final - review sheet pitt
advertisement

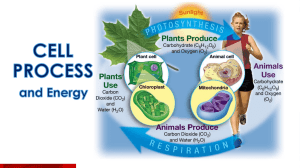
Name: _________________________________________ Final Review Sheet The biology final exam consists of 150 multiple choice questions. The questions are grouped into categories. The categories and questions may not appear in the order they were taught in class. The exam makes up 10% of your overall grade. It is very important that you take the final exam seriously! Studying is not an option, it is required. In order to eliminate stress and students being overwhelmed we are going to take some time to review what we have learned so far to remind you of what is important and what you will need to remember by the end of the semester. Portions of this review sheet will be due throughout the next week. It will be checked on the due date. To get full credit for the review you must answer the questions on a separate piece of paper. Write out detailed answers. Your answers do not have to be in sentences, but they do have to be detailed! Use your notes and the textbook to answer the questions. When you turn in the questions each day you must turn in this paper. I will record your daily grade in the checked column on the timeline below. On the last day I will add up your daily grades to give you a total out of 40. If you turn in questions late you will receive half credit. It is very important that you have the review packet with you and completed. Review Sheet Timeline Unit 1&2 3, 4a, 4b 5&6 7&8 Due Date Points value 10 10 10 10 Points earned Unit 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 Biochemistry List the 4 elements necessary for life. All organic compounds contain what element? Differentiate between a covalent and ionic bond. For each of the following, list the monomers, polymers, and major function in the body. a. Carbohydrates c. Lipids b. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids 5. For each of the following, list the type of organic compound it is, whether it is a monomer or polymer, and its major function. a. Cellulose f. Glycerol and 3 fatty acids b. Polypeptide g. Starch c. Glycogen h. Phospholipids d. Polysaccharide i. Wax e. Disaccharide j. Glucose 6. Differentiate between hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis. Include which one makes bonds and which one breaks bonds, and also which one stores energy and which one releases energy. 7. Why doesn’t oil and water mix? 8. Explain acids and bases using the pH scale: 9. What is the role of enzymes in the human body? Unit 2 Cell Structure & Function 10. List the 3 components of cell theory. 11. Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Give an example of each. 12. What is the function of each of the following organelles? a. Nucleus h. Golgi apparatus b. Cell Membrane i. Vacuoles c. Ribosomes d. Mitochondria e. Chloroplasts f. Rough endoplasmic reticulum g. Lysosomes 13. What organelles are present in a plant cell that are absent in an animal cell? 14. What are the four levels of organization from simplest to most complex? 15. Define the following terms: a. solution b. diffusion c. osmosis d. passive transport e. active transport f. facilitated diffusion g. endocytosis h. exocytosis 16. Draw an example and describe what would happen in cells of the following solutions: hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic Unit 3 Cell Cycle: 17. What are the 3 major stages of the cell cycle? 18. What significant events occur during each phase of interphase? 19. What significant events occur during each phase of mitosis? Unit 4a: Photosynthesis 20. What types of organisms use photosynthesis? Why are most of these organisms green? 21. Compare and contrast ADP and ATP. 22. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis. 23. What are the two major parts of photosynthesis? What are the reactants and products of each part? Unit 4b: Cellular Respiration 24. Write the chemical equation for respiration. 25. What is glycolysis? What are the reactants and products? 26. What are the two types of fermentation? 27. What are the major steps involved in aerobic respiration? What are the reactants and products of each step? 28. Compare the amount of ATP produced in anaerobic and aerobic respiration. Unit 5 Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis 29. What is the structure of a nucleotide? 30. What is the structure and function of DNA? 31. What are the complementary base pair rules for DNA? How are complementary bases bonded? 32. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 33. What is transcription? Where does it occur? 34. What is the function of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA? 35. What is a codon? What does it code for? 36. What is translation? Where does it occur? What is the product of translation? 37. If you were given the following mRNA sequence (UUC GUU GGA ACC), what would be the amino acid sequence and DNA template? 38. What is the difference between a somatic cell and germ cell mutation? ** We’ll go over this together ** 39. What is the difference between a gene and chromosome mutation? 40. What is a frameshift mutation? What types of mutations cause this? 41. What was the purpose of the Human Genome Project? What was accomplished? Unit 6 Reproduction: 42. What significant events occur during each phase of meiosis and describe each. 43. What is crossing over? 44. What is a karyotype? How can you tell a female from a male? 45. What is nondisjunction? What results in an embryo with an extra 21 st chromosome? 46. Differentiate between a diploid and haploid cell. 47. Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. 48. How does cytokinesis in plants differ from that in animals? 49. Compare oogenesis and spermatogenesis. 50. Sketch and describe the function of the sperm cell. 51. Place the following words in chronological order & then define them a. Fertilization e. Implantation b. Blastula f. Morula c. Gastrula g. Cleavage d. Zygote h. Gastrulation 52. What are stem cells? 53. What is the role of the placenta? 54. What are the germ layers? When do they arise and what do they produce? 55. What is the first system to develop in a growing embryo? Unit 7 Mendelian and Human Genetics 56. Define the following terms: a. Homozygous d. Phenotype b. Heterozygous e. Dominant c. Genotype f. Recessive 57. How are the following words related? DNA, gene, RNA, protein, trait 58. What is the difference between a gene and an allele? 59. What is a Punnett Square & what does it show? 60. What is a test cross? 61. What are the results of the following crosses: a. Monohybrid Heterozygote Parents (Tt x Tt) b. Dihybrid Heterozygote Parents (TtYy x TtYy) c. A colorblind male with a female carrier. (Hint: colorblindness is x linked recessive) d. A Red snapdragon with a pink snapdragon. (Hint: pink is the heterozygote showing incomplete dominance.) 62. Pedigrees – Review worksheets from class Unit 8 Microbiology 63. What are the three different shapes of bacteria? 64. How do bacteria reproduce? 65. What is the difference between facultative anaerobes and obligate aerobes? 66. How do some bacteria help humans? 67. Describe how bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. 68. Describe the structure of a virus. 69. Compare the lytic and lysogenic cycles of viral infection. 70. What is a retrovirus?