Chapter 17 Evolution of Populations
advertisement

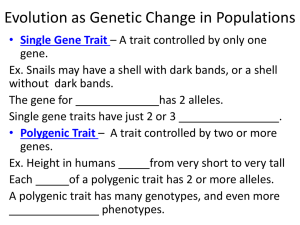
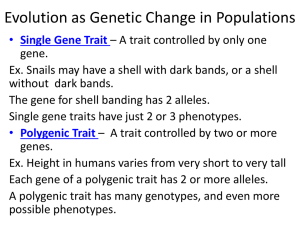
CHAPTER 17 Evolution of Populations 17.1 Genes and Variations Key Questions How is evolution defined in genetic terms? What are the sources of genetic variation? What determines the number of phenotypes for a given trait? Vocabulary you should learn: Gene pool Allele frequency Single-gene trait Polygenic trait Natural selection Quick review A population is a group of individuals of the same species that mate and produce offspring. A gene pool consists of all the genes, including all the different alleles for each gene that are present in a population. Populations and Gene Pools Researchers study gene pools by examining the relative frequency of an allele. The relative frequency of an allele is the number of times a particular allele occurs in a gene pool, compared with the number of times other alleles for the same gene occur. mutations mutations mutations mutations mutations A single-gene trait is a trait controlled by only one gene. Single-gene traits may have just two or three distinct phenotypes. The most common form of the allele can be dominant or recessive. An example is the presence of dark bands that appear on the shells of snails. Even though the allele for shells without bands is dominant, a population may show a greater frequency of the “with bands” phenotype Polygenic traits are traits controlled by two or more genes. •Each gene has two or more alleles & many possible genotypes and different phenotypes. •Human height, which varies from very short to very tall, is an example of a polygenic trait. • The bell-shaped curve in the graph is typical of polygenic traits. 17.2 Evolution as Genetic Change in Populations Key Questions How does natural selection affect single-gene and polygenic traits? What is genetic drift? What conditions are required to maintain genetic equilibrium? Vocabulary you need to learn: Directional selection Stabilizing selection Disruptive selection Genetic drift Bottleneck effect Founder effect Genetic equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg principle Sexual selection Genetic Drift •Genetic drift or allelic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling. When the beetles reproduced, just by random luck more brown genes than green genes ended up in the offspring. In the diagram at right, brown genes occur slightly more frequently in the offspring (29%) than in the parent generation (25%). The Founder Effect a particular allele or spontaneous mutation in a small or isolated population may become very common in just a few generations. Founder Effect: Kentucky Blue People These two are probably relatives of the original mutant. http://www.rootsweb.ancestry.com/~kyperry3/Blue_Fugates_Troublesome_Creek.html Activity