Motivation
Module 23 to 25
The Unique Role of
the Hypothalamus
The lateral hypothalamus is a pleasure center
The Unique Role of the
Hypothalamus
Motivation
Motivation
a need or desire that energizes and
directs behavior
Motivation - Three
Theories
Instinct
Drive Reduction
Humanistic
Motivation - Instinct
Theory
A complex, unlearned pattern of
behavior
Same for all members of the
species (e.g., nest building)
Motivation - Drive
Theory
Two Key Definitions
need = physiological state of
deprivation in the organism
drive = psychological state (e.g.,
image of the goal)
Motivation--Drive
Theory
Drive-Reduction
Physiological need creates an aroused
tension state (a drive) that motivates us
to satisfy the need
Need
(e.g., for
food, water)
Drive
(hunger, thirst)
Rest
Drive-reducing
behaviors
(eating, drinking)
Motivation--Drive
Theory
Homeostasis
tendency to keep a constant or
balanced internal state
Need
(e.g., for
food, water)
Drive
(hunger, thirst)
Rest
Drive-reducing
behaviors
(eating, drinking)
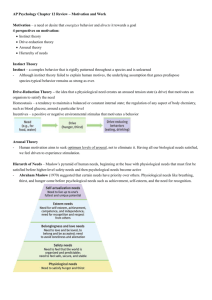
Motivation - Humanistic
Theory
Self-actualization needs
Need to live up to one’s
fullest and unique potential
Esteem needs
Need for self-esteem,
achievement, competence,
and independence; need for
recognition and respect from others
Belongingness and love needs
Need to love and be loved, to belong
and be accepted; need to avoid
loneliness and alienation
Safety needs
Need to feel that the world is organized and
predictable; need to feel safe, secure, and stable
Physiological needs
Need to satisfy hunger and thirst
Maslow: Human
Needs Hierarchy:
Begins at the base
with physiological
needs
Hierarchy: you must
work your way up
from the bottom
Drive Reduction Theory?
Eating Behavior
and
Sex Behavior
Motivation--Hunger
Stomach contractions accompany our feelings of hunger
Subject swallows
balloon, which
measures stomach
contraction
Subject presses
key each time
when hungry
Stomach contractions
Hunger pangs
0 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Time in minutes
9 10
Motivation--Hunger
Glucose
form of sugar, circulates in the blood
provides energy for body tissues
when it’s level is low, we feel hunger
Motivation--Hunger
The hypothalamus is a homeostatic mechanism, involved
in both eating and long term weight regulation.
Motivation--Weight
Regulation
Set Point
“weight thermostat” … when your
weight goes below a certain fixed point,
you seek food; Above, you don’t seek
food.
Metabolic Rate
body’s use of energy when at rest.
Motivation--Hunger
Summary: Eating and Weight
Regulation Depends on
Hunger
Glucose
Set Point
Metabolic Rate
Exercise and Eating Habits
Eating Disorders
Anorexia Nervosa
when a normal-weight person diets and
becomes significantly underweight, yet, still
feels fat
usually an adolescent female
Bulimia Nervosa
disorder: periods of overeating, usually of
highly caloric foods, followed by vomiting,
laxative use or excessive exercise
Weight Control
The thinning of Miss America
Trend in Body Mass Index (BMI) of Miss America Pageant Winners
24
BMI, kg/m² 23
•
22
•
21
• • ••• • • •
• •••• • • •
•• • • •
•
• •
•
•
•
•
• • • • • • •• •
World Health
•
Organization’s
•
cutoff point for
20
19
18
17
16
•
Trend line
•
•
undernutrition (18.5)
15
1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
Year of Pageant
Eating Disorders:
Obesity and Mortality
Obesity and mortality
2.8
Relative
risk of
death
2.6
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
18.5 18.5- 20.5- 22.0- 23.5- 25.0- 26.5- 28.0- 30.0- 32.0- 35.020.4 21.9 23.4 24.9 26.4 27.9 29.9 31.9 34.9 39.9
Men
Body-mass index (BM I)
Women
40
Weight Discrimination
Definitely
Hire
7
When women
applicants were
made to look
overweight,
subjects were less
willing to hire
6
5
Willingness
to Hire
4
3
2
1
Definitely
not Hire
0
Women
Normal
Men
Overweight
Weight Control
Effects of a severe diet
165
Metabolism:
Oxygen
consumption
in liters
per hour
26
160
25
155
24
150
23
145
22
140
21
Body
weight
in
kilograms
Caloric
intake
in
calories
per day
3000
2000
1000
0
8
16
Days
24 32
8
16
24
Days
32
8
16
24
Days
32
Weight Control
10
Weight 5
change
in pounds 0
Weight is
regained
over the
long term
for most
people
Starting
point
Normal trend for untreated obese
people: Gradually rising weight
-5
-10
After participation in behavioral
program: Much of initial weight
Loss regained
-15
-20
Post
treatment
1
2
3
Years of follow-up
4
5
Weight Control
Obesity is
more
common
among those
who watch
the most
television
Skinfold fat
measure (mm) 32
30
28
26
24
22
20
<2
2-3
>4
Hours of television watched per day
in 1990s study
Boys
Girls
Forces Affecting
Sexual Motivation
Physiological
readiness
Imaginative
stimuli
Sexual motivation
External
stimuli
Sexual Motivation
Estrogen
a sex hormone,
secreted in greater
amounts by females
than by males
in nonhuman
female mammals,
estrogen levels
peak during
ovulation,
promoting sexual
receptivity
Sexual Motivation
Sexual Response Cycle
the four stages of sexual responding
described by Masters and Johnson
excitement
plateau
orgasm
resolution
Refractory Period
resting period after orgasm, during which a
man cannot achieve another orgasm
Sexual Disorders
Problems that consistently impair sexual
arousal or functioning
In Men
premature ejaculation-ejaculation before they or their
partners wish
impotence-inability to have or maintain erection
In Women
orgasmic disorder-infrequent or absent orgasms
arousal disorder-lack of excitement
Sexual Motivation
Sexual Orientation
an enduring sexual attraction toward
members of either one’s own gender
(homosexual orientation) or the other
gender (heterosexual orientation)
Sexual Orientation
[Videoclip]
Sexual Motivation
Changing attitudes
100%
Extramarital sex is “always wrong”
80
60
Homosexual sex is “always wrong”
40
20
0
1987
Source: National Opinion Research Center
(University of Chicago) General Social Survey
1998
Year
Some other aspects of
Motivation
Achievement Motivation
Motivation in the workplace
Achievement
Motivation: TAT
What is this
boy
daydreaming
about?
Motivation
Achievement Motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment
fantasies sometimes reflect achievement
concerns
Motivation
Intrinsic Motivation
desire to perform a behavior for its own
sake
Extrinsic Motivation
desire to perform a behavior because you
will be rewarded or avoid punishment
Rewards Affect
Motivation
Mom: “I’ll give you $5 for every A.’’
Controlling reward
Child: “As long as she pays,
I’ll study.’’
Extrinsic motivation
Mom: “Your grades were great!
Let’s celebrate by going out
for dinner.’’
Informative reward
Child: “Good things happen when I do
well. I love doing well.’’
Intrinsic motivation
Motivation in the Workplace
Industrial/Organizational (I/O) Psychology
sub-field of psychology that studies and
advises on workplace behavior
I/O Psychologists
help organizations select and train
employees, boost morale and productivity,
and design products
Motivation
Task Leadership
goal-oriented leadership that sets
standards, organizes work, and focuses
attention on goals
Social Leadership
group-oriented leadership that builds
teamwork, mediates conflict, and offers
support