Powerpoint
advertisement

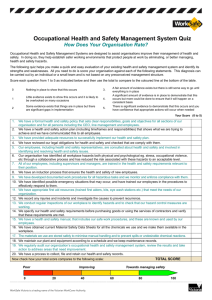
The Workplace as a setting for Health Protection and Health Promotion in Ireland Anne Drummond Associate Professor in Occupational Safety and Health UCD School of Public Health, Physiotherapy and Sports Science Occupational Health Environmental, occupational and personal risk factors Health Protection Health Promotion Work systems designed to protect workers from disease and injury by preventing and reducing risks Activities that improve or maintain health. Assisting workers in improving health behaviours • Occupational risk factors (hazards) • Personal risk factors (smoking, diet, drinking, stress) • Multi-disciplinary • • • • Ergonomics Occupational Hygiene Occupational Health Occupational Safety Health Protection • Often behaviour-orientated WHP Wellness This is the data our OSH statistics try to capture Work-related injury, illness and Fatalities Data from: • Fatality notification to HSA • HSA accident notification • Central Statistics Office (CSO), Quarterly National Household Survey (QNHS) • Occupational Injuries Scheme • THOR Accident Injury Timeline: Seconds Health Status + (Multiple) Exposure + Timeline: Days, months, years or decades Illness Occupational or work-related? Occupational Disease A case of occupational disease is defined as: “a case recognised by the national authorities responsible for recognition of occupational diseases. The data shall be collected for incident occupational diseases and deaths due to occupational disease”. Work-related illness • Work-related health problems and illnesses are those health problems and illnesses which can be caused, worsened or jointly caused by working conditions. • This includes physical and psychosocial health problems. • A case of work-related health problem and illness does not necessarily refer to recognition by an authority… Work-related Work Life Self-employed SMEs http://www.hsa.ie/eng/Publications_and_Forms/Publications/Corporate/HSA_Statistics_Report_2013-2014.pdf Work-related Illness rates are rising http://www.hsa.ie/eng/Publications_and_Forms/Publications/Corporate/HSA_Statistics_Report_2013-2014.pdf Work-related illhealth Drilled down into the CSO data MSD Stress, depression, anxiety https://www.esri.ie/pubs/RS40.pdf Illness rates rising Associated with certain work patterns WR Illness • F > M (2008-2012) • Boom > recession • Probability of illness increases with age, longer hours of work, short number of hours, highly variable working hours, shift work and working at night • Self employed do not differ from employed (pages 60-61) https://www.esri.ie/pubs/RS40.pdf Social patterning to risk Risks in agriculture, forestry and fishing, mining, quarrying and manufacturing Psychosocial risks Particularly in public sector and the health and social work sector https://www.esri.ie/pubs/RS46.pdf Occupational Health Risks to our Working Population • Rising rates of work-related illness • Commonest conditions are ‘MSD’ and ‘Stress, Anxiety and Depression’ • Presenteeism? • Leaveism? • Impact of job characteristics (working hours, shift patterns, night work) on health • Work-related illness • Sectors at risk (agriculture, construction, transport, health sector) http://www.cso.ie/en/media/csoie/census/documents/census2011profile3/Profile,3full,doc,for,web,sig,amended.pdf 4.6 million population 3.1 million in the 15 to 64 age group (working age population) 2.2 million in the labour force, of which 1.9 million are at work Among those aged 15 years and over: 939,000 males at work 839,000 females at work. Census 2011 Public Health Perspective • Rising rates of chronic illness • Highest causes of death in under 65s • cancer and diseases of the circulatory system • Modifiable lifestyle and behaviour factors http://health.gov.ie/publications-research/statistics/statistics-by-topic/causes-of-death/ Disability http://www.cso.ie/en/media/csoie/census/documents/census2011profile8/Profile,8,Full,document.pdf Work can be a contributory factor to chronic disease Safety and Health at Work • Health and Safety Authority 2001 NATIONAL Strategy for Workplace Health and Wellbeing 2008 2008 National Strategy for workplace health and wellbeing • Workplace culture … that will promote health and wellbeing, prevent ill health, and support rehabilitation to the workplace of those who are out of work through ill health or disability • Recognition that it goes beyond legislative requirements • Multi and cross-departmental response needed (HSA, HSE, DSFA, DHC, NDA, IBEC, ICTU, FOM [RCPI], IES, • Small and micro enterprises 97% of businesses • About 0.8 million workers • Public sector and medium to large enterprises • About 1.2 million workers Workplace Health Promotion Large organisations Public sector organisations Multi-nationals Small and micro enterprises Construction Workers’ Health Trust 2008 2011 Key indicator: improving the promotion of health and wellbeing at work 2011 “Work is good and unemployment bad – for physical and mental health, but the quality of work matters” 2010 “Puts ill health prevention in the context of the social determinants of health … involvement of stakeholders…schools, workplaces, home…all have the potential to help or hinder ill-health prevention” “Occupational health and vocational rehabilitation should be fully integrated into the NHS, providing a Fit for Work model….” http://www.instituteofhealthequity.org/projects/fair-society-healthy-lives-the-marmot-review Promotion of health and well-being at work 2011 prompted by Black Report Employees “… clear patterns 2010 in the data that show that provision is more prevalent in large organisations, especially those in the public sector and those with trade union presence”. Employers Findings reflected employees’ experience Larger organisations, public sector organisations and those with Unions 2011 prompted by Black Report • More than a third of employees had a health condition (spread across all occupations, industries and sizes of organisation) • 42% with a2010 health condition remained in work, despite it having a considerable effect on their work • Over a third considered that their health condition had been made worse by their work • Health and Wellbeing Policies explored were: Focus on sickness absence but followed up on health and wellbeing • Flexible working (74%) • Injury prevention training (76%) • Occupational Health Services (65%) • Independent counselling services (39%) • Stress management training (31%) Healthy Workplaces Bill currently proposed HSA is represented on Healthy Ireland Council Cross-Sectoral Group Workplace Health and Wellbeing Checklist Probable mental health problems http://health.gov.ie/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Healthy-Ireland-Survey-2015-Summary-of-Findings.pdf Changes individuals may like to make Occupational Health Cochrane Evidence Limited evidence Occupational Context Hours of work, night and shift work, job tenure Self-employed and high risk work patterns In addition to known occupational hazards National Context Ageing workforce, Retiring later, http://www.euro.who.int/en/publications/policy-documents/ottawa-charter-for-health-promotion,-1986 Ottowa Charter • “Health is...seen as a resource for everyday life, not the objective of living” It goes on to say: • “Health is a positive concept emphasising social and personal resources, as well as physical capabilities. Therefore, health promotion is not just the responsibility of the health sector, but goes beyond healthy lifestyles to wellbeing” CSHW AD http://www.enwhp.org/fileadmin/downloads/free/Luxembourg_Declaration_June2005_final.pdf Luxembourg Declaration on Workplace Health Promotion in the EU “The combined efforts of employers, employees and society to improve the health and wellbeing of people at work” “WHP is a modern corporate strategy which aims at preventing ill health at work and enhancing health promoting potentials and wellbeing at work” Jan 2007 version CSHW AD National Health Perspective • The Workplace as a setting for Health Protection and Health Promotion in Ireland ? • Health protection from work-related hazards • OSH system, albeit facing new problems • Addressed under the remit of the HSA • WHP not universal; growing but economic issues • Health protection from non-work or work-life risk factors • Public Health System; facing new problems (which follow through to the workplace) • Working-age population is a prime target for health protection and health promotion activities • Sectors and company types not in the WHP net • Multi-departmental approach • Who pays for it? • 'Well-being at work cannot be brought about simply by way of health and safety policy: there are strong links with the way work equipment is designed, with employment policy, with policy on disabled people, and with other policies like transport and, of course, health policy in general, whether it be preventative or curative” • European Commission. (2002). Adapting to change in work and society: a new Community strategy on health and safety at work 2002–06. • http://europe.osha.eu.int/systems/strategies/future/#270 CSHW AD