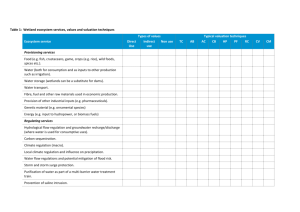
classifying valuation methods
advertisement

Valuing the environment: Methods ex ante vs. ex post ex ante valuation: desirability of proposed action ex post analysis: judge either the success or the damage done by implemented actions types of values / total WTP use: direct use of resource option can use it in the future nonuse fish / timber harvested / water extracted preserving something will never use e.g., existence value TWP = use + option + nonuse classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking revealed preference based on actual observable choices actual resource values can be inferred how much did fisherman lose from oil spill? how much did catch decline? what is value of lost consumer surplus? (area under demand curve): market price classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking stated preference used when value is not directly observable value of northern spotted owl survey respondents for WTP to preserve this species: contingent valuation contingent valuation (direct, stated) major concern is survey bias strategic bias information bias little or no experience starting point bias to influence an outcome depends on definition of range hypothetical bias contrived set of choices (no consequences) classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking travel cost (indirect / revealed) infer the value of recreational resource using info on how much visitors spent getting to a site construct demand curve for wtp for visitor day How far did they travel Entrance fee Account for different stops, etc. classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking hedonic property value (indirect / revealed) use multiple regression analysis to tease out environmental component of value use housing prices and break price into components (# bedrooms, baths, lot size, crime rates, school quality, air quality, etc) measure marginal wtp for discrete changes in each attribute coqui frogs as a form of noise pollution classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking hedonic wage (indirect / revealed) similar idea, except isolate component of wage that serves to compensate workers in risky occupations for taking on the risk high risk => high wage Tobacco CEO’s classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking averting / defensive expenditures (indirect / revealed) those designed to reduce damage caused by pollution by taking averting / defense action air purifiers / bottled water air conditioners to drown out coqui calls? lower bound estimate classifying valuation methods Methods Revealed pref Stated pref Direct market price contingent valuation Indirect travel cost attribute-based models hedonic property conjoint analysis hedonic wage choice experiments avoidance expenditures contingent ranking attribute based models (indirect / stated) useful when project options have multiple levels of different attributes survey based, but choosing different states of the world each state of the world has set of attributes and a price conjoint analysis: how to manage a forest? conjoint analysis: sample questionnaire benefit transfer transfers existing benefit estimates in new study used when gathering primary data too expensive / too little time make sure services being valued are comparable relevant population is comparable if not, are you able to make justifiable adjustments? issues in benefit estimation primary vs. secondary effects how far do you go? tangible vs. intangible sensitivity analysis for intangibles (don’t ignore) issues in cost estimation easier than benefits! approaches: survey vs. engineering survey: ask how much engineering: catalog possible technologies and estimate cost of purchasing and implementing them combined approach often best expected value much scientific uncertainty in future costs e.g., climate change, arrival of brown tree snakes assess likelihood of possible outcomes (assign probabilities) expected present value of net benefits: I EPVNB P PVNB i j i ij cost-effectiveness analysis if bca unavailable or not reliable set a policy target on some other basis than benefits and costs max acceptable pollution level? critical number of species to preserve? cost effectiveness analysis finds lowest cost means of accomplishing objective impact analysis if both bca and cost effectiveness not possible attempts to quantify consequences of various actions makes no attempt to convert all of consequences into $$$ not necessarily optimal leaves much up to policymaker