The Periodic Table and Ionic Bonding: Part 5
advertisement

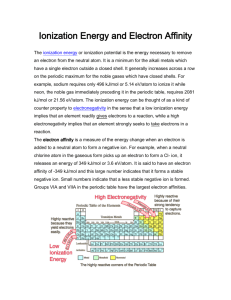
The Periodic Table and Ionic Bonding: Part 5-Periodic Table Trends 1 Objectives • -Describe what electron affinity is and how it is related to ion formation • -Explain how trends in electron affinity are shown in the periodic table 2 Periodic Trend #4: Electron Affinity (E.A) • Electron affinity- energy released when an atom gains an electron and the higher it is the greater attraction an atom had for it General Formula X (atom) + electron ---> X-1 (ion) + energy Specific Formula Cl + electron ---> Cl-1 + 83.4 kcal/mole • Negative ion with 1 more electron than proton • A negative ion = anion • Larger than the original atoms Periodic Trend #4: Electron Affinity (E.A) • ACROSS PERIODS electron affinity INCREASES to a maximum in Group VII then is a minimum in Group VIII ATOM: Na -> Cl Ar E.A.: 12.6 -> 83.4 -8.5 (kcal/mole) • DOWN GROUPS electron affinity usually DECREASES due to the positive nucleus being less attracted to the electrons further away Periodic Trend #4: Electron Affinity (E.A) • Nonmetals will gain enough electrons to have a stable electron structure like a noble gas or core atom (s2p6) • Group VII atoms (s2p5) gain 1 electron & form -1 ions • Group VI atoms (s2p4)gain 2 electrons & form -2 ions • Group V atoms s2p3)gain 3 electrons & form -3 ions Periodic Trend #4: Electron Affinity (E.A) Atom e configuration Ion e configuration Cl 1s22s22p63s23p5 Cl-1 1s22s22p63s23p6 S 1s22s22p63s23p4 S-2 1s22s22p63s23p6 P 1s22s22p63s23p3 P-3 1s22s22p63s23p6 not stable stable [Ar] Ion Summary GROUP I II III IV V VI VII VIII Electron Configuration s1 Ends in: s2 s2p1 s2p2 s2p3 s2p4 s2p5 s2p6 Electrons Lost 1 2 3 - - - - - Electrons Gained - - - - 3 2 1 - Ion Formed +1 +2 +3 - -3 -2 -1 - Remember that the group number tells you how many valen electrons there are!!! *Note – there are some exceptions to this chart! 8 Exceptions • The elements in this table can form more than one type of ion • When naming these compounds, the type of ion is expressed in the name with a roman numeral • These are all transition elements and they can form a variety of ions! Exceptional elements 9 Relating IE, EA and Metallic Properties • High in metallic properties = low ionization energy = low electron affinity • Low in metallic properties = high ionization energy = high electron affinity *Note – there are some exceptions Objectives • -Describe what electron affinity is and how it is related to ion formation • -Explain how trends in electron affinity are shown in the periodic table 11