Socialization
advertisement

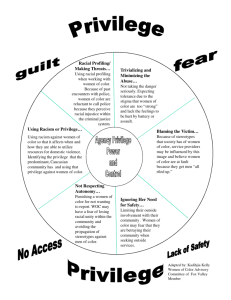
WARNING! This presentation may contain information that might actually cause you to think. Socialization Learning Culture, Building Identity AND Stratification and Inequality Examining the Implications of Class, Race, and Gender Socialization • Socialization – The life-long process of learning culture • Agents of socialization – Family, schools, work, peer groups, media, religion, etc. Constructing Identity: The “Self” • The “Self” (George Herbert Mead) – Infants only know the “I.” Through social interaction, however, they learn the “me”—the self as a distinct object to be perceived by others • “Looking Glass Self” (Charles Horton Cooley) – Sense of who we are that is defined by incorporating the reflected appraisals of others. OR “we see ourselves as we think others see us.” Becoming who we are, finding our “self,” is always a social process. Roles and Identity Formation • Roles – Expected patterns of behavior for a particular social status • Role Taking – Key to our identity and concepts of self because, we often see ourselves from the perspective of others How do you suppose these people “see” themselves? Learning Culture and Our Place In It • “We willingly play the roles we find ourselves in.” – P. Berger (1963) • We come to accept and expect the position which we occupy. Tastes, hobbies, careers, goals, and aspirations, who we partner with, etc. Switch… Social Stratification • Ranking system of groups of people that perpetuates unequal rewards and life chances in society Systems of Stratification • Slavery – Economic form of inequality in which some people are the property of others • Caste – Hierarchical stratification based on ascription (e.g. elite, warrior, merchant, servant, untouchable) • Class – Stratification based on wealth, income, education, and occupation; (SES) socioeconomic status. Theories of Stratification • Functionalist Theories – Highest rewards (e.g. salaries and prestige) are given to most important positions in society ensuring the most qualified people occupy these positions • Conflict Theories – Stratification reflects unequal distribution of power in society that serves the interests of those at the top Back to socialization… Learning Gender • What’s the difference between “sex” and “gender”? – Sex = reproductive organs, male/female/etc. – Gender = socially significant aspects, social construct • Gender specific socialization – In family – In schools – In workplaces – Where else? What are some ways in which gender is learned? We will come back to gender in a bit. Learning Race • “Race” is a social construct – “Race” is genetically the same as eye color • Race is socially significant. As such it shapes our identity and our social location. • In our culture, “whiteness” has historically been “normalized.” – The default race has privileges Switch! Racial Inequality and Stratification Racial Prejudice vs. Racism • From Beverly Tatum’s, Why Are All the Black Kids Sitting Together in the Cafeteria? – Racial Prejudice • any preconceived opinion, either favorable or unfavorable, based on one’s race – Racism • a system of institutional policies and cultural messages that is advantageous to white people and disadvantageous to people of color (e.g. housing, jobs) • prejudice + power Personal Racial Prejudice vs. Institutional Racism • We often focus on the racist actions of individuals rather than the institutions that maintain and perpetuate racial inequality For example… Disparities in Drug Sentencing as an Example of Institutionalized Racism • About 14 million Whites and 2.6 million African Americans report using illegal drugs • African Americans represent about 12% of the total population of drug users, but 38% of those arrested for drug offenses, and 59% of those in state prison for a drug offense • African Americans serve virtually as much time in prison for a drug offense (58.7 months) as whites do for a violent offense (61.7 months) (Info from NAACP and the Sentencing Project) Disparities in Drug Sentencing as an Example of Institutionalized Racism • Powder vs. Crack Cocaine – Used to be a 100 to 1 disparity in sentencing – As of 2010 Congress voted to change the law to decrease the disparity. They changed it to… • 18 to 1 disparity in sentencing!!! WHAT!!!? – The majority of cocaine users, both crack and powder, are white. But the majority of people convicted for cocaine are people of color. And crack has historically been concentrated in African American communities. Let’s talk a little more about incarceration in the United States: Incarceration Trends in the US • From 1980 to 2008, the number of people incarcerated in America quadrupled-from roughly 500,000 to 2.3 million people • Today, the US is 5% of the world’s population and has 25% of the world’s prisoners • Combining the number of people in prison and jail with those under parole or probation supervision, 1 in every 31 adults, or 3.2 percent of the population is under some form of correctional control Racial Disparities in Incarceration • African Americans now constitute nearly 1 million of the total 2.3 million incarcerated population • African Americans are incarcerated at nearly six times the rate of whites • Black and Latino Americans make up about 30% of the US population but about 60% of those incarcerated Racial Disparities in Incarceration • One in six black men had been incarcerated as of 2001. If current trends continue, one in three black males born today can expect to spend time in prison during his lifetime • Nationwide, African-Americans represent 26% of juvenile arrests, 44% of youth who are detained, 46% of the youth who are judicially waived to criminal court, and 58% of the youth admitted to state prisons (Center on Juvenile and Criminal Justice) White Privilege • It isn’t that all white people are to blame for discrimination; most are not. But white people nevertheless benefit from racism. – And I’m not just talking about incarceration! White privilege applies to jobs, housing, racial profiling while driving or at the store, etc. It is hard to see it, but it is happening all the time. [This is just as true in the case of male privilege, heterosexual privilege, or any other form of privilege.] Active Racism vs. Passive Racism • Active racism – blatant, intentional acts of racial prejudice • E.g. not serving black people at your restaurant • Passive racism – more subtle forms of racism • E.g. laughing at racist jokes, not challenging exclusionary hiring practices, accepting as appropriate the omission of the history of people of color in the curriculum Active Anti-Racism • Everyone needs to take an active anti-racist stance. But white people can play an especially powerful role since they have more access to the societal institutions in need of being changed. Not All People “Of Color” Are Equally Targeted By Racism • Other factors intersect and matter! Like what? – Class – Sex – Gender – Sexual orientation – Country of origin / immigration status – Etc. Social Class • Group of people who share similar economic/social/political position in society – Measures: income, wealth, occupational prestige, educational attainment, culture, taste – SES: socioeconomic status • Wealth = All assets owned by an individual including cash, savings, investments in property, stocks, bonds, etc. • Income = All wages and salaries earned from paid occupation. Also interest on savings. Back to socialization! Learning Class • Social Class affects values – E.g. Respecting conformity, not questioning authority • Our class background shapes our: – Opportunities – Aspirations – Expectations • Social Class helps determine the options we consider on the menu of life Back to stratification!!! Inequality and Life Chances • Working class and poor people are: – Less likely to go to college – More likely to get arrested, convicted, go to prison, and receive the death penalty than upper class people – More likely to die prematurely Our economy is worth, roughly, $188 trillion. Which is split between, roughly, 311 million people. Our country’s wealth split evenly would give everyone, roughly, $600,000. From 2009-2011, 100% of all new income went to the top 1% The bottom 99% actually saw a loss in their income. Forbes 400 Richest Americans • Have a combined net worth of over $1.54 trillion • Bill Gates = $66 billion • All 400 are billionaires ($1.1—$66 bil.) • More than half inherited their wealth Over $200 billion is inherited each year, half of which comes from just 7 percent of estates. Should inheriting wealth be allowed? Now back to gender… Gender Inequality and Stratification How many of you consider yourselves to be feminists? Gender Stratification • Social system in which socio-economic resources and political power are distributed on the basis of one’s sex and gender Wage Gap • On average women earn .81 cents for every $1 a man earns – This applies to men and women doing equal work! • Why does the gender gap in pay persist? – Occupational segregation – Discrimination – Institutional Sexism Housework – “The Second Shift” • Women still do majority of household work, including caring for children – Women working full time outside the home spend on average 19 hours/week on housework; men average 10 hours/week • This work is essential for society! Trigger Warning Rape as Social Control • Unlike men, women must worry about walking alone at night • Rape is used in war to terrorize and punish • Why no “War Against Rape” ? – 1 in 4 women are sexually assaulted in their lifetime (IN THE US!!!) – 1 in 6 women will be the victim of attempted or completed rape – 1 in 4 women in college are victims of rape • Only 5% actually report the crime!!! – 82% of sexual assaults are by people who know the victim Mr. Robinson’s #1 Rape Prevention Tip: DON’T RAPE! Reflect • Where do you fit in on the spectrum of social class and privilege? • What group or groups are you a part of? • What roles or identities do you take on? • How are your own social class/race/gender attitudes and opportunities shaping your life?