File - Dayna L. McLaughlin
advertisement

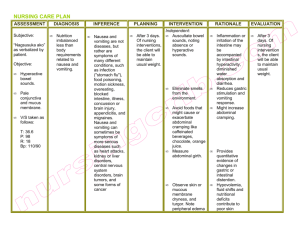
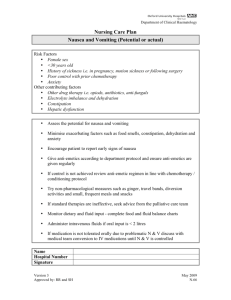
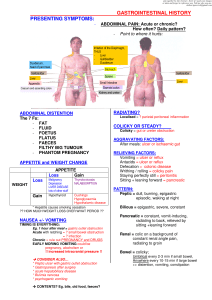
FOUR PROCESSES: (1) mechanical degradation - chewing and churning (2) liquefaction - secretion of GI accessory glands- salivary, hepatic, pancreatic secretions (3) enzymatic hydrolysis- amylases break starch molecules into monosaccharide sugar subunits (4)Absorption via the extensive mucosal membrane surface of lower GI tract. GI Drugs targeting Specificity Indications for Use Side and Adverse Effects Nursing interventions Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease(GERD) Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Laxatives Antiemetic Agents Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Irritable Bowel Syndrome Antidiarrheal Weight Loss Vitamins Herbals Contraindications and Precautions Drug interactions GERD Animation Omeprazole ( Prilosec) Peptic Ulcers Peptic Ulcer Development Video Misoprostol (Cytotec) Sucralfate (Carafate) Antacids DIFFERENTIATE D BY: Acid Neutralizing Capacity (ANC) Onset and Duration of action Effects on the Bowel Systemic Effects Special applications Antacids Magnesium Hydroxide Calcium Carbonate BOTH: Fast acting, high ANC, producing long lasting effects Differ in Adverse Effects http://vimeo.com/42835070/download?t=1380467758&v=100000350&s= a24f06398417da00f45703b5598e3e06 Actions much like that of dietary fiber Preferred agents for temporary treatment of constipation A “Stool Softener” Results in 1 to 3 days Alters consistency by lowering surface tension Surfactants inhibit fluid absorption and stimulate secretion of fluid into lumen Used for Opioid induced Constipation Plant derived Containing anthraquinones Semifluid stool in 6 to 12 hours Non-absorbable compound Alters consistency by lowering surface tension Surfactants inhibit fluid absorption and stimulate secretion of fluid into lumen Vomiting The expulsion of gastric contents -Before treating, the cause of the vomiting needs to be identified Causes Motion sickness Viral & bacterial infection Food intolerance Post operative surgery Pain, shock, & effects of radiation Disturbances of the middle ear affecting equilibrium. GI Drugs: Antiemetic Dopamine Blockers Serotonin antagonists Glucocorticoids Cannabinoids Dopamine Blocker: Prokinetic Agent: Drugs used to speed up the movement of food through the stomach and intestines can cause tardive dyskinesia which is irreversible Serotonin receptor Antagonist: Prevents emesis and nausea associated with radiotherapy and anesthesia and other causes Increased effectiveness when combined with dexamethasone Potentiates prolonged QT Risk of tardes des pointes Glucocortocoid: Used to suppress CINV Given to treat nausea and vomiting resulting from chemotherapy Suppresses immune system Cannabinoid: Used to treat nausea and vomitting from Chemotherapy Given as a second choice medication when nothing else works Can be habit forming IBS Animation Most common disorder of the GI tract Approved in Women only Can cause severe side effects-deaths have occurred due to its potential for GI toxicity Both drugs treat diarrhea and reduce the volume of discharge of ileostomies and suppress the bowel motility by decreasing fluid secretion into intestinal lumen Poorly absorbed Does not readily cross the blood brain barrier This is a class V controlled Substance Taken in high doses can elicit morphine like effects Overdose can occur Phentermine (Adipex-P) Appetite suppressant Belongs to a class of drugs called sympathomimetic amines. Decreases appetite while increasing the amount of energy used by your body, or by affecting certain parts of the brain. Take on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal Avoid taking antacids or antibiotics within 2 hours before or after taking ferrous sulfate. Ferrous sulfate is only part of a complete program of treatment that may also include a special diet. Risk of iron poisoning Give test dose and have epinephrine ready to counter iron poison. Follow up with dosage 1 hour later Used when oral iron is intolerable Risk of anaphylaxis and cardiac arrest Used to treat hypokalemia (commonly caused by taking loop diuretics) Causes severe GI upset, bleeding, perforation Take with food or a full glass of water • Essential for DNA synthesis and influences cell growth and division by catalyzing folic acid conversion • Coupled with its intrinsic factor, absorbed by interacting with receptor cells in the intestinal wall • • Stored in the liver. • Because it is stored the average adult requires about 2.4 mcg per day Without it DNA replication and cell division cannot occur Water soluable B vitamin that is not stored in the body like B12 Foods with folic acid in them include leafy green vegetables, fruits, dried beans, peas and nuts. Enriched breads, cereals and other grain products also contain folic acid Treats: symptoms of menopause, including hot flushes, vaginal dryness, palpitations, depression, irritability, and sleep disturbance. . used primarily for prophylaxis of migraine. Orally: suppresses inflammation influenza and the common cold. Topically: treats wounds, burns, eczema, psoriasis, and herpes simplex infection. Treats dyslipidemia and constipation also supplies a vegetarian source of omega-3 fatty acids. Reduces levels of triglycerides and low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and to raise levels of high-densitylipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Reduces blood pressure, suppress platelet aggregation, increase arterial elasticity Reduces the formation of atherosclerotic plaque. Treats vertigo and to suppress nausea and vomiting caused by motion sickness, morning sickness, surgery, and perhaps cancer chemotherapy. Improves age-related memory impairment, dementia, and associated conditions, including dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, headache, and mood changes. Improves painfree walking distance in patients with peripheral artery disease. HERBALS Improving mental clarity, weight loss, and prevention and treatment of stomach, skin, bladder, and breast cancer. Relieves urinary symptoms associated with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). Prevention of breast cancer, treatment of menopausal symptoms (hot flashes), and prevention of osteoporosis HERBALS Treats depression Promotes sleep. Reduces anxiety-associated restlessness. References Lehne, R. (2013). Pharmacology for Nursing Care (8th Ed.). St Louis Missouri: Elsiever Saunders Lippencott, W. (2009). Nursing Pharmacology Made Incredibly Easy (2nd Ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Vallerand, A. (2013). Davis’s Drug Guide for Nurses (13th Ed.). Philadelphia, PA : F. A. Davis Company Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Zerwekh, J. (2009) Mosby’s Pharmacology Notecards (3rd Ed.). St Louis Missouri: Elsiever Saunders