PEST - Marketing 1101
advertisement

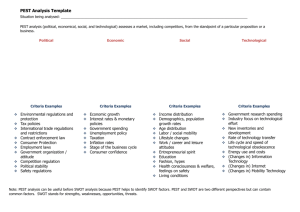
PEST & PESTEL Analysis Contents 1. Definition 2. What are PEST & PESTEL analyses? o PEST variations 3. How to perform the analysis? o Gathering PEST, PESTEL and STEEPLED information o Identifying opportunities and threats o PEST analysis example Definition 1. “PEST analysis – an analysis of the political, economic, social and technological factors in the external environment of an organization, which can affect its activities and performance.”[1] 2. “PESTEL model involves the collection and portrayal of information about external factors which have, or may have, an impact on business.”[2] What are PEST & PESTEL analyses? PEST or PESTEL analysis is a simple and effective tool used in situation analysis to identify the key external (macro environment level) forces that might affect an organization. These forces can create both opportunities and threats for an organization. Therefore, the aim of doing PEST is to: find out the current external factors affecting an organization; identify the external factors that may change in the future; to exploit the changes (opportunities) or defend against them (threats) better than competitors would do. The outcome of PEST is an understanding of the overall picture surrounding the company. Figure 1. Macro environment forces affecting a firm (PEST forces including legal, environmental, ethical and demographic forces) PEST analysis is also done to assess the potential of a new market. The general rule is that the more negative forces are affecting that market the harder it is to do business in it. The difficulties that will have to be dealt with significantly reduce profit potential and the firm can simply decide not to engage in any activity in that market. PEST variations PEST analysis is the most general version of all PEST variations created. It is a very dynamic tool as new components can be easily added to it in order to focus on one or another critical force affecting an organization. Although following variations are more detailed analysis than simple PEST, the additional components are just the extensions of the same PEST factors. The analysis probably has more variations than any other strategy tool: STEP = PEST in more positive approach. PESTEL = PEST + Environmental + Legal PESTELI = PESTEL + Industry analysis STEEP = PEST + Ethical SLEPT = PEST + Legal STEEPLE = PEST + Environmental + Legal + Ethical STEEPLED = STEEPLE + Demographic PESTLIED = PEST + Legal + International + Environmental + Demographic LONGPEST = Local + National + Global factors + PEST How to perform the analysis? The process of carrying out PEST analysis should involve as many managers as possible to get the best results. It includes the following steps: Step 1. Gathering information about political, economic, social and technological changes + any other factor(s). Step 2. Identifying which of the PEST factors represent opportunities or threats. Gathering PEST, PESTEL and STEEPLED information In order to perform PEST (or any other variation of it) managers have to gather as much relevant information as possible about the firm’s external environment. Nowadays, most information can be found on the internet relatively easy, fast and with little cost. When the analysis is done for the first time the process may take a little longer and as a beginner you may find yourself asking “What changes do I exactly look for in politics, economic, society and technology?” The following templates might be useful when gathering information for PEST, PESTEL and STEEPLED analysis. NOTE: PEST covers all macro environment forces affecting an organization. Therefore, when doing PESTEL or STEEPLED analysis, legal, environmental, ethical and demographic factors may overlap with PEST factors. Figure 2. PEST analysis template PEST analysis template Political Government stability and likely changes Bureaucracy Corruption level Tax policy (rates and incentives) Freedom of press Regulation/de-regulation Trade control Import restrictions (quality and quantity) Tariffs Competition regulation Government involvement in trade unions and agreements Environmental Law Education Law Anti-trust law Discrimination law Copyright, patents / Intellectual property law Consumer protection and e-commerce Employment law Health and safety law Economic Growth rates Inflation rate Interest rates Exchange rates Unemployment trends Labor costs Stage of business cycle Credit availability Trade flows and patterns Level of consumers’ disposable income Monetary policies Fiscal policies Price fluctuations Stock market trends Weather Climate change Data protection law Laws regulating environment pollution Socio-cultural Technological Health consciousness Education level Attitudes toward imported goods and services Attitudes toward work, leisure, career and retirement Attitudes toward product quality and customer service Attitudes toward saving and investing Emphasis on safety Lifestyles Buying habits Religion and beliefs Attitudes toward “green” or ecological products Attitudes toward and support for renewable energy Population growth rate Immigration and emigration rates Age distribution and life expectancy rates Sex distribution Average disposable income level Social classes Family size and structure Minorities Basic infrastructure level Rate of technological change Spending on research & development Technology incentives Legislation regarding technology Technology level in your industry Communication infrastructure Access to newest technology Internet infrastructure and penetration Figure 3. PESTEL analysis template PESTEL analysis template Political Economic Socio-cultural Technological Environmental (ecological) Legal Weather Climate change Laws regulating environment pollution Air and water pollution Recycling Waste management Attitudes toward “green” or ecological products Endangered species Attitudes toward and support for renewable energy Anti-trust law Discrimination law Copyright, patents / Intellectual property law Consumer protection and e-commerce Employment law Health and safety law Data Protection Figure 4. STEEPLED analysis template STEEPLED analysis template Political Economic Socio-cultural Technological Environmental (ecological) Legal Ethical Ethical advertising and sales practices Accepted accounting, management and marketing standards Attitude towards counterfeiting and breaking patents Ethical recruiting practices and employment standards (not using children to produce goods) Demographic Population growth rate Immigration and emigration rates Age distribution and life expectancy rates Sex distribution Average disposable income level Social classes Family size and structure Minorities Identifying opportunities and threats Gathering information is just a first important step in doing PEST analysis. Once it is done, the information has to be evaluated. There are many factors changing in the external environment but not all of them are affecting or might affect an organization. Therefore, it is essential to identify which PEST factors represent the opportunities or threats for an organization and list only those factors in PEST analysis. This allows focusing on the most important changes that might have an impact on the company. PEST analysis example The following table shows PEST analysis example. It lists opportunities and threats that are affecting a firm in its macro environment. PEST analysis example Political Government has passed legislation which requires further reductions of CO2, HC and NC emissions for vehicles until 2015 New political forces, which are against tax reductions, may be elected in the next years’ elections Import restrictions will increase in 2013 Government is increasing its funding to ‘specific’ industry Government is easing regulations for employment Increasing tensions between our government and our major export partner’s government Economic Socio-cultural Positive attitude towards “green” vehicles Number of individuals and companies buying through the Internet is 67% and 45% respectively and is expected to grow Immigration is increasing Increasing attitude toward jobs with shorter work hours People tend to buy more domestic rather than foreign products People change their eating habits and now tend to eat healthier food GDP will grow by 3% in 2013 Availability of credit for businesses will slightly grow or remain unchanged in 2013. The same applies for the cost of credit in the 1 half of the year Unemployment is expected to decrease to 7% Inflation will fall to 3% or 2% in 2013 Corporate tax rate will decrease by 2% next year to 23% Dollar exchange rates are expected to decrease compared to euro Disposable income level will decrease Metal and oil prices will increase by 5% and 6% respectively in 2013 Technological New machinery that could reduce production costs by 20% is in development Country’s major telecom company announced its plans to expand its internet infrastructure and install new optic fiber cables Driverless cars may be introduced in the near future “New” type of table will be introduced into the market next year Related topics