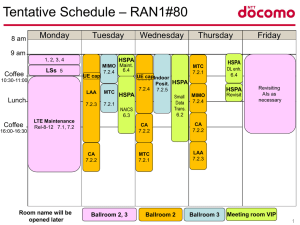
HSPA Info
advertisement
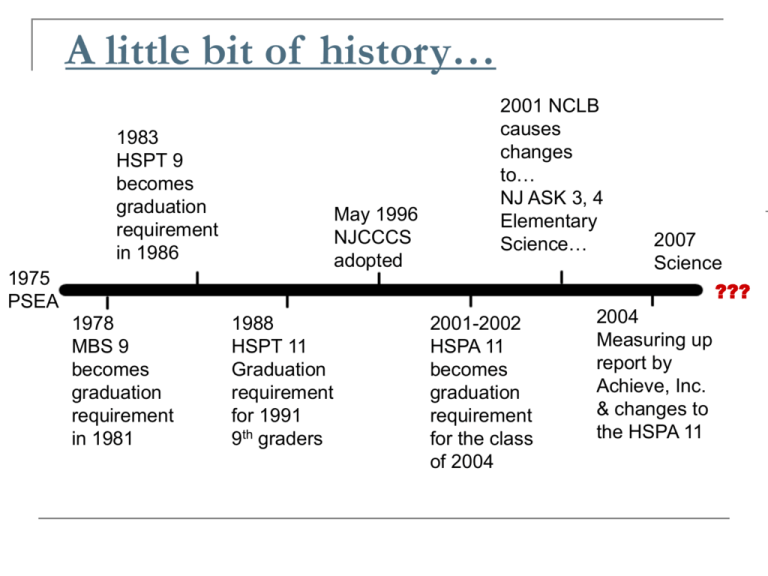
A little bit of history… 1983 HSPT 9 becomes graduation requirement in 1986 May 1996 NJCCCS adopted 2001 NCLB causes changes to… NJ ASK 3, 4 Elementary Science… 1975 PSEA 1978 MBS 9 becomes graduation requirement in 1981 1988 HSPT 11 Graduation requirement for 1991 9th graders 2001-2002 HSPA 11 becomes graduation requirement for the class of 2004 2007 Science ??? 2004 Measuring up report by Achieve, Inc. & changes to the HSPA 11 The Math HSPA “A Competency Assessment” Assesses how well students meet the NJCCCS Each of the 4 Content Strands are represented by questions on both MC and OE sections Higher order thinking skills as opposed to recall Macros by Cluster http://www.state.nj.us/education/njpep/assessment/TestSpecs/MathTestSpec/GEPAMath/MathIndex.html As a result…”The totality of New Jersey’s standards may not be manageable for all students and their teachers.” “All the mathematics expectations listed for the end of grade 12 will not be completed by the time students take New Jersey’s exit exam in grade 11. Therefore, it is a matter of some urgency for the state to prioritize these expectations and identify those expectations that are essential for the 11th-grade assessment.” Questions 4 40-minute sections 10 MC Totals 2 OE 40 MC & 8 OE http://www.state.nj.us/education/assessment/hs/ each = 48 raw points cut off varies year to year Question content 15% (7) of the points on the HSPA assess Number and Numerical Operations* 25% (12) of the points on the HSPA assess Geometry and Measurement* 30% (14) of the points on the HSPA assess Patterns and Algebra* 30% (15) of the points on the HSPA assess Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics* Questions may not be able to assess each CPI (Cumulative Progress Indicator) *from NJ DOE website Scoring HSPA Performance Level Descriptors Proficient The proficient student demonstrates evidence of knowledge in all four content clusters: 1. 2. 3. 4. Number Sense, Concepts, and Applications Spatial Sense and Geometry Data Analysis, Probability, Statistics, and Discrete Mathematics Patterns, Functions, and Algebra He or she consistently demonstrates the ability to compute and/or estimate an answer to problems involving integers, rational numbers, etc. He or she can assess, identify, and apply the appropriate formula for a variety of computational, algebraic, and geometric models. He or she can collect, organize, represent/display, and interpret data. He or she understands and applies geometric principles in relationship to real world applications. The proficient student demonstrates solid math performance in practical applications. Advanced Proficient The advanced proficient student performs at a level beyond the proficient student. He or she can analyze, synthesize, extend, and generalize math concepts in order to form conclusions and make predictions. He or she can create or extrapolate a rule or formula for a specific scenario. This student’s work displays the ability to move fluidly between the algebraic and geometric, the concrete and abstract. Answering Math Multiple Choice Each question is worth one point. Not penalized for guessing. Try to eliminate incorrect choices. Use the math reference sheet. Sample Multiple Choice distractor: 38*4 distractor: 315*4 pretty easy to rule out… correct answer = $478.80 “approximately” may throw students off possible distractor: for a student who reads too much into the problem (23+23=46%) Developing MC items Make sure that the question is clear, using grade appropriate vocabulary, and contains as few words as possible Think about how much time it will take the student to answer the MC question. It should take between 1 and 2 minutes to complete, sometimes less. The distractors for the question should be common mistakes made by the student. Help students become familiar with vocabulary (ex: circle graph vs. pie chart) Share ideas… OE Generic Scoring Rubric 0-3 points: about 10 min. per question 3 points – response shows complete understanding of the problem’s essential mathematical concepts 2 points – response shows nearly complete understanding of the problem’s essential mathematical concepts 1 point – response shows limited understanding of the problem’s essential mathematical concepts 0 points – response shows insufficient understanding of the problems essential mathematical concept The generic rubric ensures that students are scored in the same way for the same demonstration of knowledge and skills regardless of the test question. Sample Open Ended Response While looking at the problem keep the following in mind: What would qualify as a 3 point response? 2 points? 1 point? 0 points? There is always a range of responses within each score point. This helps define the tenuous line between a 2/3, 1/2 and 0/1. (low 2, high 2, low 1, high 1). Each open ended question has a unique scoring rubric. If a student makes an error in one part and uses the correct process for the second part (which incorporates the error made), the error will only be counted once. Responses are graded by humans, not machines. Therefore, students should make any attempt at a response as clear and concise as possible. Answering Open Ended Teach students to… Read & re-read questions carefully Letter each bullet point to make sure they address all parts of the problem Show all work (calculations) Include written explanations and labeled diagrams (not wordy; complete) Always make an attempt (partial answers add points!) Developing OE questions Make sure that the problem is truly open-ended, not simply multiple choice questions put together. An open-ended item allows a student to demonstrate his/her knowledge of a concept through a written explanation of the answer. There may be a correct result but should have a number of ways to answer the question correctly. Advantages to Open Ended questions Allows students to express what they know about each question in their own words. Students may communicate or clarify their responses using diagrams, graphics, and/or pictures. How can we all help? Prepare students by using multiple choice questions & teaching elimination strategies Include 4-answer multiple choice questions on assessments regardless of content you’re testing Include open ended questions on assessments and grade them using the 0-3 scoring rubric, regardless of subject area (content non-specific) Help students with reading comprehension in all subjects Require students to justify answers and model clearly written explanations in all courses Help students develop time management skills Help students “get used to the test” by providing testing environment during class (ex:students write answers in pencil, use scantrons, reference sheets, etc.) Infuse math content wherever possible within your own curriculum (ask for help) Support and encourage your students’ math confidence Help students learn to deal with test anxiety (relaxation techniques, how to cope when feeling “lost”) Share ideas… Can Exam Anxiety Be Overcome? Become familiar Relaxation techniques Talk to yourself + talk = + feelings Statewide Assessment Schedule 2009 March 3, 4, 5, 2009: Math & LA March 10, 11, 12, 2009 (Make-up) May 18, 2009: End Of Course Biology Test May 21, 2009 (Make-up) Is the HSPA a “good” test? “New Jersey’s high school test (HSPA) is not a good match with New Jersey’s end-of-grade12 standards; many items map better to the state’s grade 8 standards.” From Achieve, Inc.’s report: Measuring Up 2004, A Report on Language Arts Literacy and Mathematics Standards and Assessments for New Jersey, p. 53 Measuring up…areas for improvement “New Jersey’s lack of explicit course or grade-level standards for grades 9, 10 and 11 and clear expectations for its grade 11 exit assessment (HSPA) are problematic.” To address this: NJ’s End of Course Content Standards *From Achieve, Inc.’s report: Measuring Up 2004, A Report on Language Arts Literacy and Mathematics Standards and Assessments for New Jersey Standards Clarification Project http://www.nj.gov/education/aps/njscp/ Forward Trends to transform HSPA* 2001 NCLB causes More challenging test content and more of it 1983 changes HSPT 9 to… becomes assessments administered later “Summative” in the year NJ ASK 3, 4 graduation May 1996 Elementary requirement 2007 End in of1986 course CompetencyNJCCCS assessments inScience… Algebra 1, Geometry adopted Science & Algebra 2 1975 ??? PSEA 2004 1978 1988 2001-2002 Increased web-based score reporting and statewide student ID Measuring up MBS 9 HSPT 11 HSPA 11 report by becomes Graduation becomes Achieve, Inc. graduation Spanish language versions requirement graduation & changes to requirement for 1991 requirement the HSPA 11 in 1981 9th graders for the class of 2004 *reform initiatives led by State Assessment Advisory Committee with represetatives from educational organizations, business, and DOE High School Redesign Schools that work American Diploma Project *From www.achieve.org American Diploma Project @ Achieve.org’s 4 policy actions: 1. Align high school standards and assessments with the knowledge and skills required for success after high school. 2. Require all high school graduates to take challenging courses that actually prepare them for life after high school. 3. Streamline the assessment system so that the tests students take in high school also can serve as readiness tests for college and work. 4. Hold high schools accountable for graduating students who are ready for college or careers, and holding postsecondary institutions accountable for students' success once enrolled. H–S–P-A For fun…. Come up with an acronym that creates a silly, positive visualization for the HSPA Have Some Pizza Already! NJ DOE Assessment data & resources NJ DOE Assessment information and resources http://www.nj.gov/education/assessment/ HSPA Student Preparation Booklet (2006) http://www.nj.gov/education/assessment/hs/hspa_prep.pdf Basic HSPA Information & Data http://www.nj.gov/education/assessment/hs/ NJPEP virtual academy Tutorial with sample questions and responses scored: http://www.state.nj.us/education/njpep/assessment/hspa/hspa_math/index.htm Assessment: http://www.state.nj.us/education/njpep/assessment/helpfulhints/index.html Effective questioning strategies: http://www.pgcps.org/~elc/isquestion7.html Instruction for competency based instruction: http://www.state.nj.us/education/njpep/assessment/helpfulhints/instruct/index.html DOE Contacts HSPA Coordinator – Veronica Orsi Office #: 609/292-8739 Email: veronica.orsi@doe.state.nj.us Mathematics Coordinator – Tim Giordano Office #: 609/633-8015 Email: timothy.giordano@doe.state.nj.us Director of State Assessments Timothy Peters Office #: 609/984-6311 Email: timothy.peters@doe.state.nj.us Reference Sheet