Single Gene Trait
advertisement

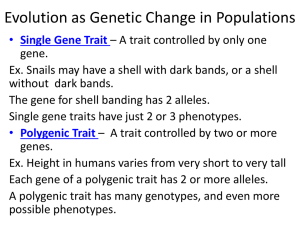
Evolution as Genetic Change in Populations • Single Gene Trait – A trait controlled by only one gene. Ex. Snails may have a shell with dark bands, or a shell without dark bands. The gene for has 2 alleles. Single gene traits have just 2 or 3 . • Polygenic Trait – A trait controlled by two or more genes. Ex. Height in humans from very short to very tall Each of a polygenic trait has 2 or more alleles. A polygenic trait has many genotypes, and even more phenotypes. Single Gene Trait Polygenic Trait Evolution as Genetic Change in Populations Examples of Genetic Change in Populations 1. Pesticide Resistant Insects -Farmers use pesticides to kill crop eating insects. -Some insects possess a trait that makes them resistant to the pesticide, so they are not killed. -The resistant insects pass the gene for resistance to offspring. -After a few generations the population is mostly insects that are resistant to the pesticide. (insects have evolved) -Pesticide used is no longer effective in killing these insects. 2. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria -Dr.s prescribe antibiotics to kill infections caused by bacteria. Common exs. include strep throat or sinus infections. -Some bacteria possess a trait making them resistant to the antibiotic and are not killed. -Bacteria that survive pass the gene for resistance to offspring. -Repeated infections can be harder to treat with antibiotics if the infection is caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria. How Natural Selection Works How does natural selection affect single gene traits? Can lead to changes in allele and Phenotype . Ex. Lizard Color Normal lizard is brown. Mutations in one gene for body color can cause lizards. Red lizards are seen and eaten easily by . Black lizards absorb more , move faster to avoid predators, eat better, and leave more offspring. Result: there is a change in allele and phenotype frequencies. Later populations have increased frequency of alleles for black lizards. How Natural Selection Works How does natural selection affect polygenic traits? 1. Directional Selection – Occurs when individuals at one end of the curve have higher than individuals in the middle or other end of the curve. Ex. Beak Size How Natural Selection Works How does natural selection affect polygenic traits? 2. Stabilizing Selection – Occurs when individuals near the of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve. Ex. Mass of human infants at birth. How Natural Selection Works How does natural selection affect polygenic traits? 2. Disruptive Selection – Occurs when individuals at the outer ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the of the curve. Ex. Beak Size Genetic Drift What is genetic drift? • change in allele frequency that occurs in small populations. • Individuals with a allele may leave more offspring than other individuals, just by chance. (not due to natural selection) • Over time, a series of occurrences can cause an allele to become more or less common in a population. Two Types of Genetic Drift 1. Genetic Bottlenecks A change in allele frequency following a dramatic in the size of a population. -Genetic diversity is sharply . -Caused by disaster, such as killing many individuals. -The smaller population’s gene pool may have different allele frequencies than population’s. Two Types of Genetic Drift 2. The Founders Effect Allele frequencies change as a result of the of a small subgroup of a population. -A few individuals colonize a new habitat. -Founding individuals may carry alleles that differ in frequency to the main population, just by . (not due to natural selection) -Ex. Migration and evolution of fruit flies on Hawaiian islands. Evolution Versus Genetic Equibrium What conditions are required to maintain genetic equilibrium? • Genetic equilibrium occurs if a population is not evolving, meaning the allele frequencies in its gene pool do not change. • Hardy-Weinberg principle predicts that five conditions can disturb genetic equilibrium and cause evolution to occur: 1. N (artificial selection, sexual selection causes evolution) 2. Small size (genetic drift causes evolution) 3. Immigration or (loss or gain of alleles causes evolution) 4. M (new alleles causes evolution) 5. Natural (different fitness levels causes evolution)