assistive technologies team2
advertisement

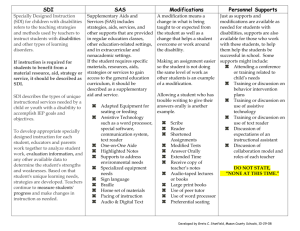
Digital Natives- people who spend their entire lives surrounded by technology such as computers, video games, DVD players ect….. Digital Immigrants- experienced a childhood without cell phones, personal computers and the Information Highway. ( usually over 30) “Today’s students are no longer the people our educational system was designed to teach.” Technological breakthroughs for individual with disabilities being in the 1800’s. ( military and medical advancements. o 1803 begin the use of raised dots for military messenger known as night writing . Used for communication after dark. Later used for Braille. o 1892 the Braille typewriter was developed. o 1926 the first audiometer was developed o 1966 the laser can was developed for the blind o 1957 the launch of Sputnik (Russian) o 1996 the government made GPS available for everyone to use According to the Assistive Technology Act (PL 108364) an assistive device is any item, piece of equipment, or product system whether acquired commercially off the shelf, modified, or customized that is used to increase, maintain, or improves functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities Academic outcomes No Tech Low Tech High Tech Service Dog No Tech: no technology involved in finding a solution in completing a task or achieving the desired outcome. High Tech: Specialized software and advanced hardware devices. Low Tech: Solutions involves simple technologies. Learner Needs and Preferences Providing guidance and support Encouraging students in trying different ways to approach the task. Establish a shared vision Create community Capitalize on Similarities and Differences Build on Leadership/Expertise Model Collaborative Relationships Maintain Professional networks Link Collaboration to Student Learning Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: ``````````````````````` Consideration Process for selective the most appropriate assistive technology aids for students Identifies areas of concerns from all parties involved Identifies barriers to learning and participation Explores potential solutions Implements solutions Gathers and documents information Tracks and monitors progress and adjusts any plans developed utilizing the Assistive Technology Aids Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: IDEA FACTS 1997 Schools are required to provide AT at no cost to the parents if it is needed for a student to receive a free and appropriate education The IEP team is responsible for determining whether the child requires assistive technology to benefit from their educational program The 97 IDEA requires that the IEP team considers the assistive technology needs of the student during the development of their IEP Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: MEMBERS OF THE TEAM MAY INCLUDE BUT NOT LIMITED TO: Student Parent (s) Assistive Technology Specialist Special Education Teacher General Education Teacher Occupational Therapist Speech and Language Pathologist School Administrator Physical Therapist School Psychologist/Counselor Para – Educator Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: STUDENT When selecting/determining the most appropriate AT for a student the IEP team must take in consideration all parties involved concerns. LOOK AT: Appropriate for student, Training (for all involved) Needs Abilities Age Functional Weight Environment (size, and space) Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: ENVIRONMENT (S) Are the settings in which the student is expected to perform/function academically as well as socially Areas to consider when selecting ATAs: What activities is the student expected to participate in? Tools must be student centered. Describe tool features that are needed. Is the area conducive to mobility Everything is needed to help the student succeed Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: TASK (S) Are the activities that the student will participate in and complete during instruction or in other settings What to consider: What specific tasks occur in the environment enables progress towards mastery of the IEP goals/objectives? What are the students special needs and abilities? What are the functional areas of concern? What are the students currents abilities? What materials , resources, and supports are available to complete tasks? Accommodations: Simplify task by breaking them into smaller more approachable tasks Identify strategies, tools, and technologies that can be used to complete one or multiple tasks Framework For Selecting ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY AIDS: TOOLS Are devices that are used by the student within their environment that assist with completing tasks that are presented to them. These tools may be the use of technology, assistive devices, and strategies that may be implemented which increases the students academic success. Examples of TOOLS: Pencil grips Slanted surfaces Enlarged worksheets Adaptive eating utensils Books on tapes Text readers Voice recognition Talking spell checker, dictionary Highlighters Word processor LOW-MID-HIGH TECH TOOLS Technology provides students with an environment that encourages collaboration , problem solving, role playing, and the development of critical thinking skills. Technology can actively engaged students in the learning process and increase motivation. BLOGS Blogs provide students with the opportunity writing space. Blogs can provide and opportunity for collaboration and peer mentoring and can be an active place to housed student productivity and academic artifacts. WIKI Wiki technology is a web-based tool that enables multiple users to work together on the same document or content. Wiki allows students in your class to approach a topic and participate in an online collaborative creation. PODCASTING Is a term resulting form the Apple Computer Corporation’s iPod. Podcasting is enabling education to become portable. Podcasting support different learners and learning styles. ( e.g. auditory learners and English language learners) GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGIES Include geographic information system(GIS), Global Positioning System (GPS) These are increasingly being used as a part of lessons in geography, environment science, biological science, economics, and mathematical studies. EXAMPLES COMMUNICATION AIDS Designed/implemented to assist with language and communication tasks Communication aids are needed when a student is unable to communicate their needs through traditional means such as speech, listening, reading and writing. AUGMENTATION COMMUNICATION Used by individuals with severe speech and language disabilities Devices used with students will vary and be personalized to meet their needs May use: gestures, communication boards, pictures, symbols, drawings or a combination of all. Communication boards (computerized, picture teacher made) Communication software Single message switches Voice output device Device with speech synthesis When to consider using: If a student shows a documented difference between comprehension of language and ability to express it, demonstrates delayed expressive language, or if their speech is not understandable to those around them Sensory aids are use for disabilities such as those who are blind, visually impaired, deaf, hearing impaired, or have difficulty with the sense of touch . Sensory aids make learning materials and the learning environment more accessible. Environmental Aids Environmental aids reduce or eliminate physical barriers for individuals with disabilities. Ergonomic Aids Ergonomic aids assist us in completing everyday repetitive tasks without causing undue stress to parts of our bodies. Sensory aids are use for disabilities such as those who are blind, visually impaired, deaf, hearing impaired, or have difficulty with the sense of touch . Sensory aids make learning materials and the learning environment more accessible. Personal amplification system Braille transcription Screen magnifiers Audio books Hearing aids Assistive listening device large-print books DEFINITION: Provide a means for which students with disabilities to gain independence when moving within their school/home environment Increase independence and self-confidence Plan activities, use designated learning areas so student will be able to maneuver safely and effectively EXAMPLES: Standers Wheelchairs Stair lifts Scooters Walking devices Transfer aids (device used to move individuals without having to physically lift them) can enable people with disabilities to accomplish daily living tasks assist them in communication, education, work or recreation activities help them achieve greater independence and enhance their quality of life. help improve physical or mental functioning, overcome a disorder or impairment help prevent the worsening of a condition, strengthen a physical or mental weakness help improve a person's capacity to learn, or even replace a missing limb. Screen readers Alternative and adaptive mice Adapted keyboards Key guards Head-operated pointing devices Switch access Voice recognition software Onscreen keyboards Examples adapted or modified sports, recreations, and leisure activities addresses the individualized needs of the disable Aids for these activities include modified sports equipment, audio descriptions, modified musical instruments, spinners or game pieces, and caption These activities, although modified, give options, provides encouragement, and empowers students to make choices. Daily living aids are devices that increase participation in daily activities. Daily living activities include but are not limited to bathing, cooking, dressing, and toileting. Because these task can have both a positive and negative effect on the classroom, therefore it is the job of the classroom teacher to make sure that daily living needs are being meet. Make sure they are adaptable Can time limitation removed? Can access methods be changed? (touch screen, switch or mouse) Can background colors be changed? Is text in narrative or video? Seating and positioning aids assist students with mobility impairments or other disabilities. Seating and positioning aids provide greater body stability , posture, and needed support. Occupational and physical therapists work closely with individual students and often consult with classroom teachers to make sure seating and positioning needs are being met. Support cushions or braces Chairlifts Seat wedges Standing tables Dave Edyburn. (2004). Measuring Assistive Technology Outcomes in Reading. Journal of Special Education Technology, 19(1), 60-64. Retrieved July 28, 2010, from ProQuest Education Journals. (Document ID: 638784611). Izzo, M., Yurick, A., & McArrell, B.. (2009). Supported eText: Effects of Text-to-Speech on Access and Achievement for High School Students with Disabilities. Journal of Special Education Technology, 24(3), 9-20. Retrieved July 28, 2010, from ProQuest Education