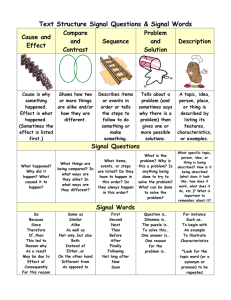
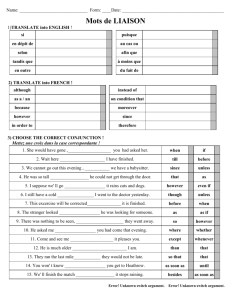
modulos 1 2 3 students guide - English Practice's Blog
advertisement

MODULOS 1 2 3 STUDENTS GUIDE MODULO 1 EKT UFPS Students’ guide july 2010 ENGLISH COURSE TO HELP STUDENTS WHO WILL PRESENT THE EKT-U.F.P.S. (ENGLISH KNOWLEDGES TEST AT THE U.F.P.S.) C. A.: ruling 200 06/11/2007; C. A. : agreement 11/05/2010 Dear student: Joven estudiante: Res. 200/06/2007 issued by C.A. stated that in order to get a degree one of the requirements is to pass a proficiency test in English (or other language). This is been done by now only on Written Competences: grammatical, textual, textual coherence and reading comprehension. On the other hand C.D. stated the vocational courses for preparing for the test on proficiency in English. Fir that reason, the language area has organized a course of 60 class-hours plus virtual ones and the student’s work. This course is designed for preparing in vocabulary, grammar usage and reading comprehension. It’s divided in three sections: part 1, part 2 and part 3. These guide the learning or feed back on pronouns, determinants, use of there+be, tenses, passive voice, questions and answers, use of special verbs, parts of the sentence, conditionals, phrasal verbs (idioms). At the end of it, it is annexed a series of vocabularies and common expressions in English. El C.A. por resolución 200/06/2007 ordenó que para poderse graduar uno de los requisitos exigidos es pasar una prueba de suficiencia en inglés (otro idioma). Esta se hace en el momento para Competencias por escrito: grammatical, textual, coherencia textual and comprension de lectura. Igualmente el C. D. ordenó la realización de cursos vacacionales de preparación para la prueba de suficiencia en inglés. Por tal razón se ha organizado en el area de idiomas la realización de un curso de 60 horas presenciales más horas virtuales y de trabajo del estudiante. Este curso está diseñado para prepararse en vocabulario, uso gramatical y comprensión lectora. Dividido en tres secciones: parte 1, parte 2 y parte 3. Estas orientan el aprendizaje o refuerzo de pronombres, determinantes, uso de there+be, tiempos, voz pasiva, preguntas y respuestas, usos de ciertos verbos especiales, palabras parte de la oración, condicionales, verbos modales (modismos). En a parte final se anexa una serie de vocabularios y expresiones comunes del inglés. Hay dos ayudas más, un módulo de modelos de preguntas tipo ICFES/ECAES y un módulo adicional del lingüista Sheraton en el cual se pueden hacer consultas y ampliación de conocimientos. Consulte en el blog: www.bepenglishworks.Wordpress.com Este módulo esta desarrollado en cuadros y varios de estos tienen la traducción al castellano para mayor ayuda y comprensión. Es importante recordar que usted aprende lo que realmente quiere aprender y que tiene que trabajar duro para lograrlo. Su profesor es un orientador, una ayuda y un consultor. La evaluación del aprendizaje se realizará como de costumbre: primer previo, segundo previo, tercer previo y examen final. There arre two more helps, a module of examples of questions and answers on ICFES/ECAES tests, and, adtional module from Mr. Sheraton in which you can look up and widen your knowledges. You can find it in a blog: www.bepenglishworks.Wordpress.com This module is written in tables and some of them have the translation into Spanish for better help and comprehension. It is important to remember that you learn what you really want to learn and that you have to work hard to do it. Your teacher is a leader, collaborator and consultant. The evaluation of the learning will be performed as usual: first previous, second previous, third previous and final test. N° 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CONTENTS Information about the course Placement test PRONOUNS & DETERMINANTS THERE +BE INTRODUCTION TO TENSES (SHORT FORMS) GOING TO SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE PRESENT CONTINUOUS PAST CONTINUOUS SIMPLE PAST TENSE LIST OF IRREGULAR VERBS & REGULAR VERBS 1ST PREVIOUS 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE PAST PERFECT TENSE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE PASSIVE VOICE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USE OF WH WORDS BE AND HAVE 2ND PREVIOUS 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ADJECTIVES ADVERBS CONJUNCTIONS & OTHER FUNCTION WORDS PREPOSITIONS DO/MAKE MODAL VERBS CONDITIONAL PHRASAL VERBS (IDIOMS) VOCABULARIES & COMMON EXPRESIONS FINAL TEST Percentage Grading Units THIRD PREVIOUS 1ST PREVIOUS 23,3% 1,15 1-9 Units 1-31 2ND PREVIOUS 23,3% 1,15 10-16 THIRD PREVIOUS 23,4% 1,20 17-25 HS/C ∑/H 1 1 2 3 6 3 8 2 10 2 12 2 14 2 16 2 18 2 20 2 22 2 24 2 25 1 27 2 28 1 29 1 31 2 4 35 1 36 2 38 2 40 1 41 2 43 3 46 1 47 2 49 2 51 3 54 3 58 2 60 Page 3 4 5 7 7 8 9 9 10 OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK 13 14 14 14 15 16 22 OK OK OK OK OK OK OK 23 24 27 30 32 33 35 36 38 OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK FINAL TEST 30% 1,50 1-25 AVERAGE 100% 5,00 Participation, classworks, homeworks, short tests, etc. ENGLISH COURSE TO HELP STUDENTS WHO WILL PRESENT THE EKT-U.F.P.S. - (ENGLISH KNOWLEDGES TEST AT THE U.F.P.S.) Council of Acad. ruling 200/6/11/07;Council of Adm.: agreement 11/5/10 N° 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 FIRST PART - CONTENTS Information about the course Placement test PRONOUNS & DETERMINANTS THERE +BE INTRODUCTION TO TENSES GOING TO SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE PRESENT CONTINUOUS PAST CONTINUOUS SIMPLE PAST TENSE LIST OF IRREGULAR VERBOS 1ST PREVIOUS 1 I you he she it we you they PRONOUNS & DETERMINANTS me you him her it us you them myself yourself himself herself itself ourselves yourselves themselves my your his her its our your their mine yours his hers its ours yours theis everybody everyone everything nobody no one nothing HS/C ∑/H 1 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 3 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 3 6 somebody someone something anybody anyone anything OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK who which that whom whose 1B. (TEXTS) USING PRONOUNS AND DETERMINANTS I like to write novels for my students. They read them with enthusiasm. Mary is a good writer too. She likes to read poems. She sent me a poem about the flowers of her garden. She said: “These novels are yours but these poems are mine. Every student should do his/her own tasks. So he himself will learn a lot or she herself will have success. When a girl found a small calculator she started asking “was it lost by you, or by her, or by us, or by them” Somebody, a boy replied that it must be his, or hers, or yours, or ours or theirs. The homeworks were well written by the students but the teacher began to doubt about it so he questioned every one with these words: -Did you do it yourself? -Yes, I did it myself. –Did Peter do it himself -No he didn’t do it himself, somebody did it for him. Did Lucy did it herself? Yes, she did it by herself, even her mother helped her a little. Did you know that everybody here has a motorcycle but nobody has a bus. Somebody said that it was possible to get something for the lunch but no one had a single dollar. Anthony asked if anybody had anything to be sold, but there was nothing. Mary asked: -Did you see anybody at the restaurant? -No, I didn’t see anybody there, answered John. I saw somebody near the door replied Lou Who is that tall boy over there? -Which one, the one whose shirt is blue? Yes, please tell him to come here. Excuse me whom did you say to come here? Do you see the man with a blue shirt that is holding a vase? That one is the one I need to talk too, please ask him to come here. 2 THERE +BE There is (singular) There are (plural) There was (s) There were (p) There has been (s) There have been (p) There had been There will be There is going to be (s) There are going to be (p) There was going to be (s) There were going to be (p) Hay Hay Hubo, había Hubo, había Ha habido Ha habido Había habido Habrá Va a haber Va a haber Iba a haber Iba a haber 2 8 OK There is a house There are two houses There was a party last night There were many people There has been a hurricane There have been two hurricanes There had been many problems There will be a party tonight There is going to be a celebration There are going to be many guests There was going to be a party yesterday There were going to be many guests 2B. THERE BE (TEXTS) USING THE EXPRESSION THERE + BE There is a house near the hospital, but there isn’t any near the Red Cross. There are two small orange trees in the middle of the yard and for that there wasn’t the party for new students. There were many people waiting to know where the party was going to be. Somebody said that there has been a storm and therefore everybody should go back home. The police said that there have been two storms lately and because of that the security of the people was first. For that decision there had been many problems with young people who wished to dance rock and roll. The organizers informed that there will be a party next Saturday because there was going to be the city celebration of hundreds of years. The major also communicated that there were going to be many guests. 3 INTRODUCTION TO TENSES Tense Present continuous Presente progresivo Simple past tense Presente simple Past continuous Pasado progresivo Simple past tense Pasado simple Future continuous Futuro progresivo Simple future tense Futuro simple Near future Futuro próximo Present perfect continuous Presente perfect progresivo Present perfect Presente perfecto Past perfect continuous Pasado perfecto progresivo Past perfect Pasado perfecto Future perfect progressive Futuro perfecto progresivo Future perfect Futuro perfecto Example 2 Translation 10 OK Explanation Are you drinking tea? Está tomando té? Esta ocurriendo Do you drink tea? Tomas té? Costumbre Were you drinking tea? Se estuvo haciendo Did you drink tea? Estabas tomando té? Tomaste té? Will you be drinking tea? Estarás tomando té Lo que se planea hacer Will you drink tea? Tomarás té Deseo, predicción, futuro Are you going to drink tea? Vas a tomar té? Lo que se planea hacer Have you been drinking tea? Have you drunk tea? Has estado tomando té? Has tomado té Ocurrió y ocurre Had you been drinking tea? Ocurrió Had you drunk tea? Habías estado tomando té? Habías tomado té? Will you have been drinking tea? Will you have drunk tea? Habrás estado tomando té? Habrás tomado té? Predicción o futuro Actividad realizada Ocurrió, ocurre aún Ocurría cuando … Predicción por futuro 3B SHORT FORMS (& TAG QUESTIONS) 01 You can work here, can’t you? Yes, I can. (No, I can´t). 02 03 You couldn´t play everywhere, could you? (Yes, I could). No, I couldn’t. He may type it, may he not? Yes, he may. (No, he may not) 04 05 She might not watch it, might she? (Yes, she might). No, she might not. We shall laugh, shan’t we? Yes, we shall. ( No, we shan’t) They shouldn’t play, should they? (Yes, they should). No, they shouldn´t 06 He will learn English, won’t he? Yes, he will. (No, he won’t). 07 John wouldn’t mow the lawn, would he? (Yes, he would). No, he wouldn’t) 08 Mary closes the door, doesn’t she? Yes, she does. (No, she doesn’t) 09 Doctors earn a lot of money, don’t they? Yes, they do. (No, they don’t) 10 They didn’t visit it, did they? (Yes, they did). No they didn’t. 11 We must begin to do it, musn’t we? Yes, we do. (No, we musn´t) 12 You dare say it, don’t you? Yes, I do. (No I don’t). 13 She is catching the ball, isn’t she? So is he. (He is too) 14 15 The dog is digging in the yard. So is Kaiser. (Kaiser is too) 16 They are wearing old clothes. So are we. (We are too) 17 It was falling down So was the pencil. (The pencil was too) 18 They were cutting the best woods So were we. (We were too) 19 He drinks cheap beer. So does Pete. (Pete does too) 20 I drive the biggest truck So do they. (They do too) 21 They ate sea food So did we. (We did too) 4 GOING TO (IMMEDIATE FUTURE) I am going to travel to Paris. I am going to visit my grandmother. She is going to make a cake for me. They are not going to remember that We are not going to go anywhere. Who is going to come today? Are you going to buy a new car? Are they going to help you? What are you going to bring? When is she going to arrive? 2 12 7 (Voy a viajar a París) (Voy a visitar a mi abuela) (Ella va a hacer una torta para mi) . (Ellos no se van a acordar de eso) (Nosotros no vamos a ir a ninguna parte) (¿Quién va a venir hoy?) (¿Vas comprar un nuevo auto?) (¿Ellos te van a ayudar?) (¿Qué vas a traer?) (¿Cuándo va a llegar ella?) OK 4B. (TEXTS) USING GOING TO I am going to travel to Paris next year. I am going to visit my grandmother who lives in that beautiful city. As soon as I get there I know she is going to make a cake for me. She is going to make an apple cake which is my preferred cake. My sisters and parents are not going to remember that I used to ride on horseback on weekends but as they are not going to go to the hippodrome, we will be going anywhere else as a Museum of fine arts. My mother always like to ask “Who is going to walk today?” or “What are you going to buy at the Mall?” -“Daddy are you going to buy that new Renault Logan at the Car Center?” -Yes, will say my Daddy, -“But are all of you going to help me choose the color?” I don’t know what I am going to bring back to Colombia by July. Anyhow we are going to arrive at Paris airport in January and we are going to come back in July or August. 5 SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE 2 14 7 OK SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE I drink You drink He drinks She drinks It drinks We drink You drink They drink I don't drink You don't drink He doesn't drink She doesn't drink It doesn't drink We don't drink You don't drink They don't drink Do I drink? Do you drink? Does he drink? Does she drink? Does it drink? Do we drink? Do you drink? Do they drink? 5B (TEXTS) USING PRESENT (simple) “What do you do every day and what you don’t like to do?” was the announcement in a local newspaper. The investigators wanted to know what were the interests and actions of the citizens. And there was a nice prize: A tour on a sea boat around the world. I answered: “I drink beer every evening and I don’t like to eat pizzas”. John said he likes to ride on bicycle in the morning but he doesn’t like to have breakfast”. Mary answered that she loves sleeping with her cat but that she doesn’t wake up late”. I know that my cat runs in the yard but doesn’t go to the kitchen.” “We prepare hotdogs in the morning but we don’t eat sandwiches”. My parents practice jogging in the early morning but they don’t get on buses to travel. -What does your mother do in the morning? -She washes dishes in the kitchen and cleans the house but she doesn’t like to wash clothes. -What does your father do? -He works in a factory every afternoon but he doesn’t like to pack the merchandise. –What does the pet do at night? -it sleeps on a sofa but it doesn’t eat anything at night. All the answers of the search were sent in an envelope to the newspaper office and there was an answer thanking them for the collaboration and a week later there was a receipt with a number for the lottery wishing good luck. The number reads 23.453 out of 100.000 participants. 6 PRESENT CONTINUOUS I am drinking You are drinking He is drinking She is drinking It is drinking We are drinking You are drinking They are drinking 2 I am not drinking You aren’t drinking He isn't drinking She isn't drinking It isn't drinking We aren't drinking You aren't drinking They aren't drinking 16 8 OK Am I drinking? Are you drinking? Is he drinking? Is she drinking? Is it drinking? Are we drinking? Are you drinking? Are Do they drinking? 6B (TEXTS) USING PRESENT (CONTINOUS) The inspector asked the teacher what the students were doing in class. Here are some of the answers she gave him. Right now I am controlling the work they are doing. Lou is painting a tree on piece of paper. He isn’t using his notebook for the task. Fanny is drawing a house in her notebook. She isn’t coloring it. Pete and Nancy are building up a small project of a mini-city. They aren’t using clay but wet paper. The fan is flowing high currents of air but it isn’t moving to the sides. The inspector very seriously asked again: “And what is that boy over there doing now? –He isn’t doing anything because he is sick. He has a terrible toothache. –“And what about that girl over here?”. Oh she is my daughter, she is keeping my company as long as her teacher comes to class. A little angry said: -“ and what the hell are those kids doing out of class, are they playing?” - Oh I’m sorry but they are preparing themselves for the next sport competitions. 7 I was drinking You were smoking He was writing She was sleeping It was eating We were playing You were studying They were working PAST CONTINUOUS Was I drinking Were you smoking Was he writing Was she sleeping Was it eating Were we playing Were you studying Were they working I wasn´t drinking You weren’t smoking He wasn’t writing She wasn’t sleeping It wasn’t eating We weren’t playing. You weren’t studying They weren’t working 2 18 OK (Yo) no estaba bebiendo (Ud.) no estaba fumando (El) no estaba escribiendo (Ella) no estaba entendiendo (El) no estaba comiendo (Nos.) no estabamos jugando (Uds.) no estaban estudiando (Ellos) no estaban trabajando Estuvo, estuvieron 7B (TEXTS) USING PAST (CONTINOUS) Why were you drinking beer yesterday, ¡Little and unconscientiously boy! Last week we were telling you how dangerous it is to drink at your age. You weren’t studying for your tests. Your mother was asking you to be responsible. She wasn’t cooking that cake for us because of you. The teachers at school were saying that if the boys and girls weren’t preparing for their final tests they were going to repeat the semester. We were working hard for giving you a high education but if you don´t pay attention you will be flunked. I think I told you and your sisters and brothers to go ahead by working hard. Were you paying attention or weren’t you paying attention? I think you were sleeping on your dreams of rock and dance. When I was as young as you are I wasn’t losing my time, I was working day and night. Please,Little boy¡ grow up, you are sixteen now. Oh, my dear daddy I promise I will be good at the tests. You weren’t looking at me when I was concentrated on my studies and responsibilities. I was studying both Math and Chemistry. I wasn’t being irresponsible I was just having a rest. You’ll see my evaluations. 8 SIMPLE PAST TENSE I drank You smoke He wrote She slept It ate We played You studied They worked Did I drink? Did you smoke? Did he write? Did she sleep? It it eat Did we play Did you study Did they work 2 I didn´t drink You didn’t smoke He didn’t write She didn’t sleep It didn’t eat We didn’t play. You didn’t study They didn’t work 20 OK (Yo) no bebí (Ud.) no fumó (El) no escribió (Ella) no durmió (El) no comió (Nos.) no jugamos (Uds.) no estudiaron (Ellos) no trabajaron 8B (TEXTS) USING SIMPLE PAST TENSE There were lots of tasks for the secretaries to be done before the boss came back from his business trips. As soon as he arrived at the office he called the coordinator and asked her about each employee for his/her work. He said, well tell me what did each person exactly do while I was on my business trip. –Boss I controlled the work of each one and wrote in the control book every detail. For example: -Andrew copied all the records and made out a file with the name of “pending informations” -Katherine typed about 30 letter offering our services and sent them to the different companies. – She kept control of it by receipts from the companies. Mark and Lucy cleaned the office and repaired two computers. –The other one must be sent to a special technician. –The other two secretaries attended all clerks and sold a lot of articles. – The employees didn’t lose their time and kept on working. They learned from your responsibility and hard work and for that reason we are having success in business 9 LIST OF IRREGULAR VERBS (& REGULAR) 2 22 OK Simple form Past form Past participle form Spanish awake (auéik) become (bicám) begin (biguín) bend (bend) bet (bet) bind (báind) bite (báit) bleed (blíid) blow (blóu) break (bréik) bring (bring) build (bild) buy (bái) catch (cátch) choose (chúus) come (cam) do (du) draw (dro) drink (drink) drive (dráiv) eat (íit) fall (fol) feed (fíid) feel (fíil) fight (fáit) find (fáind) awoke (auóuk) became (bikéim) began (bigán) bent (bent) bet (bet) bound (báund) bit (bit) bled (bled) blew (blu) broke (bróuk) brought(brot) built (bilt) bought (bot) caught(cot) chose (chóus) came (kéim) did (did) drew (dru) drank (draank) drove (dróuv) ate (éit) fell (fel) fed (fed) felt (felt) fought (fot) found (fáund) awoke (auóuk) become (bicám) begun (bigán) bent (bent) bet (bet) bound (báund) bitten (bíten) bled (bled) blown (blóun) broken (bróuken) brought (brot) built (bilt) bought (bot) caught (cot) chosen (chóusen) come (cam) done (doon) drawn (droon) drunk (drank) driven (dríven) eaten (íten) fallen (fólen) fed (fed) felt (felt) fought (fot) found (fáund) despertarse convertise en comenzar doblar apostar atar morder sangrar soplar romper traer construir comprar agarrar, coger elegir venir hacer dibujar, atraer beber conducir comer caer dar de comer sentir pelear encontrar, hallar fly (flái) forget (forguét) get (guét) give (guív) go (góu) grow (gróu) hang (jang) have (jav) hit (jit) hold (jóuld) keep (kíip) know (nóu) lead (líid) leave (líiv) lend (lend) lose (lúus) make (méik) mean (míin) meet (míit) pay (péi) put (put) read (ríid) ride (ráid) run (ran) say (séi) see (síi) sell (sel) show (shóu) flew (flu) forgot (forgót) got (got) gave (guéiv) went (uént) grew (gru) hung (jaang) had (jad) hit (jit) held (jeld) kept (kept) knew (niú) led (led) left (left) lent (lent) lost (lost) made (méid) meant (ment) met (met) paid (péid) put (put) read (red) rode (róud) ran (raan) said (sed) saw (so) sold (sóuld) showed (shóud) flown (flóun) forgotten (forgóten) got(ten) (góten) given (guíven) gone (gón) grown (gróun) hung (jaang) had (jad) hit (jit) held (jeld) kept (kept) known (nóun) led (led) left (left) lent (lent) lost (lost) made (méid) meant (ment) met (met) paid (péid) put (put) read (red) ridden (ríden) run (ran) said (sed) seen (síin) sold (sóuld) shown (shóun) volar olvidar conseguir dar ir crecer colgar tener golpear sostener asir guardar, mantener saber, conocer guiar dejar irse prestar perder hacer significar encontrarse con pagar poner leer montar, andar en correr decir ver vender mostrar sing (sing) sink (sink) sit (sit) sleep (slíip) speak (spíik) spend (spend) swim (suím) take (téik) teach (tíich) tear (ter) tell (tel) think (zink) throw (zróu) understand(-stáand) wear (wer) win (win) write (ráit) sang (sang) sank (saank) sat (sat) slept (slept) spoke (spóuk) spent (spent) swam (suáam) took (túk) taught (tot) tore (tor) told (tóuld) thought (zot) threw (zru) understood (-stúd) wore (wor) won (won) wrote (róut) sung (saang) sunk (sank) sat (sat) slept (slept) spoken (spóuken) spent (spent) swum (suám) taken (téiken) taught (tot) torn (torn) told (tóuld) thought (zot) thrown (zróun) understood (-stúd) worn (worn) won (won) written (ríten) cantar hundir sentarse dormir hablar gastar nadar llevar tomar enseñar desgarrar decir pensar arrojar entender usar (ropa) ganar escribir 9B LIST OF REGULAR VERBS Simple form Simple past tense D or ED work wash type laugh watch push pick brush like crash mark pass D or ED play learn mow close earn open plan (Pronounce /t/ ) worked washed typed laughed watched pushed picked brushed liked crashed marked passed (Pronounced /d/) played learned mowed closed earned opened planned Past participle Spanish meaning worked washed typed laughed watched pushed picked brushed liked crashed marked passed trabajar lavar digitar reir vigilar empujar recoger cepillar gustar chocar marcar pasar played learned mowed closed earned opened planned jugar aprender podar cerrar ganar abrir planear live love water program flower D or ED visit need mount fit seed adjust omit admit load grant list dot lived loved watered programmed flowered (Pronounced / i d/ visited needed mounted fitted seeded adjusted omitted admitted loaded granted listed dotted lived loved watered programmed flowered vivir amar regar programar florecer visited needed mounted fitted seeded adjusted admitted admitted loaded granted listed dotted visitar necesitar montar encajar sembrar ajustar omitir admitir cargar conceder enlistar graficar MODULO 2 EKT UFPS Students’ guide july 2010 ENGLISH COURSE TO HELP STUDENTS WHO WILL PRESENT THE EKT-U.F.P.S. - (ENGLISH KNOWLEDGES TEST AT THE U.F.P.S.) Council of Acad. ruling 200/6/11/07;Council of Adm.: agreement 11/5/10 N° 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 SECOND PART - CONTENTS SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE PAST PERFECT TENSE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE PASSIVE VOICE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USE OF WH WORDS BE AND HAVE 2ND PREVIOUS 10 SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE: (will-shall; won’t shan’t) I will drink You will smoke He will write She will sleep It will eat We will play You will study They will work Will (shall) I drink? Will you smoke? Will he write? Will she sleep? Will it eat? Will (shall) we play? Will you study? Will they work? I won’t (shan’t) drink You won’t smoke He won’t write She won’t sleep It won’t eat We won’t (shan’t) play You won’t study They won’t work HS/C ∑/H 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 2 25 27 28 29 31 35 36 38 OK OK OK OK OK OK OK 1 25 OK (Yo) no beberé (Ud.) no fumará (El) no escribirá (Ella) no dormirá (El) no comerá (Nos.) no jugaremos (Uds.) no estudiarán (Ellos) no trabajarán 10B (TEXTS) USING SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE What will you plan for your future? Will you be a lawyer or a Technician? Man likes to dream about the future. What will you do if you won a million dollars? What will you do if you were in the United States? Let’s see what our dear students and teachers will do. Let’s know what they and their relatives will do. Margaret: I will buy a new house in Miami and will start a business on hair styling”. My mother will have a full make up. Nancy: “I will travel around the world in a modern ship and my father will go to get a degree at MIT in Boston”. Ralph: “I will go to study medicine in London and my sister Julie will get married and buy a mansion”. George: “I will learn to dive and my cousin will help me at the sea. Mr. and Mrs. Smith: “We will go on our second honey moon to Mexico and will stay at the best hotel downtown, our sons will be having vacations in Argentina. They will meet the best soccer player of Argentina, Maradona. 11 PRESENT PERFECT TENSE 2 27 OK I You He She It We You they Have Have Has Has Has Have Have have found drunk driven eaten fallen fed felt fought Have Have Has Has Has Have Have have I You He She It We You they found? drunk? driven? eaten? fallen? fed? felt? fought? I You He She It We You they Haven’t Haven’t Hasn’t Hasn’t Hasn’t Haven’t Haven’t haven’t found drunk driven eaten fallen fed felt fought No he encontrado No has bebido No ha conducido No ha comido No se ha caído No hemos alimentado No han sentido No han peleado 11B (TEXTS) USING PRESENT PERFECT TENSE I have eaten too much meat lately. What have you drunk with your foods? – I haven’t drunk anything because I prefer dry things for my stomach. -Did you know that Fanny has fed her cat everyday but it isn’t fat, it’s too skinny? -She has fought with her brothers because they hit it at every moment. So she has felt very uncomfortable at home. She hasn’t found a new place for it. Their brothers have forgotten to obey their parents’ orders of respecting each other. They have received the guidance but nothing has changed. Mary has gone to many homes in search of a new home for her pet. As people have seen that it is thin they have said that they are not interested in keeping the pet. Well, tell her that I might have that little cat and that she can go to my house whenever she wishes to. Now she has found a new shelter for it. 12 I You He She It We You they PAST PERFECT TENSE Had Had Had Had Had Had Had Had flown forgot got given gone grown hung had Had Had Had Had Had Had Had Had I You He She It We You they flown forgot got given gone grown hung had 1 I You He She It We You they Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t Hadn’t flown forgot got given gone grown hung had 28 OK No había volado No habías olvidado No había conseguido No había dado Nohabía ido No habíamos crecido No habían colgado No habían tenido 12B (TEXTS) USING PAST PERFECT TENSE They said they had forgotten to do their tasks, but I know they had played instead of studying. My father had spoken to them but they didn’t listen to him. I think they had grown up as kids and not as responsible young men. I also knew that they had spent all the money they had received from their mother. Teachers had taught them to be good guys and do what should be done at the right moment and not to spend time or money in nonsense things. Their grandma had sung a beautiful picture of fruit trees on the wall but a little later they had taken it away and had sold it for a few cents. At last when they had gone to the park and had ragged some banks they were caught by a policewoman who took them to the police station. There they said that they had thought the banks were for waste. 13 FUTURE PERFECT TENSE I WILL HAVE HIT YOU WILL HAVE HELD HE WILL HAVE KEPT WILL I HAVE HIT? WILL YOU HAVE HELD WILL HE HAVE KEPT 1 I WON’T HAVE HIT YOU WON’T HAVE HELD HE WON’T HAVE KEPT 29 No habré golpeado No habrás sotenido Nop habrá cuardado OK SHE WILL HAVE SEEN IT WILL HAVE LED WE WILL HAVE LEFT YOU WILL HAVE LOST THEY WILL HAVE READ WILL SHE HAVE SEEN WILL IT HAVE LED WILL WE HAVE LEFT WILL YOU HAVE LOST WILL THEY HAVE READ SHE WON’T HAVE SEEN IT WON’T HAVE LED WE WON’T HAVE LEFT YOU WON’T HAVE LOST THEY WON’T HAVE READ No habrá visto No habrá conducido No habremos dejado No habrás perdido No habrán leído 13B (TEXTS) USING FUTURE PERFECT TENSE By the time when I be settled in my new home in Boston and this will be within five years I will have seen many modern plays. I will also have lost weigh, and I will have led an art exposition. I also know that I will have kept many collections of coins and whisky bottles. On the other hand my uncle will have won lots of money with his new invention. My mother will have visited all of our friends in USA. My father will have made sculptures of Indian groups. My sister will have read at least 100 books. And, of course, we all will have met hundreds of artisans, artists and actors. -Can you imagine what I will have done by then? 14 PASSIVE VOICE Active voice I am drinking coffee You are eating bread He is driving a bus She was selling a skirt We were buying shoes They (do) play soccer He (does) teach Italian She (did) visit the doctor You will type letters They would paint the house She can swim 100 mts. He could steal the papers We may watch the game They might do the homeworks I shall repeat the course They should brush the metal She must learn the vocabulary I have brought the books She has written the word We had seen a policeman 2 Passive voice Coffe is drunk by me. Bread is being eaten by you A bus is being driven by him A skirt was being sold by her Shoes were being bought by us Soccer is played by them Italian is taught by him The doctor was visited by her Letters will be typed by you The house would be painted by them 100 mts can be swum by her The papers could be stolen by him The game may be watched by us The homeworks might be done by them The course shall be repeated by me The metal should be brushed by them The vocabulary must be learned by her The books have been brought by me The word has been written by her A policeman had been seen by us 31 OK El café es tomado por mí El pan está siendo comido por usted. Un bus está siendo conducido por él Una falda estaba siendo vendida por ella Los zapatos estaban siendo comprados por nos. El balonpié es jugado por ellos El Italiano es enseñado por él. El doctor fue fisitado por ella. Las cartas serán digitadas por usted La casa sería pintada por ellos Los 100 ms. pueden ser nadados por ella Los documentos podrían ser robados por él El partido puede ser visto por nosotros Las tareas podrían ser hechas por ellos El curso será repetido por mí El metal debería ser pulido por ellos El vocabulario debe ser aprendido por ella Los libros han sido traídos por mí La palabra ha sido escrita por ella. Un policía había sido visto por nosotros 14B (TEXTS) USING PASSIVE VOICE English is spoken in many countries all around the world. It is used by many businessmen and artists. Negotiations could be done in this language. English is taught in many institutes everywhere. English was brought by English men at the time of the american conquest. The MIT was visited by some teachers. Three famous museums were attended by some elder men. There was a boat race near Logan airport which could be run by anyone. There was a suspicions man near Boston Bank. The bank has been robbed by some one twice and the policemen think that that man is the responsable of it. The man has been caught by the police many times but nothing has been proved against him. The pictures have been taken by him said some one. His brother appeared and said that his brother was a photographer. The city has been photographed by him, specially the rout of freedom downtown in Boston. The pictures have been seen by many people and they agree that they are wonderful. Art compositions have been digited by a strange photographer. 15 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS -USE OF WH WORDS 4 35 OK General English practice: A] Answer each question. B] Create your own questions and answers There are “wh” questions and an answer in each group: you can replace the underlined words and have your own questions and answers (There is some help in your language) What do you do? ¿Qué haces? What do you [play]? ¿Qué tocas? Where do you [play tennis]? ¿Dónde juegas tenis? When do you [play tennis at school]? ¿Cuándo juegas tenis en el colegio? Why do you [play tennis on Sundays]? ¿Por qué juegas tenis los domingos? (I play tennis at school on Sundays because I like this sport) What does she do? What does she teach? Where does she teach French? When does she teach French at home? Why does she teach French every day? (She teaches French at home every day because she needs money) ¿Qué hace ella? ¿Qué enseña ella? ¿Dónde enseña ella Francés? ¿Cuándo enseña ella Francés en casa? ¿Por qué ella enseña Francés todos los días? What did you do? What did you study? Where did you study English? When did you study English in Europe? Why did you study English last month? (I studied English in Europe last month because I won a scholarship) ¿Qué hiciste? ¿Qué estudiaste? ¿Dónde estudiaste Inglés? ¿Cuándo estudiaste Inglés en Europa? ¿Por qué estudiaste Inglés el mes pasado? What will you do? What will you write? Where will you write letters? When will you write letters in the hall? Why will you write letters every week? (I will write letters in the hall every week because there is no other place to do it.) What can you do? What can you drive? Where can you drive a taxi? When can you drive a taxi in the city? Why can you drive a taxi on Saturdays? ¿Qué harás? ¿Qué escribirás? ¿Dónde escribirás cartas? ¿Cuándo escribirás cartas en el may? ¿Por qué escribirás cartas todas las semanas? ¿Qué puedes hacer? ¿Qué puedes conducir? ¿Dónde puedes conducir un taxi? ¿Cuándo puedes conducir un taxi en la ciud? ¿Por qué puedes conducir un taxi los sábado? (I can drive a taxi in the city on Saturdays because there isn’t too much traffic) What should he do? What should he visit? Where should he visit a clinic? When should he visit a clinic at Btá? Why should he visit a clinic now? (He should visit a clinic at Bogotá now because he is very sick) What are you doing? What are you preparing? Where are you preparing your tests? When are you preparing your tests? Why are you preparing your tests? (I am preparing my tests at the office in the mornings) What were you doing? What were you drinking? Where were you drinking coffee? When were you drinking coffee? Why were you drinking coffee? (I was drinking coffee at the restaurant yesterday morning because I was tired) ¿Qué debería hacer él? ¿Qué debería visitar él? ¿Dónde debería el visitar una clínica? ¿Cuándo debería visitar una clínica en Btá? ¿Por qué él debería visitar una clínica ahora? ¿Qué estás haciendo? ¿Qué estás preparando? ¿Dónde estás preparando tus exámenes? ¿Cuándo está preparando tus exámenes? ¿Por qué está preparando tus exámenes? ¿Qué estabas haciendo? ¿Qué estabas tomando? ¿Dónde estabas tomando café? ¿Cuándo estabas tomando café? ¿Por qué estabas tomando café? 15B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USING “WH” WORDS Study guide: Pair questions and answers. Practice orally with mates. Give own answers. Create your own questions and answers 01) What’s your name? 02) Where were you born? 03) How old are you? 04) What’s your address? 05) What’s your phone number? 06) What are your parents’ names? 07) What does your father do? 08) What does your mother do? 09) How many brothers and sisters do you have? 01) My name is Albert White Johnson. 02) I was born in Cúcuta. 03) I’m 20 years old. 04) It’s 4-30 6th Street. 05) My phone number is 7567503. 06) They are Pete Johnson and Mary White? 07) He works in a factory. 08) She works at home. She’s a housewife. 09) I have two brothers and one sister. 10) What do they do? 11) Where do you study? 12) What level are you in? 13) How much do you pay for your study? 14) What subjects do you like best? 15) What subject don’t you like? 16) Which sport(s) do you practice? 17) What are your favorite hobbies? 18) What do you like best?: (reading, writing, or) … 19) Who is your favorite personage? 20) Why do you think English will be for? 21) What would you do if you had ten million bucks? 22) What career are you studying at this institution? 23) How do you define yourself? (quiet, passive, or…) 24) Would you like to be diligent or lazy?. 25) What were you doing last Sunday night? 10) They are studying 11) I study at the university. 12) I’m in the sixth semester. 13) I pay a minimum salary a year. 14) I like Math, English and Communication 15) I don’t like Physics. 16) I practice soccer and basketball. 17) My favorite hobbies are reading and dancing 18) I like swimming 19) My favorite personage is Leonardo D’Avinci. 20) It will be for getting better jobs. 21) If I had $10.000 I would travel around the world 22) I’m studying Systems engineering here. 23) I’m a quiet, well spoken and honest person. 24) I would like to be diligent. 25) I was dancing at a party last Sunday night. 15C QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USING “WH” WORDS Study guide: Pair questions and answers. Practice orally with mates. Give own answers. Create your own questions. 26) What does the new queen look like? 27) Why did(n’t) you agree with the election? 28) Where will the queen go to next December? 29) What would you tell her if she were here? 30) Why will you need more information? 31) When should we begin to practice English? 32) Where can(n’t) you go on weekends now? 33) Why could(n’t) you travel to Ocaña? 34) Where may I ask you to do it? 35) What might your classmates be doing now? 36) Who must teach you how to be polite? 37) Why are the people menaced by the war? 26) She is the most beautiful and nice girl in the world. 27) I agreed because she has a great personality. 28) She will go to her hometown next December. 29) I would tell her that she is lovely and charming. 30) I will need it because I don’t know what to do. 31) We should begin to practice English immediately 32) I can’t go out of town on weekends now. 33) I couldn’t travel to Ocaña because it is dangerous. 34) You may I ask me to do it anywhere. 35) They might be chattering because there is no teacher. 36) The family must teach us how to be polite. 37) Because it is impossible to make the peace. 38) What have you been studying these days? 39) Where has your father worked lately? 40) Why had we met in class every week? 41) What is there at this institute next month? 42) Why aren’t there any fruit trees here? 43) Why are you sleepy in the morning? 44) Why are you hungry at midday? 45) Where were you angry at your teachers? 46) How were you after the game? 47) Who is older than you? 48) What do you wear on Sundays? 49) What do you like to do in vacations? 50) What can we do to get the peace? 38) I have been studying grammar and vocabulary. 39) He has worked at a tile factory lately 40) We had done it because we have to discuss a task. 41) I don’t know. I’m new here 42) There aren’t any fruit trees because they were cut. 43) I’m sleepy because I have to go to study. 44) I’m hungry at midday because I work hard. 45) I was angry at my teachers in the auditorium. 46) I was too thirsty after the game. 47) My sister is older than me. 48) I wear tennis shoes, a flannel, and Bermudas. 49) I like to watch T.V. and visit my friends. 50) We can try to help others to get the peace. 15D QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USING “WH” WORDS Study guide: Pair questions and answers. Practice orally with mates. Give own answers. Create your own questions. 51) What am I teaching you? 52) Where is Park Victory? 53) Where are the children playing? 54) Why was Montoya out of the run? 55) What were you doing last weekend? 56) Where do women go shopping in Cúcuta? 57) When does a child ask for help? 58) Why did Colombians begin to suffer? 59) What can you do for your country? 60) Where could you learn how to drive? 61) When will vacations take place? 62) Why would people take care on the streets? 63) What shall I inform you about English? 64) Where should policemen be at night? 51) You are teaching me how to learn by myself. 52) Park Victory is on second Av. and twelfth St. 53) They are playing in the park. 54) Because his car had the motor broken. 55) I was preparing for my tests last weekend. 56) Women go shopping to Ventura Plaza. 57) A child asks for help when he can’t do something 58) Colombians began to suffer a long time ago. 59) I can vote correctly. 60) I could learn how to drive at a car school 61) Vacations will take place in June and December. 62) Because streets are dangerous because of the cars. 63) You will I inform me on how I can write it well. 64) They should be on the dark streets at night 65) When may I ask you to answer this test? 66) Why might all Colombians be together? 67) What do you have to do to pass this test? 68) Where have the teachers had a party? 69) When has the director spoken to the students? 70) Why had they elected a new president? 71) What did you use to do when you were ten? 72) Why isn’t German taught at this institute? 73) Where were trolleys driven in Colombia? 74) When was the vocabulary learned by you? 75) Why were all the games seen on T.V.? 65) You may ask me to answer this test right now. 66) All of them might be together in order to have peace. 67) I have to study hard in order to pass it. 68) They have had a party at their club. 69) He has spoken to the students on Mondays. 70) They had elected him because of the Constitution. 71) I used to play and laugh when I was ten years old. 72) It isn’t taught here because there aren’t teachers. 73) They were driven in Bogotá. 74) The vocabulary was learned by us last week. 75) They were seen on it because of the rain. 15E QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS USING “WH” WORDS Study guide: Pair questions and answers. Practice orally with mates. Give own answers. Create your own questions. 76) Why will it be written in English? 77) Why can’t old stories be told to kids? 78) What could be said after elections? 79) Where had votes been deposited in elections? 80) What thin has been said about politicians? 81) Where had tequila been drunk? 82) Why is there a new president in Colombia? 83) Where were there many problems? 84) When were there too many accidents? 85) How long does a car race last? 86) How much did a new taxi cost in 1970? 87) How many kinds of trees are there in Cúcuta? 88) How far is it from Cúcuta to San Antonio? 89) Which candidate did you like best? 90) Who won the presidency of Colombia? 91) Whose shoes are you wearing now? 92) How do you feel today? 76) Because it is for English speakers 77) Because the television is absorbing them. 78) It could be said “most people made a hard election”. 79) They have been deposited in the election boxes. 80) It is said that they look for their interests only. 81) It had been drunk in the Mexican pubs. 82) Because the Constitution states the new election. 83) There were only a few problems during elections. 84) There were many accidents last Sunday. 85) A car race lasts about four hours. 86) I cost about two million pesos in 1970. 87) There are 2.000 kinds of trees in Cúcuta. 88) It is about ten kilometers. 89) I liked (NN). 90) (NN) won the presidency of Colombia, 2010-2014. 91) I’m wearing my own shoes. 92) I feel very well today. 93) What are you looking for? 94) Why have you called me up lately? 95) How about some more study to learn it? 96) What do you think about your classmates? 97) Why have you had your car washed lately? 98) Why has your moher visited the doctor? 99) How many words do you know in English? 100)Why have you got tired of studying English? 16 BE AND HAVE BE (SER, ESTAR, TENER) I am a farmer Soy un granjero You are tired Estás cansado He/She/It is sick Está enfermo We are musicians Somos músicos You are shouting (Uds) están gritando They are rich Son ricos I am not a farmer No soy un granjero You are not tired No estás cansado He/She/It is not sick No está enfermo We are not musicians No somos músicos You are not shouting 93) I’m looking for a new job. 94) Because I need some information from you. 95) Sure, I’m interested in learning English. 96) I think they are very good people. 97) I have had it washed lately because it was dirty. 98) My mom has visited him because she is been sick. 99) I know (5000) words in English. 100) I have got tired of it because I haven’t had a break. 1 36 HAVE (TENER) I have a farm Tengo una granja You have to rest Tienes que descansar He/She/It has fever Tiene fiebre We have instruments Tenemos instrumentos You have to shut up (Uds) tienen que callarse They have money Tienen dinero I don't have a farm No tengo una granja You don't have to rest No tienes que descansar He/She/It doesn't have fever no tiene fiebre We don't have instruments No tenemos instrumentos You don't have to shut up OK Uds no están gritando They are not rich No son ricos Am I a farmer? ¿Soy un granjero? Are you tired? ¿Estás cansado? Is he/she/it sick? ¿Está enfermo/a? Are we musicians? ¿Somos músicos? Are you shouting? ¿Están (Uds) gritando? Are they rich? ¿Son ricos (ellos)? Uds no tienen que callarse They don't have money No tienen dinero Do I have a farm? ¿Tengo una granja? Do you have to rest? ¿Tienes que descansar? Does he/she/it have fever? ¿Tiene fiebre? Do we have instruments? ¿Tenemos instrumentos? Do you have to shut up? ¿Tienen (Uds) que callarse? Do they have money? ¿Tienen (ellos) dinero? MODULO 3 EKT UFPS Students’ guide ENGLISH COURSE TO HELP STUDENTS WHO WILL PRESENT THE EKT-U.F.P.S. - (ENGLISH KNOWLEDGES TEST AT THE U.F.P.S.) Council of Acad. ruling 200/6/11/07;Council of Adm.: agreement 11/5/10 N° 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 17 THIRD PART - CONTENTS ADJECTIVES ADVERBS CONJUNCTIONS PREPOSITIONS DO/MAKE MODAL VERBS CONDITIONAL PHRASAL VERBS (IDIOMS) VOCABULARIES HS/C ∑/H 40 41 43 46 47 49 51 54 58 60 OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK OK FINAL TEST 2 1 2 3 1 2 2 3 3 2 ADJECTIVES 2 40 OK 17A. COMPARISONS 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 Cali is a beautiful Colombian city. Medellin is larger than Cali Bogotá is the largest city in Colombia Barranquilla is as large as Medellin Bucaramanga is a commercial city Medellin is more commercial than Bucaramanga Bogotá is the most commercial city of them all. Medellin is beautiful Cali is as beautiful as Medellin Barranquilla isn’t as beautiful as Cali. Cali isn’t so cool as Medellin. It’s [………] It’s […….…] than good better bad worse little less far farther much more many more It’s the [……….] Best Worst least farthest most most good/well - bueno, bien bad/badly - mal much/many - mucho/muchos little - poco far - lejos better - mejor worse - peor more - más less - menos farther/further - más lejos 17B. ADJECTIVE FORMATION: agreeable disagreeable similar dissimilar afraid unafraid clear unclear fair unfair healthy unhealthy direct indirect complete incomplete existent nonexistent political nonpolitical faithful unfaithful continuous discontinuous active inactive natural unnatural perfect imperfect selfish unselfish educational noneducational fortunate unfortunate (the) best - el mejor (the) worst - el peor (the) most - el/los más (the) least - el menos (the) farthest/furthest - el más lejano They seemed to be (...) eventful uneventful formal informal respectful disrespectful pure impure wealthy unwealthy friendly unfriendly beautiful worthless dangerous accidental basic childish different pleasant comfortable sensible active imaginative crowded surprising wonderful marvelous ordinary easy hard complicated good nice salty hot 17C. BASIC ADJECTIVES OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE afraid bad big black blind blue bright broad brown busy certain clean clear cold cool dark dear deep different fair famous fat first five foreing four fresh full gentle glad good great green happy hard heavy high hot little long loud low mad middle necessary nervous new nice old one pleasant poor possible pretty probable proud public rich sad safe second seven short sick simple single six slow small soft sorry special straight strange strong sweet three twelve twenty two warm weak white wide wild wise worth wrong yellow young next sure half important forward direct distant double easy eight electric humble hungry ill kind large left pure quick quiet ready real red talk tall ten thick thin third human dead due equal past perfect 17D. BASIC ADJECTIVES OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE Awake – despierto Beautiful – hermoso Big - grande Bitter - amargo Black - negro Careful - cuidadoso Dark - oscuro Dead - muerto Deep - profundo Difficult - difícil Dirty - sucio Drunk - borracho Expensive - caro Far - lejano New - nuevo On - encendido Past - pasado Polite - cortés, atento Rich - rico Right - derecho Right - correcto Rough - áspero Safe - seguro Same - mismo Fast - rápido Asleep - dormido Ugly - feo Small - pequeño Sweet - dulce White - blanco Careless - descuidado Light - claro Alive - vivo Shallow - superficial Easy - fácil Clean - limpio Sober - sobrio Cheap - barato Near - cercano Old - viejo Off - apagado Future - futuro Rude - grosero Poor - pobre Left - izquierdo Wrong - equivocado Smooth - suave, liso Dangerous - peligroso Different - diferente Slow - lento Fat - gordo Full - lleno Glad - contento Good - bueno Happy - feliz Hard - duro Healthy - saludable Heavy - pesado High - alto Hot - caliente Interesting - interesante Late - tarde Long - largo Simple - simple Single - soltero Straight - derecho Strong - fuerte Tall - alto Thick - grueso True - verdadero Useful - útil Warm - cálido Wet - mojado Wide - ancho Young - joven Thin - flaco Empty - vacío Sad - triste Bad - malo Sorry - apenado Soft - blando Sick - enfermo Light - liviano Low - bajo Cold - frío Boring - aburrido Early - temprano Short - corto Complex - complejo Married - casado Crooked - torcido Weak - débil Short - bajo Thin - delgado False - falso Useless - inútil Cool - fresco Dry - seco Narrow - angosto Old - viejo 18 ADVERBS 1 41 OK COMMON ENGLISH ADVERBS He’s working [.............] Place: here, there, near, far, far from, inside, out, out of, up, down, ahead, in back of, over, under, behind Time: I work [...] I worked [...] I’m working[...] I will work[...] today, yesterday, the day before yesterday, tomorrow, last night, now, before, after, then late, early, soon, always, never, seldom, rarely, frequently, usually, ever, sometimes, often, recently, already, yet, every month, every week, every year, last month, next week, next time, now and then, in an hour, every other day. Mood He works [...] He worked [...] He will work [...] He’s working [...] well, badly, better, slowly, promptly, correctly, gladly, foolishly, weekly, monthly, perfectly, sadly, softly, suddenly, plainly, happily, formally, daily, instantly, yearly Quantity How much paper did you buy? How many papers did you buy? much, a little, a few, more, less, enough, nothing, some everything, something, many, a lot of, lots of, plenty, a great deal. Order first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, successively, respectively, lately, (the) former, (the) latter ninth, tenth, yes, also, certainly, sure, surely, effectively, no, nor, clearly, neither, either, never, maybe, perhaps 18B. STRUCTURE OF ADVERBS IN ENGLISH bad, badly/ quick, quickly/ luxurious, luxuriously/ public, publicly/ faithful, faithfully/ cheap, cheaply/ easy, easily/ true, truly/ sad, sadly/ probable, probably/ honest, honestly/ happy, happily/ nice, nicely/ beautiful, beautifully/ changeable, changeably/ perfect, perfectly/ 19 CONJUNCTIONS AND OTHER FUNCTION WORDS 2 19. CONJUNCTIONS and but for or nor so yet They were drinking and laughing. He likes to do everything but study. He went there for he was thirsty. Would you like to speak about Lucy or Fanny? I’d neither speak about Lucy nor Fanny. He didn’t call me up, so I called him up. We haven’t finished our study yet. 43 OK 19B. DETERMINANTS the a an my your his her its our their this that these those each every no both some any all many much few several either neither more most These are the basic function words in English. This is a very important exercise. That is an interesting practice. Those are my university books. Where’s your teacher’s signature? Which are his technical works? Why is her decision unimportant? When is its library open? How are our letters delivered? How long are their kids going to be here) This experiment is very hard. Which structure shows that engineer? Did you plan these operations? Could you attend those organizations? Would each one produce a larger amount? Does every company build up a bridge? We have no time to lose. Have both subjects been studied? Some people do not like to take trips. Should any technician be invited to the forum? All of them like to investigate in their field Many electricians work in the country. Do you eat much food at night? Very few people go to the university in Colombia. Several nurses teach special programs in Cúcuta. Don’t forget to take either this map or the other. Neither this lawyer nor the other were right. Shall we need more experiments? Most people lose lots of time doing nothing. 19C. INTENSIFIERS very quite somewhat rather pretty mighty little so too more most less least enough It is very important that you know yourself. We were quite tired after such a work. It is somewhat difficult to be used. It is rather easy to learn a language. It could be pretty well understood. They were mighty important for everyone. Do you feel a little better now? They have so little time to study that subject. Life in Cúcuta is too expensive. We have to get more money for living. It is the most beautiful place in the world. Indians and farmers shouldn’t be less important. Tallness is the least important thing. This climate is good enough for living things. 19D. SUBORDINATES After although as As if because before how if provided since than that though until what when whenever where which whereas whichever while who whoever whom whose You shouldn’t play after lunch. He came although he didn’t want to. Does every man speak as he thinks? Some people pretend to live as if they were rich. You are here because you want to succeed. You have to get money before you plan to go. Do you know how to speak in French? Would you travel if you had money? You will get a degree provided you pass the test. He hadn’t studied English since he was sixteen. It is bigger than you think. The books that he bought weren’t new. He got the money, though he didn’t work for it. Do not leave until you are told to. It wasn’t what I told you to do. They were reading when she arrived. You can drive it whenever you wish to. There is where it was done. This is the university which he preferred. He’s responsible, whereas his sister isn’t. Select the car whichever you like best. I was flying while they were sailing. That is the man who plays the guitar. It isn’t true whoever said so. Those are for whom he was working. That is the boy whose father won a lottery. 19E. SENTENCE CONNECTORS therefore accordingly also at least besides consequently for example furthermore hence however indeed in addition in fact moreover nevertheless then thus They went to the movies; therefore, John couldn’t see them. It was locked. They, accordingly, with it left at once. Gasoline was increased. They also increased all other prices. It’s difficult to be obtained. At least we must get one. He doesn’t come on time, besides, he forgets everything. He was a bad employee, consequently, he was fired. It is easy to be understood if, for example, you speak slowly. They couldn’t paint the wall and, furthermore, they shouldn’t. The computer was out of order; hence, the answers were wrong. He was a tennis player; however, he couldn’t play table tennis. They were in the farm, indeed, they forced to work there They lost a lot of money, in addition to it, there was an accident. They were published. They were, in fact, very good. She is a fast typist, moreover, she is diligent. The tests were given; nevertheless, nobody answered them. They were stated, and then they could take right decisions. It was settled so, thus, no one can change it. 19F. INTERROGATIVE WORDS what where when why How which whose who(m) who What is the importance of the university? Where was the meeting taking place? When is the party going to be over? Why would you like to go there? How could you do it again? Which career do you like best? Whose house are you going to buy? Who(m) did you visit yesterday? Who visited you? 20 PREPOSITIONS 3 46 about above across after against along among around at Acerca de Por encima de A través de Después de Contra A lo largo de En medio de Alrededor de En This guide is about English structures. The university is above high school. We walked across the International Bridge. Study one word after another. Prepare yourself against any adversity. Be yourself along your pass over this planet There are many thinkers among Colombians Let’s take a trip around our country. We are at the university. before behind below beneath beside besides between beyond by despite down during for from in inside into like near of off on Antes Detrás de Por debajo de Por debajo de Al lado de Además de Entre Más allá de Por A pesar de Abajo Durante Por, para De, desde En, dentro de Dentro de Dentro de Como Cerca de De Fuera En Make plans before you start anything. You can’t stay behind others, go ahead. The temperature in Cúcuta isn’t below 30°C. Your words must not be beneath your thought. The Erasmos Meoz Hospital is beside the I.S.S. Did you study another career besides this one? La Don Juana is between Cúcuta and Pamplona Is the moon beyond man’s reach now? Hamlet was written by William Shakespeare. You will learn English despite its problems. Let’s go down the river. Have a break during your work You should be learning for yourself Where are you from? Business used to be the main occupation here. Have you ever been inside a theater for plays? Change your sorrows into happiness by working Life is like a chess game, isn’t it? There is a hospital near U.F.P.S. We all are part of the education system. In december you are off your studies and work. St. Joseph Cathedral is on fifth avenue. OK onto over since through throughout till-until toward under up upon with within without 21 Sobre Por encima de Desde A través de En todo Hasta Hacia Debajo de Arriva Sobre Con Dentro de sin The seed were spread onto the dessert. Jets fly over this beautiful city Cúcuta. U.F.P.S. has been functioning since 1962. UFPS has grown through the work of people. It is well known throughout the country. Read carefully till (until) you understand. You are going toward a better future. Your percentage can’t be under 64% Climb up any stairs, step by step. Don’t climb upon the clouds of your dreams. Do you live in peace with yourself? San Antonio is within 10 kms from Cúcuta. You cannot go ahead without others. DO/MAKE 1 47 OK 21A. DO/MAKE Mrs. Jones is a housewife - La señora Jones es una ama de casa She has to do the housework Ella tiene que hacer el trabajo de la casa She has to do the cooking Ella tiene que cocinar She has to do the washing up Ella tiene que fregar los platos She has to do the washing/the laundry Ella tiene que lavar la ropa sucia She has to do the shopping Ella tiene que hacer las compras She has to do the ironing Ella tiene que planchar la ropa She has to do the dusting Ella tiene que quitar el polvo a las cosas She has to make the beds Ella tiene que hacer las camas She has to make breakfast Ella tiene que hacer el desayuno She has to make lunch Ella tiene que hacer el almuerzo She has to make dinner Ella tiene que hacer la cena She has to make coffee/tea Ella tiene que hacer café/té She has to make a cake Ella tiene que hacer un torta She has to make sure that the house is in order Ella tiene que asegurarse que la casa esté en orden 21B. DO/MAKE Mr. Jones is a businessman - El señor Jones es un empresario He is doing business with important companies Él está haciendo negocios con firmas importantes He is doing well in his job Va bien en su trabajo He does his best to improve his company Hace lo mejor que puede para mejorar su empresa He is making a lot of money Está haciendo un montón de dinero He is making a fortune Está haciendo una fortuna He doesn't like to make mistakes He would like to make a long trip/journey Le gustaría hacer un largo viaje His employees make fun of him Sus empleados se burlan de él He has to make a speech for a meeting Tiene que hacer un discurso para una reunión His secretary makes appointments for him Su secretaria arregla citas para él She also makes telephone calls and reservations También hace llamadas telefónicas y reservas He says that his employees make trouble No le gusta equivocarse Sometimes he makes a fuss when something goes wrong Algunas veces arma un lío cuando algo sale mal He rarely makes jokes Casi nunca hace chistes He doesn't have much time to make friends No tiene mucho tiempo para hacer amigos He is making an effort to increase sales Está haciendo un esfuerzo para aumentar las ventas Él dice que sus empleados causan problemas He also says that women make a lot of noise También dice que las mujeres hacen mucho ruido He often makes a fool of himself A menudo se pone en ridículo He makes use of his authority to threaten people Utiliza su autoridad para amenazar a las personas Some of his decisions don't make sense Algunas de sus decisiones no tienen sentido 21C DO/MAKE other examples John is doing badly at school (he is not doing well) John no va bien en la escuela He doesn't like to do his homework - No le gusta hacer su tarea The hurricane did a lot of damage in the area El huracán causó mucho daño en la zona The policeman was doing his duty when he arrested the thief El policía estaba cumpliendo con su deber cuando arrestó al ladrón Mary did her hair and her face and left for the party Mary se peinó, se maquilló y salió para la fiesta "Can you do me a favor ?" - ¿Me puedes hacer un favor? "I want to make a complaint about the service in this hotel" Quiero presentar una queja sobre el servicio en este hotel The man and the woman were making love in the back seat of their car El hombre y la mujer estaban haciendo el amor en el asiento trasero de su auto Johnny made a mess in his room - Johnny hizo un desorden en su cuarto Bill made his way to the university - Bill se dirigió a la universidad Jane made an excuse and left - Jane se disculpó y se marchó "What are you doing here?" - ¿Qué estás haciendo aquí? 22 MODAL VERBS (helping verbs with another verb) MODALS (A) USO Expresar habilidad Pedir y dar Permiso Preguntar Expresar Necesidad Ejemplos She can read in French She could read when she was four She was able to read French stories Can I go out, teacher? Could you turn on the T.V.? You may leave now Can you erase the board, please? Could you erase the board, please? You have to go to bed now You have got to go to bed now. 2 49 Traducción y explicación Ella lee en Francés Ella sabía leer cuando tenía cuatro años Ella podía leer cuentos en Francés Puedo salir, profe? (Uso común) Puedes encender la T.V? (Uso popular) Puedes salir ahora. (Uso popular) Puede borrar el tablero (Poco cortés) Podrías borrar el tablero (Más cortés) Debes irte a dormir Tienes que irte a dormir OK Tuvo que acostarse temprano Debes acostarte ya Debes apresurarte o llegarás tarde (con poder sobre otro=must) No tienes que irte sino hasta las 8:00 Ella no tuvo que escribir cartas. He had to go to bed early You must go to bed now You must run or you’ll be late Expresar carencia Dar consejo Dar Ordenes Expresar certidumbre E imposibilidad Hablando del Futuro Expresar Posibilidad Hablar del pasado MODALS (B) Can Could May Might Shall Must Have to Are to Should Ought to You don’t have to leave until 8:00 She didn’t have to write letters You should study every day. You ought to study every day He shouldn’t have brought that He ought not to have brought that. Deberías estudiar todos los días Tu tienes que estudiar todos los días. El no debería haber traído eso. El no tenía que haber traído eso. (Se usan para acciones (in/correctas) No debes fumar tanto. Debes cuidar tu salud. No debes estar afuera. Debes estar aquí You mustn’t smoke so much. You must take care of your health You are not to be out You are to be here He has played all day. He must be tired He has not played. He can’t be tired. She is not at school. She must have gone home. It will rain tonight. I shall invite you when we have made some money It may rain tonight It might rain tonight I used to play pebbles when I was a boy. We would rarely stay out at night (not) --- (n’t) El ha jugado todo el día. Debe estar cansado. El no ha jugado. No puede estar cansado. Ella no esta en el colegio. Debe haberse ido a casa. Must y can’t son opuestos en significado. Lloverá esta anoche. Te invitaré cuando hayamos ganado más dinero. (Will es más común que shall. Shall es usado familiarmente solo con (I y WE) Puede que llueva esta noche. (+) Podría llover esta noche. (-) Yo jugaba canicas cuando era niño. Rara vez estaríamos afuera de noche Preguntas Describiendo lo que alguien dijo He can not speak German He can’t speak German I couldn’t swim when I was a little girl You may not go to the river today. We might not be at home Can he speak German? He said he could speak German Could you swim When you were a little girl? May I go to the river? She said she could swim when she was a little girl I said you may not go Where might they be? They said they might stay at the hotel. We shall not work on Saturday They must not walk Shall we go to work on Saturday? Must they walk now? He said we should go to the park on Saturday. She said they must walk now. You don’t have to study Do you have to study? I said you have to study You aren’t to leave your work He should visit the doctor Are you to leave your work? Should he visit the doctor? He said they were to leave their work You ought not to teach Ought you to teach there? They said you ought to teach there I said you should visit the doctor. Will Used to Would 23 there. It won’t be a sunny day Will it a sunny day? I said it wouldn’t be a sunny day I didn’t use to smoke at the office I would not come back tomorrow Did you use to smoke at the office? Would you come back tomorrow? She said she used to smoke at home. CONDITIONAL He said I wouldn’t come back tomorrow 2 51 OK Type I Present If he is busy now, I will come back tomorrow If I have time, I'll visit my parents this afternoon If it is warm tomorrow, we'll go to the beach If it is cold, you must wear warm clothes Will / can / may / must + V1 Si está ocupado ahora, regresaré mañana Si tengo tiempo, visitaré a mis padres esta tarde Si está caluroso mañana, iremos a la playa Si está frío, debes usar ropa abrigada Type II Past If I were in Brazil, I would go to Río de Janeiro If I were you, I would buy that car If he were in my place, he wouldn't do this If I had more money, I would buy a nice appartment Would / could / might + V1 Si yo estuviese en Brasil, iría a Río de Janeiro Si yo fuera vos, compraría ese auto Si él estuviese en mi lugar, no haría esto Si yo tuviese más dinero, me compraría un lindo apartamento Type III Past Perfect If I had seen him, I would have told him about you If I had known the answer, I would have raised my hand If she had come on Saturday, I would have seen her If they had left earlier, they would have arrived on time Would / could / might + have V3 Si lo hubiese visto, le habría contado acerca de ti Si hubiese sabido la respuesta, habría levantado mi mano Si ella hubiese venido el sábado, la habría visto Habitual Present If I have time, I usually go to the movies If she eats hamburgers, she gets an allergy If they come here, they always bring a present If she doesn't know the answer, she keeps silent Present Si tengo tiempo, generalmente voy al cine Si ella come hamburguesas, le da alergia. Si ellos vienen aquí, siempre traen un regalo Si ella no sabe la respuesta, se mantiene en silencio Imperative Present If they are busy, don't disturb them If it is raining, please bring me my umbrella If she phones, don't tell her I was here If you don't want to go, don't go Imperative Si ellos están ocupados, no los molestes Si está lloviendo, por favor, traéme mi paraguas Si ella llama, no le digas que estuve aquí Si no querés ir, no vayas Si ellos hubiesen salido más temprano, habrían llegado a tiempo 24 PHRASAL VERBS (IDIOMS) 3 54 24A. SOME BASIC COMMON IDIOMS OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE (Meanings can change) Above all As to As usual As yet At all At first At last At least At once At times Be up Be used up Blow up Break down Break off Bring about Bring out Call for Call off Call up Check up Come about Come away Come back Come in Come on Cross out Cut off Cut out Do over Fall through Find out For good Get along Get back por encima de todo con respecto a como de costumbre todavía del todo al comienzo al final por lo menos inmediatamente a veces hallarse estar desgastado explotar romper interrumpir ocurrir producir solicitar cancelar telefonear revisar ocurrir desprenderse regresr siga vamos tachar cortar eliminar hacer fracasar hallar para siempre llevarsela bien regresar Get in Get lost Get off Get on Get out Get over Get ready Get rid of Get through Get together Get up Get used to Give away Give in Give out Give place Give up Go on Go wrong Hand in Have got Have in hand Have on Right away I had a suit made. I have a suit made. I have to go In a hurry In time It’s cold. It’s early It’s hot. It’s late. It’s one o’clock It’s up to you entrar perderse bajarse de (bus) subirse a (bus) salir terminar estar listo deshacerse terminar reunirse levantarse soler regalar ceder repartir dar lugar darse por vencido continuar equivocarse entregar conseguir tener a mano tener inmediatament tenia un traje tengo un traje tengo que ir de prisa a tiempo hace frio es temprano hace calor es tarde la una en punto depende de ud. OK 24B. SOME BASIC COMMON IDIOMS OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE (Meanings can change) Keep back Keep in mind Keep on Keep out Keep out of Look for Look into Look over Look up Make clear Make good Make out Make up Make up your mind Mix up Now and again Now and then Off and on On purpose On the whole On time Once in a while Out of order Over and over Pick out Pick up Point out Put away Put off Put off Put on Put out Put together Put up Quite a few Wear out retener tener en mente seguir mantenerse afuera prohibir entrada buscar examinar revisar mejorar aclarar cumplir distiinguir hacer haga su voluntad mesclar una y otra vez de vez en cuando de vez en cuando a propósito del todo a tiempo de vez en cuando fuera de uso una y otra vez seleccionar recoger señalar botar cancelar apagar ponerse apagar reunir terminar unos pocos desgastar Right away See about Set forth So far Take a walk Take advantage Take after Take apart Take care of Take off Take on Take out Take over Take part Take part in Take place Take turns Take up Take up with Talk over There are There is There was There were Throw away Throw out Time is over Time is up To be (x) years old. To be angry. To be hungry To be over To be thirsty Try on Turn off Up to date inmediatamente ver exponer hasta la presente caminar tomar ventaja parecerse a separar cuidar quitarse asumir sacar ocupar participar participar tener lugar turnarse tomar llevarsela con discutir hay hay había había botar sacar se acabo el tiempo se acabo el tiempo tener (x) años estar enojado tener hambre acabar tener sed probarse apagar hasta la presente 24C. (TEXTS) USING SOME BASIC COMMON IDIOMS OF THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE (Meanings can change) The use of phrasal verbs (or idioms) (or two or more word verbs) is above all a very common way of expressing in English. The idioms have different meanins. You can say “Please take off your hat” or “The plane can’t take off because of the rain”. In the first case it referes to uncover the head and the second one about a plane that can’t start its flight. At first it is a little difficult but with at least a couple of hours of practice you will be ready to use them properly. I think you are getting ready for this practice. I advice you not to break down your studies easily. If you give up you won’t learn a lot. Don’t be afraid of going wrong, nobody is perfect. If you have a list of words or sentences for study you can cross out those you are understanding. Any how it’s up to you to learn. You got to get along well with your mates. You have to be in time for your practices. Don’t say it’s too hot or it’s too cold for not doing what you should do. Keep in mind the importance of getting the knowledges in grammar competences. If there are words you don´t know you better look for them in a good dictionary. You can make up many things if you have the decision for it. Make up your mind but don’t offend any one. Remember that your rights end where those of your neighbor begins. On purpose, you should practice more hours at home by yourself, take part in the role of playing dramas with your classmates and friends. You should take up with every one, that is a good rule of politeness. Point out the significance of knowing a second language. Don’t put out the flame of you interest, put on the suit of hard work. What things do you do in a common day? You wake up at five in the morning, then yo get up and go to take a shower. You brush your teeth, and then you get dressed. Go down the stairs to the dining room and have breakfast in a hurry because you´re late and have to get on a bus to go to your work. Near your office you get off the bus and walk in a hurry to your office. There you sit down at your desk and jot down the objectives of the day. You call up your secretay and ask her to digit some letters and have them sent by mail as soon as possible. You are working hard the entire morning and by midday you are to come back home for eating and resting. You get home and take off your clothes, watch news on T.V. and go to the dining room for having lunch. Before two in the afternoon you go back to your work to finish the journey. At the office you pick up the correspondence and read it all. Put apart the important ones and throw away the others. By five in the afternoon you have a break and go to the self-service restaurant for having some tea or cold drink. Buy the newspaper and read the profit-making news bulletin. It doesn't matter by if you haven’t understood yet this practice. Never mind, you will be able to get it. Of course! You have to work hard or you are wrong with your decitions. Don’t forget to check in and out your activities in the schedule. You are heading for abetter comprehension of this language. Do you mind if I open up your spirit for working? If you don't care for any of these experiences you won´t go ahead. Hold on! Don't hang up the interest of your imagination. If you've got a terrible headache you should have a break and have a pill. 25 VOCABULARIES 3 58 OK 25A. GENERAL VOCABULARY BRUSH UP (1a) CARDINAL NUMBERS: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven, twelve, thirteen, fourteen, fifteen, sixteen, seventeen, eighteen, nineteen, twenty; twenty one, twenty two, twenty three, twenty four, twenty five, twenty six, twenty seven, twenty eight, twenty nine, thirty: Ten, twenty, thirty, forty, fifty, sixty, seventy, eighty, ninety, [one] hundred; [one] thousand; [one] hundred thousand; [one] million ORDINAL NUMBERS: first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, eleventh, twelfth, thirteenth, fourteenth, fifteenth, sixteenth, seventeenth, eighteenth, nineteenth, twentieth; twenty first, twenty second, twenty third, twenty fourth, twenty fifth, twenty sixth, twenty seventh, twenty eighth, twenty ninth, thirtieth; Tenth, twentieth, thirties, fortieth, fiftieth, sixtieth, seventieth, eightieth, ninetieth, [one] hundredth; [one] thousandth, [one] millionth, TIME: Clock, hour hand, minute hand, face, watch, o’clock, 9 to 10 , nine five, five past nine; Morning, afternoon, midday, midnight, night, quarter, half, noon, [3:45] what time is it? (It’s three forty five) (It’s a quarter to four) Now, yesterday, tomorrow, next week, last month, next year, last weekend, on Sunday, in the winter, in December, the day before yesterday, the day after tomorrow; Frequency: ever, never, always, seldom, rarely, usually; Weather: (Freezing, cold, temperate, hot); winter, autumn, spring, summer PLACES: at home, in the office, at the restaurant, at the hotel, in the hospital, in the garage, at the university, at the drugstore, in the supermarket, at the mall, in the church, at the cinema, at the theater, in the parking place, at the bus station, at the airport, at the bus terminal, downtown, in the swimming pool, in the river, in the library, in the room, in the classroom, in the school coliseum, in the kitchen, in the living room, in the bathroom, in the bedroom, in the yard, in the patio, in the kitchen, on the street, in the avenue, in the park. CALENDAR: Days: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday Months; January, February, March, June, July, August, September, October, November, December; Holidays: 1st of May (Labor day), 25th of December (Christmas day), 1st of November (All saints day), 20th of July (Independence day), 12th of October (Discovery of America), 7th of August (Boyaca’s battle), 6th of January (Kings day), April (Holly week) SHAPES: Cube, square, triangle, rectangle, circle, oval, ellipse, cylinder sphere, Long, depth, height, side, width, length, diagonal, circumference, diameter, radius, parallel, spiral, perpendicular, hypotenuse, MONEY: Dollar, dime, quarter, cent, penny, nickel, traveler’s check, money order, credit card, debit card, teller, bank, bank vault, deposit, cash machine, withdrawal slip; euro, dollar. GEOGRAPHY DESCRIPTIONS: Forest, lake, meadow, mountain, valley, waterfall, rapids, hill, field, stream, pond, plateau, cliff, canyon, river, dam, desert, dune, jungle, seashore, bay, ocean, island, road, street, avenue, diagonal, gulf, map, globe, atlas, state, city, town, village, peak, snow crested, oasis, sea, ocean, POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY: America, south America, Europe, north America, Asia, Africa, England, United States, Germany, Italy, France, Spain, Cuba, Mexico, Canada, Japan, China, India, WORKERS, ARTISTS, AND PROFESSIONALS: Actor, actress, artist, model, painter, cartoonist, pianist, singer, Architect, computer programmer, lawyer, accountant, pilot, teacher, translator, Pharmacist, veterinarian, scientist, doctor, pediatrician, nurse, dentist, journalist, Assembler, baker, barber, bookkeeper, bricklayer, bus driver, butcher, carpenter, cashier, chef, cook, construction worker, messenger, custodian, data processor, delivery person, electrician, farmer, firefighter, fireman, fisherman, foreman, gardener, mechanic, newscaster, photographer, plumber, police officer, real estate agent, receptionist, repairman, salesman, seamstress, secretary, security guard, clerk, tailor, taxi driver, travel agent, waiter, welder, car dealer, typist, hunter, window washer, sanitation worker, truck driver, welder, florist, secretary, teller, hairdresser, barber, tailor, customer, shopper, cashier, cash register EMOTIONAL AND PHYSICAL STATES: Tired, sleepy, exhausted, active, hot, cold, hungry, thirsty, full, sick, ill, happy, sad, unhappy, pleased, displeased, disappointed, upset, annoyed, frustrated, angry, mad furious, disgusted, surprised, shocked, nervous, worried, scared, afraid, bored, proud, embarrassed, ashamed, jealous, confused, miserable, determined, shy, suspicious, introverted, extroverted, RELATIVES (family): Great grand father (mother), grand father(mother), father, mother, brother, grand (children/son/daughter/), sister, uncle, aunt, son, daughter, cousin, nephew, husband, wife, father/mother/son/daughter-in-law THE BODY: Face, hair, eye, ear, nose, mouth, lip, chin, chest, stomach, arm, forearm, writs, hand, finger, thumb, nail, leg, thigh, knee, shin, foot, toe, head, neck, back, shoulder, upper arm, elbow, waist, hip, buttocks, palm calf, ankle, heel, forehead, temple, eyebrow eyelid, eyelash, pupil cheek,. Mustache, tooth, beard, tongue, brain, artery, vein, throat, lung, heart, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, tissue, bone SUPERMARKET: Check-out area, , checkbook, groceries, packer, bag, sack, frozen (vegetables-dinner, juicemeat-chicken), yogurt, cheese, eggs, margarine, butter, milk, canned goods, bacon, roast, pork chops, chicken, roaster, ground meat, steak, lamb chops, fish, shrimp, bread, cereal cookies, crackers, macaroni, rice, peas; Steak, baked potatoes, roast beef, stuffed tomatoes, pork chops, spaghettis, meatballs, roast chicken, baked beans, hero sandwich, roast beef sandwich, pizza, fried squid, fried chicken, potato chips, tortilla chips, pretzels, popcorn, peanuts, candy bar, chewing gum donut, milk shake, hamburger, hot dog, French fries, onion rings, mustard, ketchup relish, pickles; (Tomato-orange-papaya-custard apple-strawberries-pineapplecucumber-watermelon)juice; Apple, pear, grapes, kiwis, mango, coconuts, avocado, banana, nectarines, plums, cherries, apricots, lemons, limes, grapefruits, oranges, pineapples, papayas, peaches, strawberries, raspberries, watermelon, custard apple, pineapple, peaches, apple pie, chocolate cake, ice cream, jelly; Lettuce, green onions, radish, watercress, tomatoes, cucumbers, celery, (yellow-green-red) pepper, potatoes, (red-pearl) onions, cauliflower, spinach, garlic, (green-string) beans, eggplants, asparagus, broccoli, ginger, cabbage; Coffee, Chocolate, tea, milk, juice, soft drink, soda, lemonade, beer, whisky, syrup, water ADJECTIVES: Afraid, bad, big, black, blind, blue, bright, broad, brown, busy, certain, clean, clear, cold, cool, dark, dear, deep, different, direct, distant, double, easy, eight, electric, fair, famous, fat, first, five, foreign, four, fresh, full, gentle, glad, good, great, green, happy, hard, heavy, height, high, hot, humble, hungry, ill, kind, large, left, little, long, loud, low, mad, middle, necessary, nervous, new, nice, old, one, pleasant, poor, possible, pretty, probable, proud, public, pure, quick, quiet, ready, real, red, rich, sad, safe, second, seven, short, sick, simple, single, six, slow, small, soft, sorry, special, straight, strange, strong, sweet, talk, tall, ten, thick, thin, third, three, twelve, twenty, two, warm, weak, white, wide, wild, wise, worth, wrong, yellow, young, next, sure, half, important, forward, human, dead, due, equal, past, perfect NOUNS: Account, age, air, amount, anger, animal, apple, arm, army, art, article, baby, bag, ball, bandit, bank, basket, battle, bay, bean, bear, beauty, bed, bell, bill, bird, bit, blood, board, boat, body, bone, book, bottom, box, boy, branch, bread, bridge, brother, bug, building, bus, business, butter, cake, captain, car, case, cent, center, century, chain, chair, chance, Character, chief, child, children, church, circle, city, class, clock, cloth, clothes, cloud, club, coal, coat, college, color, command, company, condition, corn, corner, country, course, cup, daughter, day, deal, decision, degree, dinner, doctor, dog, dollar, door, duty, ear, earth, east, edge, effort, egg, enemy, evening, experience, eye, face, fact, fall, family, farm, father, favor, feet, fellow, fence, field, finger, floor, flower, food, fool, foot, force, forest, friend, front, fruit, future, game, garden, gate, general, gentlemen, gift, girl, glass, god, good-bye, grain, grave, gravy, group, gun, hair, hall, hat, head, health, heart, heaven, hill, history, hole, home, honor, horse, hour, house, hundred, husband, ice, idea, inch, income, industry, interest, iron, island, job, journey, joy, king, kiss, kitchen, knee, lady, lake, land, law, leg, length, letter, life, line, lip, lord, loss, lot, machine, mail, man, manner, march, market, master, material, matter, measure, meat, meeting, member, men, method, mile, milk, mill, million, mind, minute, modern, moment, money, month, moon, morning, mother, mountain, mouth, Mr., Mrs., mud, music, name, nation, nature, neck, neighbor, news, night, nine, noise, noon, north, nose, note, number, object, ocean, office, oil, opinion, order, page, pain, pair, paper, part, party, peace, people, period, person, picture, piece, plain, pleasure, point, position, post, president, price, problem, purpose, quarter, queen, question, race, reason, result, rifle, rim, river, road, rock, room, rose, round, row, salt, scene, school, sea, season, seat, seed, sense, service, shade, shape, ship, shirt, shoe, shop, shore, shot, shoulder, side, sight, sign, silver, sister, size, skin, sky, soil, soldier, son, song, soul, south, space, spirit, spot, square, St., star, station, stock, stone, storm, story, stream, street, strength, sugar, suit, summer, sun, system, table, tail, taste, thing, thousand, time, top, town, trade, train, tree, trip, trouble, true, trust, uncle, valley, value, view, village, voice, wagon, wall, war, water, way, weather, week, weight, west, wheat, wheel, wife, wind, window, wing, winter, woman, women, wood, word, world, yard, year, care, fancy, fine, today, tomorrow, yesterday, self, cause, change, charge, cook, date, delight, demand, desire, device, doubt, dream, dress, dust, end, fear, fight, figure, fish, fly, hand, heat, hope, join, judge, lie, light, list, mark, miss, need, notice, pass, place, plan, plant, power, pray, present, press, rain, rule, shout, show, sort, sound, spring, state, step, store, strike, subject, success, supply, surprise, tie, travel, visit, wave. ADVERBS: able, almost, already, also, always, away, beat, best, better, early, especially, fast, likely, lonely, often, once, only, perhaps, soon, alone, ever, never, always, rarely, seldom, usually, frequently, late, well, bad, happily, sadly, honestly, proudly, properly VERBS: abort, accept, act, add, admit, advance, agree, allow, am, answer, appear, are, arrive, ask, attempt, be, became, become, been, began, begin, being, believe, belong, bless, blow, born, break, breath, bring, broken, brought, build, built, burn, buy, call, came, can, can’t, carry, catch, caught, choose, come, complete, consider, contain, continue, cost, could, cut, dance, dare, decide, declare, destroy, did, die, discover, divide, do , does, done, dry, eat, enjoy, enter, escape, expect, explain, express, fail, feed, feel, fell, fill, find, finish, fix, follow, forget, found, free, gain, gather, gave, get, give, given, go, gone, got, govern, grew, ground, grow, guard, guess, had, hang, happen, has, have, hear, heard, held, hold, hunt, hurry, hurt, include, is, jump, keep, kept, kill, knew, know, known, laugh, lay, lead, learn, lease, leave, led, let, listen, live, look, lose, lost, made, make, marry, may, mean, meet, met, might, move, pick, prepare, prove, pull, put, raise, ran, reach, read, realize, receive, remain, remember, reply, require, roll, run, rush, sat, save, saw, say, see, seek, seem, seen, sell, send, sent, separate, serve, set, settle, shake, shall, share, shine, should, sing, sit, sleep, sold, speak, spend, spoke, spread, start, stick, stood, stop, suffer, suppose, take, taken, teach, tear, tell, thank, think, threw, throw, told, took, try, understand, vary, wait, walk, want, was, wash, watch, wear, went, were, will, won’t, wonder, would, write, pay, close, please, control, count, cover, cross, crowd, cry, drink, drive, drop, felt, fire, firm, fit, form, guide, help, hit, increase, lift, love, must, offer, open, ought, paint, play, produce, promise, report, rest, return, rise, sail, smile, smoke, snow, stand, stay, study, thought, touch, turn, use, wish, work FUNCTION WORDS: a, about, above, according to, across, after, again, against, ago, all, along, although, among, an, and, another, any, around, as, at, back, because, before, behind, below, beside, between, beyond, both, but, by, down, during, each, either, else, enough, even,. Ever, every, few, from, further, he, her, here, him, his, how, however, I, if, in, indeed, instead, into, it, its, just, last, late, least, less, many, e, mine, more, most, much, my, near, neither, never, no, none, nor, not, nothing, now, oh, or, other, our, quite, rather, same, several, she, since, so, some, still, such, sudden, than, that, the, their, them, then, there, therefore, these, they, this, those, though, through, till, together, too, toward, until, us, usual, very, we, what, when, where, whether, which, while, who, whole, whom, whose, why, with, within, without, you, your, far, well, yes, yet, hello, except, for, of, off, on, out, outside, over, to, under, up, upon, own, PRONOUNS: I, you, he she, it, we, you, they; me, you, him her, it, us, you, them; mine, yours, his hers, Its, ours, yours, theirs; myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves; POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES: my, your, his, her, its, our, your, their 25B. COMMON EXPRESSIONS IN ENGLISH [a] English Good morning Good afternoon Good evening Good night Good bye So long! Hi (Hello)! How are you? How are you doing? I am well (fine), thank you Where are you from? What do you do? Do you speak Spanish? What's your name? It doesn't matter Never mind Congratulations! May I introduce myself? Thank you. -You are welcome Excuse me, please I am sorry Really? Of course! Sure That's too bad What happened? What does that mean? You are right You are wrong I guess so I don't think so I want a one-way (round-trip) ticket to Dallas I would like to reserve a flight for Chicago When should I confim the flight ? Is it a direct flight? Is there a stopover? When does the plane leave (arrive)? Do I have to change planes? How long before the flight must I check in? To the airport, please Which gate must I go to? What's my flight number? Is the plane delayed (on time)? Look at the timetable Do you have your boarding pass? Where is my seat (baggage)? Fasten your belts please! The plane is landing (taking off) I have nothing to declare Español Buen día, buenos días Buenas tardes Buenas noches (saludar) Buenas noches (al despedirse) Chau Hasta luego! Hola! ¿Cómo estás? ¿Cómo te va? Estoy bien, gracias ¿De dónde es Ud? ¿Qué hace Ud? ¿A qué se dedica? ¿Habla Ud español? ¿Cuál es su nombre? ¿Cómo se llama Ud? No importa No importa ¡Felicitaciones! ¿Puedo presentarme? Gracias. -De nada Disculpe, por favor Lo siento ¿En serio? ¡Por supuesto! Seguro ¡Qué lástima! ¿Qué pasó? ¿Qué significa eso? Ud. tiene razón Ud. está equivocado Creo que sí Creo que no Quiero un boleto de ida (de ida y vuelta) a Dallas Quisiera reservar un vuelo a Chicago ¿Cuándo debería confirmar el vuelo? ¿Es un vuelo directo? ¿Hay una escala? ¿Cuándo sale (llega) el avión? ¿Tengo que cambiar aviones? ¿Cuánto tiempo antes del vuelo debo registrarme? Al aeropuerto, por favor. ¿A qué puerta debo ir? ¿Cuál es el número de mi vuelo? ¿Está demorado (en tiempo) el avión? Mire el horario de vuelos ¿Tiene Ud. su pase de abordar? ¿Dónde está mi asiento (equipaje)? Abróchense los cinturones, por favor! El avión está aterrizando (despegando) No tengo nada que declarar 25B. COMMON EXPRESSIONS IN ENGLISH [b] Is it necessary to make a reservation? Do you have any rooms available? What's the daily (weekly) rate? Is there air conditioning (heating) in the room? I would like a single (double) room I'd like a room with twin beds Is breakfast included in the price? Where can I park my car? Could I see the room? OK, I'll take it My room key please This room is too small (noisy/dark) Could you wake me up at 7 a.m.? Where can I leave my valuables? What time do I have to check out? Can I pay with traveler's checks (credit c.)? Could she bring some towels up to my room? Is there a laundry (dry-cleaning) service? I’d like to make a reservation for this evening I would like a table near the window Could you call the waiter (waitress) please? Could you bring me the menu, please? Where are the rest rooms? I would like to order now What do you recommend? May I have a bottle of wine (beer, soda)? Excuse me, I have no spoon (knife,fork) These napkins are dirty May you bring more rolls (toasts) please? I'll have a steak with French fries Would you like anything to drink? What kind of desserts do you have? Waiter, the check please Can we pay separately? Thank you. Keep the change How much is the round-trip (one-way) ticket? What's the fare to Chicago? What time does the bus (train) leave (arrive)? From what platform does the (bus) leave? How long does it take from here to Chicago? Is this the bus to New York? Will I have to change buses (trains)? Could you show me the schedule please? Is the bus (train) delayed (on schedule)? Can I buy a map here? I missed the bus (train) Excuse me, but you are sitting in my seat Where are you heading for? Must we change buses at this terminal? How long does the bus (train) stop here? ¿Es necesario hacer una reserva? ¿Tiene Ud. habitaciones disponibles? ¿Cuál es la tarifa diaria (semanal)? ¿Hay aire acondicionado (calefección) en la habitación? Quisiera un cuarto sencillo (cama doble) Quisiera un cuarto con camas gemelas ¿El desayuno está incluído en el precio? ¿Donde puedo estacionar mi auto? ¿Podría ver la habitación? OK. La tomaré La llave de mi cuarto, por favor La habitación es demasiado pequeña (ruidosa, oscura) ¿Podría despertarme a las 7 de la mañana? ¿Dónde puedo dejar mis objetos de valor? ¿A qué hora tengo que irme del hotel? ¿Puedo pagar con cheques de viajero (tarjeta de crédito) ¿Podría ella traer algunas toallas a mi cuarto? ¿Hay un servicio de lavandería (tintorería)? Quisiera hacer una reserva para esta noche Quisiera una mesa cerca de la ventana ¿Podría llamar al camarero (camarera) por favor? ¿Podría traerme el menú, por favor? ¿Donde están los baños? Quisiera ordenar ahora ¿Qué recomienda Ud? ¿Podría traerme una botella de vino (cerveza, gaseosa)? Disculpe. No tengo cuchara (cuchillo, tenedor) Las servilletas están sucias ¿Podría traerme más panecillos (tostadas) por favor? Comeré un bife con papas fritas ¿Desea Ud. algo para tomar? ¿Qué clase de postres tienen? Camarero, la cuenta por favor ¿Podemos pagar separadamente? Gracias. Guárdese el cambio ¿Cuánto cuesta un boleto de ida y vuelta (de ida)? ¿Cuánto cuesta el boleto a Chicago? ¿A qué hora sale (llega) el autobús (tren)? ¿De qué plataforma sale el (bus) ? ¿Cuánto tiempo toma desde aquí hasta Chicago? ¿És este el autobús a New York? ¿Tendré que cambiar autobuses (trenes)? ¿Podría mostrarme el itinerario, por favor? ¿Está el autobús (tren) retrasado (en tiempo)? ¿Puedo comprar un mapa aquí? Perdí el autobús (tren) Disculpe, pero Ud. está sentado en mi asiento ¿Hacia dónde se está dirigiendo Ud.? ¿Debemos cambiar de bus en esta terminal? ¿Cuánto tiempo se detiene el bus (tren) aquí? 25B. COMMON EXPRESSIONS IN ENGLISH [c] What's the next stop? How many more stops before we arrive? I can't find my baggage! It is missing Do I have to get off here? Is there a bus stop around here? Where can I get a taxi (cab)? Is there a subway entrance nearby? How often do the buses run? I think every 10 minutes I need to take the subway (a bus, a taxi-cab) How much is the bus fare? Can you give me a transfer please? How many passengers can you take in this cab? I want to go to... Please take me to... I need to get to the airport as quick as possible Could you drive faster please? Do you mind if I open the window? I get off here What is the next stop? How much is it? Thanks. Keep the change Where is the nearest shopping center (supermarket)? How do I get there? What time does the market open (close)? Where is the men's (ladies') clothing department? (Furniture/ baggage/ footware/ cosmetics/ lingerie) department Take the elevator to the third floor I want to buy a gift for my girlfriend How much is this article? Ask the saleswoman (salesman) How much is it? How much does it cost? How much do you charge for this? This is too expensive. Don't you have something cheaper? Could you show me a bigger (smaller/nicer) one? May I try this dress on? Where are the trying rooms? This doesn't fit me. I want a bigger one Are these articles on sale ? I don't care for any of these Please, can you wrap it up? Can I pay by credit card? Is there a post office nearby? ¿Cuál es la próxima parada? ¿Cuántas paradas más antes de que lleguemos? No puedo encontrar mi equipaje! Está faltando ¿Tengo que bajarme aquí? ¿Hay una parada de autobús por aquí? ¿Dónde puedo conseguir un taxi? ¿Hay alguna entrada al subterráneo por aquí cerca? ¿Con qué frecuencia pasan los autobuses? Creo que cada 10 minutos Necesito tomar el subterráneo (un autobús, un taxi) ¿Cuánto está el precio del boleto del bus? ¿Podría darme un pase para transbordar, por favor? ¿Cuántos pasajeros puede llevar en este taxi? Quiero ir a... Por favor, lléveme a... Necesito llegar al aeropuerto lo antes posible ¿Podría conducir más rápido por favor? ¿Le importa si abro la ventanilla? Me bajo aquí ¿Cuál es la próxima parada? ¿Cuánto es? Gracias. Guarde el cambio ¿Dónde queda el shopping center (supermercado) más cercano? ¿Cómo llego hasta allí? ¿A qué hora abre (cierra) el mercado? ¿Dónde queda el departamento de ropa de hombres (de mujeres)? Departamento de (muebles, equipaje, calzados, cosméticos, lencería) Tome la el ascensor al tercer piso Quiero comprar un regalo para mi novia ¿Cuánto cuesta este artículo? Pregúntele a la vendedora (vendedor) ¿Cuánto es? ¿Cuánto cuesta? ¿Cuánto cobran por esto? Esto es demasiado caro. ¿No tiene algo más barato? ¿Podría mostrarme uno más grande (más pequeño/ más lindo)? ¿Podría probarme este vestido? ¿Dónde están los probadores? Este no me queda. Quiero uno más grande ¿Estos artículos están en oferta? No me gusta ninguno de estos Por favor. ¿Puede envolverlo? ¿Puedo pagar con tarjeta de crédito? ¿Hay una oficina postal cerca de aquí? 25B. COMMON EXPRESSIONS IN ENGLISH [d] What time does it open? I need some stamps for this letter Is there any mail for me? I want to send it via air-mail please Could you weigh this package for me please? How long does it take to get to Argentina? Where is the mailbox? I don't know the Zip-Code of this city I want to register these letters Can I send a money order from here? Can you help me fill out this form please? Where can I buy envelopes? How can I send this the quickest? Operator, I wish to make a long distance call. Operator, I wish to make a collect call. I'd like to speak to Mr. Simpson please. Could you speak louder please? Could you speak more slowly please? Could you spell that for me please? Could you call back later please? Could I leave a message? I need a phone directory I need to know the area-code for Miami Where can I find a pay phone? Hold on! Don't hang up! Who is calling? Wrong number The line is busy You must dial this number... I would like to make an appointment to see the doctor I am not feeling well I am feeling very sick (ill) What are the symptoms? I've got a terrible (earache, stomach ache, headache, toothache) I've got a terrible (flu, cold, cough) I've got a broken (fractured ) arm (leg) My whole body hurts I have a pain in my back (chest) I have been feeling dizzy and sweating a lot I will check your blood pressure I have chills (nausea, diarrhea, fever, allergy) I have a burn (a cut, an insect bite) Is it serious? Must I follow a diet? Must I stay in bed? Will you give me a prescription? ¿A qué hora abre? Necesito algunas estampillas para esta carta ¿Hay alguna correspondencia para mí? Quiero enviarla por correo aéreo, por favor ¿Podría Ud. pesarme este paquete por favor? ¿Cuánto tiempo tarda en llegar a Argentina? ¿Dónde está el buzón? No sé el código postal de esta ciudad Quiero certificar estas cartas ¿Puedo enviar un giro postal desde aquí? ¿Puede Ud ayudarme a rellenar este formulario por favor? ¿Dónde puedo comprar sobres para cartas? ¿Cómo puedo enviar esto, lo más rápido posible? Operadora. Deseo hacer una llamada de larga distancia Operadora. Deseo hacer una llamada por cobrar Quisiera hablar con el señor Simpson por favor ¿Podría Ud. hablar más fuerte por favor? ¿Podría Ud. hablar más lento por favor? ¿Podría deletrearme eso por favor? ¿Podría Ud. llamar de nuevo más tarde por favor? ¿Podría dejar un mensaje? Necesito una guía de teléfonos Necesito saber el código de área de Miami ¿Dónde puedo encontrar un teléfono público? ¡Aguarde! ¡No corte! ¿Quién está llamando? Número equivocado La línea está ocupada Ud. debe marcar este número... Quisiera un turno para ver al doctor No me estoy sintiendo bien Me estoy sintiendo muy enfermo ¿Cuáles son los síntomas? Tengo un terrible dolor (de oído, de estómago, de cabeza, de muelas) Tengo una terrible (gripe, resfriado, tos) Tengo un brazo (pierna) rota (fracturada) Me duele todo mi cuerpo Tengo un dolor en mi espalda (pecho) Me he estado sintiendo mareado y sudando mucho Revisaré su presión sanguínea Tengo escalofríos (náuseas, diarrea, fiebre, alergia) Tengo una quemadura (un corte, una picadura de insecto) ¿Es grave? ¿Debo seguir una dieta? ¿Debo quedarme en cama? ¿Me dará una receta para la farmacia? 25B. COMMON EXPRESSIONS IN ENGLISH [e] What medicine should I take? May I help you? I would like something for a sunburn (a sore throat, a cold, a fever, an indigestion, a constipation, a headache) Could I have some sleeping pills? May I have a bottle of vitamin C? I would like some aspirins and a laxative Do you want a large or small bottle (package, box, tube)? I want a tube of shaving cream (toothpaste) please I would like a box of cough drops I'd like a box of condoms Here you are. That'll be $12.50 Where is the nearest bank? Where can I find an ATM? Can I cash these traveler's checks here? Can I cash personal checks here? I would like to open up a current account Could you give me some change? I need some coins (small bills) I want to withdraw (deposit) some money How much is the rate of exchange? Do I have to endorse (sign) this check? I need to make a bank draft I would like to send money to Argentina Which window should I go to? Do you have some painkillers? Do I need a prescription for this medicine? I need a bandage, alcohol and iodine please I would like to apply for a loan What are the interest rates? Where can I get an entertainment guide of this city? Where is the ticket-office? Are there any seats left? I want two tickets please Do we have to wait in line to buy the tickets? Where are our seats? Must we tip the usher? Which orchestra (band) is playing? What's on at the movies tonight? What time does the (show) (start)? How long does it last? What kind of film is it? It is a horror (science fiction, war) film It is a thriller (western, cartoon, comedy, musical) What is it about? The plot (script) is very good Who is the main actor (actress)? ¿Qué remedio debo tomar? ¿Puedo ayudarlo? Quisiera algo para una quemadura (un dolor de garganta, un resfriado, fiebre, una indigestión, una gripa, un dolor de cabeza) ¿Me podría dar pastillas para dormir? ¿Me podría dar una botella de vitamina C? Quisiera algunas aspirinas y un laxante ¿Quiere Ud. un frasco (paquete, caja, pomo) grande o chico? Quiero un tubo de crema de afeitar (dentífrico) por favor Quisiera una cajita de pastillas para la tos Quisiera una cajita de condones Aquí tiene Ud. Son $12.50 ¿Dónde queda el banco más cercano? ¿Dónde puedo encontrar un cajero electrónico? ¿Puedo cobrar aquí estos cheques de viajero? ¿Puedo cobrar aquí cheques personales? Quisiera abrir una cuenta corriente ¿Me podría dar algo de cambio? Necesito algunas monedas (billetes chicos) Quiero retirar (depositar) algo de dinero ¿Cuál es el tipo de cambio? ¿Tengo que endosar (firmar) este cheque? Necesito hacer un giro bancario Quisiera enviar dinero a Argentina ¿A qué ventanilla debería ir? ¿Tiene algunos calmantes? ¿Necesito una receta médica para este remedio? Necesito un vendaje, alcohol y yodo, por favor Quisiera solicitar un préstamo ¿Cuáles son las tasas de interés? ¿Dónde puedo obtener una guía de entretenimientos de esta ciudad? ¿Dónde está la oficina de boletería? ¿Quedan asientos? Quiero dos boletos, por favor ¿Tenemos que hacer cola para comprar los boletos? ¿Dónde están nuestros asientos? ¿Debemos dar propina al acomodador? ¿Qué orquesta (banda) está tocando? ¿Qué hay en el cine esta noche? ¿A qué hora (comienza) (el espectáculo)? ¿Cuánto tiempo dura? ¿Qué clase de película es? Es una película de terror (de ciencia ficción, de guerra) Es una película de acción (una del oeste, una de dibujos animados, una comedia, un musical) ¿De qué se trata? La trama (el guión) es muy bueno ¿Quién es el actor (actriz) principal? 25C. GENERAL ENGLISH PRACTICE[a] Is this an [umbrella]? 1 Esta es una sombrilla Is that a [long ruler]? 2 Esa es una regla larga Are these [green windows]? 3 Estas son ventanas verdes Are those [cheap apples]? 4 Aquellas son manzanas baratas Is it an [ugly dog]? 5 Es un perro feo Is it a [main door]? 6 Es una puerta principal Are they the [old notebooks]? 7 Son los cuadernos viejos Is there a [paper on the desk]? 8 Hay un documento sobre el escritorio Are there [two red pens on the floor]? 9 Hay dos lapiceros rojos en el piso Was there a [new pencil in the drawer? 10 Había un lápiz nuevo en la gaveta Were there [three machines there]? 11 Había tres máquina acá Will there be a [teacher at home]? 12 Habrá un profesor en casa Could there be a [doctor at the office]? 13 Podría haber un doctor en la oficina Are you [drinking] your [coffee]? 14 Te estás tomando tu café? Is he [painting] his [house]? 15 El está pintando su casa? Am I [doing] my [homework]? 16 Estoy haciendo mi tarea? Was he [writing] a [letter]? 17 El estaba escribiendo una carta? Were you [reading] a [book]? 18 Usted estaba leyendo un libro? Do you [see] your [tests]? 19 Ves tus exámenes? Does she [watch] her [kids]? 20 Ella vigila a sus hijos? Did they [eat] their [bananas]? 21 Ellos se comieron sus bananas? Will he [jump] our [desk]? 22 El saltará nuestro escritorio? Are you going to [travel next month]? 23 Vas a viajar el próximo mes? Was he going to [draw a map]? 24 El iba a dibujar un mapa? Were you going to [see a movie]? 25 Usted iba a ver una película? Would she [fly] to their [cities]? 26 Ella volaría a sus ciudades? Can you [do] it yourself? 27 Puedes hacerlo tu mismo? Could they [do] it themselves? 28 Ellos mismos pudieron hacerlo? May I [try] it myself? 29 Puedo intentarlo por mí mismo? Might he [make] it himself? 30 El mismo podría hacerlo? Shall I [type] them? 31 Yo los escribiré? Should he [visit a doctor] now? 32 El debería visitar a un doctor ahora? Must she [prepare] them herself? 33 Ella misma debe prepararlos? Have you [sung the hymn]? 34 Has cantando el himno? Has she [done the homeworks]? 35 Ella ha hecho las tareas? Had they [played tennis] here? 36 Ellos había jugado tenis aquí? Will they have [learned the words]? 37 Ellos habrán aprendido las palabras? Have you been [working]? 38 Usted ha estado trabajando? Has he been [walking] there? 39 El ha estado caminando allí? Had she been [selling newspapers]? 40 Ella había estado vendiendo periódicos? Will they have been [studying] hard? 41 Ellos habrán estado estudiando duro 25C. GENERAL ENGLISH PRACTICE [b] Are those [pink desks] his? Aquellos escritorios rosados son de él. Is that [fancy bag] yours? Ese bolso de fantasía es tuyo. Is this [mouse] hers? Este ratón es de ella. Are the [bad tests] ours? Los exámenes malos son nuestros. Are the [good scores] theirs? Los puntajes buenos son de ellos. Is the [clean water] its? El agua limpia es de este. Is John’s watch [beside the notebook]? El reloj de John está al lado del cuaderno Is Pete’s clock [next to the sofa]? El reloj de Pedro está al lado del sofá Are Mary’s cats [under the tree]? Los gatos de María están bajo el árbol How many [dollars] do you [have]? Cuántos dólares tienes? I [have] a [million dollars]. Tengo un millón de dólares How much [sugar] do you [need]? Cuánta azúcar necesitas? I [need] a [kilo of sugar] Necesito un kilo de azúcar Is there any [coffee in the kitchen]? Hay café en la cocina? Yes, there is a [pound of coffee]. Sí, hay una libra de café What time is it? Qué hora es? It’s [six] o’clock. Son las seis en punto. How old [are you]? Cuantos años tienes? [I’m] 14 years old Tengo catorce años Where were you born? Donde naciste? I was born in [Cucuta]. Nací en Cúcuta What’s your addres? Cuál es tu dirección? It´s [4-55 7th street, Caobos] Es calle 7ª, N° 4-55, Los Caobos What do you [do at home]? Qué haces en casa? I [play chess at home] Juego ajedrez en casa Where did you [learn French]? Dónde aprendiste Francés? I [learned French in France]. Aprendí Francés en Francia When will you [go to USA]? Cuándo irás a EE UU I will [go to USA next year] Iré a EE UU el próximo año Why have you worn [old shoes]? Por qué has usado zapatos viejos? Because they’re [smooth] Porque son suaves Who [performs the act]? Quién hace el acto? [Fanny performs the act] Fanny hace el acto. Which [singer do you prefer]? Cuál cantante prefieres? I [prefer Shakira] Prefiero a Shakira Whose [jacket] do you like best? Cuál chaqueta te gusta más? I like [Henry’s Jacket] Me gusta la chaqueta de Henry How long ago did you [visit Athens] Cuánto hace que visitaste Atenas? I [visited] it [four years ago] La visité hace cuatro años You like to [read], don’t you? Te gusta leer, no es verdad? Yes, I like to [read] Sí, me gusta leer You don’t like to [write], do you? No te gusta escribir, cierto? No, I don’t like to [write] No, no me gusta escribir. 25D TIME EXPRESSIONS Afternoon April August Century Day Decade December early morning Era Eternity Evening fall / autumn February Friday Hour At night At noon Every week In a week\'s time In the afternoon In the early morning In the evening in the morning last Friday last month last night last week last year January July June March May Midnight Millennium Minute Monday Month Morning Night Noon November October next Friday next week next year the day after the day after tomorrow the day before the day before yesterday this evening this Friday this month this week this year Saturday Second September Summer Sunday Sunrise Sunset Thursday Tuesday Wednesday Week Winter Year At dawn At dusk three weeks ago today tomorrow tomorrow afternoon tomorrow evening tomorrow morning tonight two days ago two days earlier two days later yesterday yesterday evening yesterday morning small - pequeño tall - alto young - joven long - largo big - grande fat - gordo lazy - perezoso, vago funny - gracioso, divertido happy - feliz, alegre crazy - loco noisy - ruidoso 25E-1. SHORT ADJECTIVES smaller - más pequeño taller - más alto younger - más joven longer - más largo bigger - más grande fatter - más gordo lazier - más vago funnier - más divertido happier - más feliz crazier - más loco noisier - más ruidoso (the) smallest – el más pequeño (the) tallest- el más alto (the) youngest – el más joven (the) longest – el más largo (the) biggest- el más grande (the) fattest- el más gordo the laziest- el más vago the funniest- el más divertido the happiest- el más feliz the craziest- el más loco the noisiest- el más ruidoso expensive - caro modern - moderno beautiful - hermoso elegant - elegante interesting - interesante dangerous - peligroso 25E-2. LONG ADJECTIVES more expensive more modern more beautiful more elegant more interesting more dangerous the most expensive- el más caro the most modern the most beautiful the most elegant the most interesting the most dangerous 25E-3. ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS ADJECTIVE Alive - vivo Asleep - dormido Beauty- hermoso Sweet - dulce Black - negro White - blanco Dark - oscuro Dead - muerto Deep - profundo Difficult - difícil Dirty - sucio Clean - limpio Fat - gordo Full - lleno VERB To live- vivir To sleep - dormir To beautify - embellecer To sweeten - endulzar To blacken - ennegrecer To whiten - blanquear To darken - oscurecer To die - morir To deepen - profundizar To complicate - dificultar To dirty - ensuciar To clean - limpiar To fatten - engordar To fill - llenar ADJECTIVE Empty - vacío Hard - duro Soft - blando Sick - enfermo Low - bajo Hot - caliente Long - largo Short - corto Rich - rico Poor - pobre Simple - simple Straight - derecho b - fuerte Wide - ancho VERB To empty - vaciar To harden - endurecer To soften - ablandar To Sicken - enfermar To lower - bajar To heat - calentar To lengthen - alargar To shorten - acortar To enrich - enriquecer To impoverish – empobrecer To simplify - simplificar To straighten - enderezar To strenghen - débil To widen - ensanchar 25E-4. ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS ADJECTIVE Careful - ciudadoso Slow - lento Strong - fuerte Simple - simple Bad - mal Frecuent - frecuente ADVERB Carefully - cuidadoso Slowly - lentamente Strongly - fuertemente Simply - simplemente Badly - malamente Frecuently - frecuentemente Good - bueno Hard - duro Well - bien Hard - duramente ADJECTIVE Clear - claro Possible - posible Probable - probable Deep - profundo Quick - rápido Normal - normal Fast - rápido ADVERB Clearly - claramente Possibly - posiblemente Probably - probablemente Deeply - profundamente Quickly - rápidamente Normally - normalmente Fast - rápidamente 25E-5. ADJECTIVES AND NOUNS ADJECTIVES Long - largo Short - corto Big - grande / Small - pequeño Heavy - pesado / Light - liviano Deep - profundo / Shallow - poco profundo Wide - ancho / NOUNS ADJECTIVES NOUNS Length – longitud Difficult - difícil Difficulty - dificultad Size – tamaño Sad - triste Sadness – tristeza Weight – peso Beautiful - hermoso Beauty – belleza Depth - profundidad Strong - fuerte Strength – fuerza Width – anchura Weak - débil Weakness - debilidad Narrow - angosto Fast - rápido / Slow - lento Tall - alto / Short - bajo White - blanco / Black - negro Far - lejano / Near - cercano Bitter - amargo / Sweet - dulce Careful - cuidadoso / Careless - descuidado Speed – velocidad Dirty - sucio Dirt – suciedad Height – altura Clean - limpio Cleanliness - limpieza Color – color Safe - seguro Safety - seguridad Distance - distancia Dangerous - peligroso Danger – peligro Taste – sabor True - verdadero Truth – verdad Care – cuidado