Unit 6
advertisement

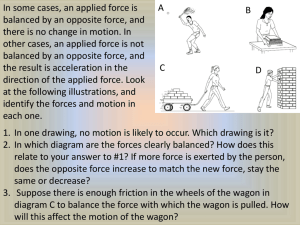
Unit 6: Bell Ringer. If you are sitting still in your seat on a bus that is traveling 100 km/h on a highway, is your body at rest or in motion? Explain. Unit 6: Force and Motion. Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) Although he did not discover all three laws of motion, he explained them in a way that helped many people understand them. Unit 6: Force and Motion. Newton’s First Law of Motion “An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force.” Unit 6: Force and Motion. What is force?! Force is simply a push or pull. Forces have SIZE AND DIRECTION Unit 6: Force and Motion. The unit for force: Newton (N) BrinPop on Force: https://www.brainpop.com/science/motionsforcesandtime/force/ Unit 6: Force and Motion. What does this mean? Basically, an object will “keep doing what it was doing” unless acted on by an unbalanced force. If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary. If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving. Unit 6: Force and Motion. Newton’s First Law is also called the Law of Inertia Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion Unit 6: Force and Motion. An object with a small mass has less inertia than an object with a large mass. This means… it is easier to start and change the motion of an object with a small mass! Unit 6: Force and Motion. Real Life Inertia Examples Inertia makes it easier to push the lawn mower than it does to start pushing a car! Unit 6: Force and Motion. Momentum: property of a moving object that depends on the mass and velocity. The more momentum, the harder it is to stop or change the direction of the object! Unit 6: Force and Motion. But wait… If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why don’t moving objects keep moving forever? Unit 6: Force and Motion. Friction: is a force that oppose motion between two surfaces that are touching Example: A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. Friction song!! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U5f7SyvHUac Unit 6: Force and Motion. In outer space, away from gravity and any sources of friction, a rocket ship launched with a certain speed and direction would keep going in that same direction and at that same speed forever. Unit 6: Force and Motion. Pushing a solid over a solid. Unit 6: Force and Motion. Wheels reduce friction so things are easier to move. Unit 6: Force and Motion. The force between solids and a liquid or gas. Unit 6: Force and Motion. This force balances others so the object does not move Unit 6: Force and Motion. How to reduce friction Unit 6: Force and Motion. Inertia Ball LAB 1. Work on Newton's Laws vocabulary. Study. Go over notes. Read through lab/ try to answer any that you can. Read through textbook pg 145-147. 2. Perform lab when sent into the hall. (5-10 minutes) 3. Answer lab questions with group. HAND IN ONE LAB FOR THE group (SUMMATIVE)! 4. When done, start homework. (20 point SOL Menu) Unit 6: Force and Motion. Bell Ringer: 1. This crash dummy is NOT wearing a seat belt. Explain, using Newton’s first law of motion, what will happen if he were to get into a collision. (think about momentum and inertia) Unit 6: Force and Motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion “The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied.” Unit 6: Force and Motion. What does that mean?... Let’s look at the law on 2 parts… 1) Acceleration depends on mass! If given the same force Less mass -> greater acceleration Greater mass -> less acceleration Unit 6: Force and Motion. 2) Acceleration depends on force! If given the same mass Less force-> less acceleration Greater force -> greater acceleration Unit 6: Force and Motion. How to express Newton’s second law mathematically F = ma Unit 6: Force and Motion. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQmYBF_Sd8I Unit 6: Force and Motion. Let’s try: A little boy pushes a wagon with his dog in it. The mass of the dog and the wagon together is 45 kg. The wagon accelerates at 0.85 m/s2. What force is the boy pulling with? Unit 6: Force and Motion. Now your turn… try the rest of the question on the “Newton’s Second Law of Motion- Worksheet” Unit 6: Force and Motion. Suppose you drop a large rock and a small rock at the same time from the same height. Which do you think will land first? Gravity BrainPop: https://www.brainpop.com/science/motionsforcesandtime/gravity/ Misconcceptions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_mCC-68LyZM Unit 6: Force and Motion. All objects accelerate towards the ground at the SAME rate. 2 9.8 m/s = acceleration due to gravity Unit 6: Force and Motion. Show in class vacuum tub demo Unit 6: Force and Motion. On Earth, falling objects will be slowed down by air resistance. (fluid friction between the falling object and the air) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-cCt9JobjOg Unit 6: Force and Motion. You may watch any of the following BrainPop videos: Play Gizmo games… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Go to Google. Click on the first link after searching GIZMO. Click on Enroll in a Class Enter the Class code: XYWWEWVCYR Click on “I need to create an ExploreLearning Account” Type in your first name, last initial, create a user name, and password Play with Gizmos on forces! Try answering the questions that are underneath each game as you go! OR work on SOL menu project due NEXT CLASS Unit 6: Force and Motion. HAND IN SOL MENU PROJECT Bell Ringer: 1. The whale shark is the largest of all fish and can have the mass of three adult elephants. Suppose that a crane is lifting a whale shark into a tank for delivery to an aquarium. The crane must exert an unbalanced force of 2500 N to lift the shark from rest. If the shark’s acceleration equals 1.25 m/s2, what is the shark’s mass? Unit 6: Force and Motion. Newton’s Third Law of Motion “Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first.” Unit 6: Force and Motion. All forces act in pairs Unit 6: Force and Motion. What are some examples of action and reaction force pairs? Unit 6: Force and Motion. Time for Rocket Balloon Lab!! ALL lab group members needs to turn in COMPLETED lab COMPLETE the next handouts “Newton’s Third Law” & “Newton’s Graphic Organizer”… do not turn these in! (we will go over it) If you have COMPLETED everything above, YOU MAY: • Watch BrainPop videos on Force and Motion • Do your HW: JLab FIXED SET 4 • Read through textbook pages 150-151 Unit 6: Force and Motion. Law of Universal Gravitation: all objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational forces; the size of the force depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. Unit 6: Force and Motion. • Gravitational force is small between objects with small masses. • Gravitational force is large between objects with larger masses. • If the distance between two objects is increased, the gravitational force pulling them together is reduced Unit 6: Force and Motion. Bell Ringer: What did we learn from the rocket balloon lab last class? Unit 6: Force and Motion. DONE WITH THE QUIZ?: Please take out the 2 sheets from last class, and be working on those, we will be going over them! Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work and Power. Work Occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. Work only occurs when there is movement in the same direction as the force! Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work and Power. Work or no work? Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work and Power. Calculating Work W=F×d Work = Force × distance SI Units of Measurement Work = joules (J) Force = Newtons (N) d = meters (m) Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work increases when the amount of force OR distance moved increases Work = Force × distance Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work and Power. Power The rate at which work is done. (Power is how fast the work happens!) Unit 6: Force and Motion. Work and Power. Calculating Power P=W÷t Power = Work ÷ time SI Units of Measurement Power = watt (W) Work = joules (J) t = seconds (s) Unit 6: Force and Motion. Power increases when the time it takes to do work decreases Power = Work ÷ time Unit 6: Force and Motion. Brick on a Stick Lab EACH person hands in a lab When you are done… 1. Work on unit vocab sheet (front and back) 2. Do Jlab #5 Fixed set on device. 3. Watch BrainPop videos on Work/ Power