Evolution - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement

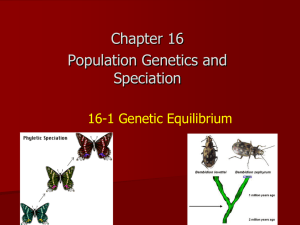
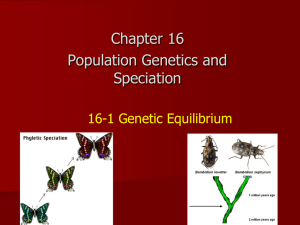
Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Evolution Homework Packet Section 16.4 Evidence of Evolution (pgs. 465-473) 1. What is biogeography? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 2. Why do distantly related species in very different places sometimes share similar traits? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 3. Why are fossils important evidence for evolution? ______________________________________________________ 4. Explain the difference between homologous and analogous structures. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ a. Which are more important to evolutionary biologists? WHY? ______________________________________________________ 5. How do vestigial structures provide evidence for evolution? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 6. How do DNA and RNA provide evidence for common descent? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 7. What is the relationship between Hox genes and embryological development? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 8. Organism A and B have very similar Hox genes, and their embryos, in the earliest stages of development, are also very similar. What do these similarities indicate about the ancestry of organisms A and B. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 9. How do the Grants’ data show that genetic variation is important in the survival of a species? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 1 Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Section 17.1 Genes and Variation (p. 482-486) 1. Define gene pool. ______________________________________________________ 2. Define allele frequency. ______________________________________________________ a. In genetic terms, what indicates that evolution is occurring in a population? ______________________________________________________ 3. Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that allele in the population? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. List three causes of genetic variation. a) ________________ b) ________________c) ________________ 5. How does gene shuffling result in more genetic variation? ______________________________________________________ 6. Why does sexual reproduction provide more opportunities of genetic variation than asexual reproduction? ______________________________________________________ 7. What is a single-gene trait? ______________________________________________________ 8. What is a polygenic trait? ______________________________________________________ a. What shape is characteristic for a graphical representation of a polygenic trait? ______________________________________________________ 9. How does the range of phenotypes for single-gene traits differ from the range for polygenic traits? ______________________________________________________ 10. A black guinea pig and a white guinea pig mate and have offspring. All of the offspring are black. Is this trait of coat color in guinea pigs a single-gene trait or polygenic trait? ___________________ . WHY? ______________________________________________________ 2 Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Section 17.2 Evolution as Genetic Change in Populations (p. 487-492) 1. What is fitness in genetic terms? ______________________________________________________ 2. How does natural selection affect a single-gene trait? ______________________________________________________ 3. List three possible selections that results from natural selection affecting a polygenic trait? 4. Contrast Stabilizing Selection with Disruptive Selection. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 5. What are the results of Directional Selection? ______________________________________________________ 6. What is genetic drift? ______________________________________________________ 7. How does the founder effect lead to changes in the gene pool? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 8. What is genetic equilibrium? ______________________________________________________ 9. What five conditions disrupt genetic equilibrium? a. b. c. d. _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ e. 10. A road built through a forest split a population of frogs into two large groups. The allele frequencies of the two populations remained identical. What evidence do we have that genetic drift did NOT occur? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 11. DDT an insecticide that was first used in the 1940s to kill mosquitoes and stop the spread of malaria. As time passed, people began to notice that DDT became less effective. Explain in genetic terms, how the insect became resistant to the pesticide. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 3 Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Section 17.3 The Process of Speciation (p. 494-497) 1. Define species. ______________________________________________________ 2. What is speciation? ______________________________________________________ 3. What happens in reproductive isolation? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. Why does behavioral isolation results? ______________________________________________________ 5. What is the difference between geographic isolation and temporal isolation? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 6. A newly formed lake divides a population of a beetle species into two groups. List another factor besides isolation might lead to the two groups becoming separate species? ______________________________________________________ 7. Explain the type(s) of reproductive isolation may have been important in Galapagos finch speciation. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 8. Explain how the vegetarian tree finch, which feeds on fruit, might have evolved. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 9. A botanist (plant biologist) identifies two distinct species of violets growing in a field. Also in the field are several other types of violets that, although somewhat similar to the two known species, appear to be new species. Develop a hypothesis explaining how the new species may have originated. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4 Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Section 17.4 Molecular Evolution (p. 498-501) 1. What is a molecular clock? ______________________________________________________ 2. Why do molecular clocks use mutations that have no effect on phenotype? ______________________________________________________ 3. How do researchers check the accuracy of molecular clocks? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. How can crossing-over result in gene duplication? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 5. Describe how duplicate genes form. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 6. Why is gene duplication important in evolution? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 7. Use the evolution of the insect body plan to explain the significance of Hox genes in evolution. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 8. In evolution, why have small changes in Hox genes had a great impact? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 9. Describe the relationship between evolutionary time and the similarity of genes in two species. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 5 Name: _____________________________ Pd. ____ Section 19.2 Patterns of Evolution (p. 546-552) 1. How does variation within a clade affect the clade’s chance of surviving environmental change? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 2. What is a background extinction? ______________________________________________________ 3. How is a background extinction different from a mass extinction? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4. Major geologic changes often go hand in hand with mass extinctions. Why do you think this is true? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 5. What is gradualism? ______________________________________________________ 6. What is punctuated equilibrium? ______________________________________________________ 7. Explain how punctuated equilibrium is different from gradualism? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 8. Why would evolution speed up when a small group of organisms migrates to a new environment? ______________________________________________________ 9. What is adaptive radiation? ______________________________________________________ 10. What is convergent evolution? ______________________________________________________ 11. When might adaptive radiation result in convergent evolution? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 12. What is coevolution? ______________________________________________________ 13. Describe an example of coevolution. ______________________________________________________ 14. Why is rapid evolution especially likely to occur in a small population that has been separated from the main population? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 6