3. 13x - 12 = 22 4. 13x = 34 SOLVE (PRE-ALGEBRA) EQUATIONS in one variable (w/coefficients represented by letters) ab + c = d Solve for b. SYSTEMS 8.EE8.a.b.c. (p.55) Does the line through (2,6) and (3,5) intersect with the line going through points (4,8) and (2,4)? EXPLAIN or model how you know! SAMPLE 8.EE (PRE-ALGEBRA) Work with radicals and integer exponents. 1. Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 x 3-5 = 3-3 = 1/33 = 1/27 GRADE-8 (PRE-ALGEBRA) Overview (p.53) • • • • • Number Sense Expressions & Equations Functions Geometry Statistics & Probability ALGEBRA Overview (p.57) • Seeing Structure in Expressions • Arithmetic w/Polynomials & Rational Expressions • Creating Equations • Reasoning w/Equations & Inequalities Use the CCSS Grade-8 PRE-ALGEBRA STANDARDS Middle School – think grade-7 students HS – think grade-8 students what was not experienced by last year’s pre-algebra students. DISCUSS PRE-ALGEBRA Use the CCSS ALGEBRA STANDARDS Middle School – think grade-8 students HS – think grade-9 students Low-level Algebra class Middle-level Algebra class SET UP FORMAT MIDDLE-SCHOOL ALGEBRA Algebra 8 Geom 9 Use distance Apply formula dist. formula Honors 6 Honors 7 PeAlg Use distance Apply formula dist. formula Hon.Alg 8 Review on own HIGH SCHOOL ALGEBRA LOW ALG. 9 ALGEBRA Use Dist.Formula LOW GEOM 10 LOW ALG2 11 Use & Apply Dist. formula Apply Dist. formula SEN.MATH 12 Textbook + STEM statistics GEOMETRY ALGEBRA-II Pre-Calculus Apply Review Dist.Formula on own All + STEM statistics Textbook WHERE: ALGEBRA? HIGH SCHOOL √ content for each level of Algebra topics to appropriate course CCSS not completed gr.8 and HSPA MIDDLE SCHOOL √ content to be included from CCSS Alg. topics to learn on own CCSS skills not completed grade-7 NJASK-8 content, format, vocabulary FORMAT ALGEBRA STANDARDS: DOMAIN: A-SSE Seeing Structure in Expressions CLUSTER: Interpret the structure of expressions STANDARD: 1. Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context. a. Interpret parts of an expression (terms, factors, coefficients) b. Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one or more of their parts as a single entity. Interpret P(1+r)n as the product of P and a factor not depending on P. ALGEBRA (NEW CONTENT) QUADRATIC EQUATIONS in one variable -completing the square x2 + 6x -9 = x2 + 6x + (3x)2 -9 –(3x)2 DISCUSS ALGEBRA REASONING & SENSE MAKING PROBLEM-SOLVING ACTIVITY What is the perimeter of this shape? (long bars represent ‘x’, squares are 1 x 1) WORK ALONE; SHARE STRATEGIES with your GROUP Why is this a good REASONING & SENSE MAKING task? OVERARCHING MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. AS THE CROW FLIES STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET (Beginning Algebra) NCTM Suppose that the city in which you live has a system of evenly spaced perpendicular streets forming square city blocks. The map below shows your school; your house, which is located two blocks west and five blocks north of the school; and your best friend’s house, which is located eight blocks east and one block south of the school. See questions 1-5 on pages 20-21 MAXIMIZING AREA BEGINNING ALGEBRA (p.30-31) Question 1. What happens to the perimeter and area when you begin with a rectangle, cut a strip off the rectangle, and rearrange this piece to form a new figure as shown? See also Questions 2-5. SHARING W/OTHERS BEYOND THE TEXTBOOK PORTFOLIOS (Basic Algebra samples) PROJECTS - Restaurant (modified for collab. Algebra) - Cell Phone (any level Algebra) - Probability and Genetics (Gr. 9 aligns w/Biology) PRACTICE (vocabulary and form of Algebra EOC test) EOC PACKETS: Algebra by chapter TEST: Sample ALG EOC 14 example test(JBS) TEST: Official sample ALG EOC TEST (ACHIEVE) AND WE CONTINUE … http://www.pascack.k12.nj.us [curriculum instruction] [ mathematics]; can also link to [staff] http://www.nctm.org/ Judith T. Brendel jbrendel@pascack.k12nj.us