Introduction to MATLAB
advertisement

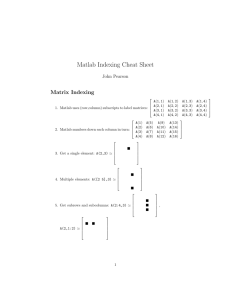
Introduction to MATLAB The language of Technical Computing MATLAB MATrix LABoratory- Everything is represented by matrices! It is a program for doing Numerical Computation. Also used widely as a programming language to develop tools for Machine Learning. Why MATLAB? Large toolbox of numeric/image library functions. Very useful for displaying, visualizing data. High-level: focus on algorithm structure, not on low-level details. allows quick prototype development of algorithms. It is an Interpreter, not as fast as compiled code. The MATLAB Environment Variables MATLAB treats all variables as matrices. For our purposes a matrix can be thought of as an array, in fact, that is how it is stored. Vectors are special forms of matrices and contain only one row OR one column. Scalars are matrices with only one row AND one column. MATLAB Programming The symbol “%” is used to indicate a Comment. A “;” at the end of the line implies MATLAB won’t print the output of the statement. Otherwise it will print the output, which is sometimes useful for printing variable values. MATLAB Programming a = [1,2,3,4] MATLAB Output: a= 1 2 3 4 a=[1,2,3,4]; %Notice the semicolon MATLAB Output: <Empty> Command Line MATLAB's command line is like a standard shell: - Up arrow to recall commands without retyping and down arrow to go forward. Opening a new file in editor: >> edit test.m MATLAB source file extension is .m. Running a program : >> test MATLAB Programming a = [1 2; 3 4]; % Creates a 2x2 matrix The simplest way to create a matrix is to list its entries in square brackets. The ";" symbol separates rows; the (optional) "," separates columns. N = 5 % A scalar v = [1 0 0] % A row vector MATLAB Programming v = [1; 2; 3] % A column vector v = v’ Transpose a Vector or Matrix(row to column and column to row) v = [] Empty Vector MATLAB Programming m = zeros(2, 3) Creates a 2x3 matrix of zeros v = ones(1, 3) Creates a 1x3 matrix (row vector) of ones m = eye(3) %Identity matrix (3x3) v = rand(3, 1) Randomly filled 3x1 matrix (column vector) Indexing in MATLAB REMEBER: Indices always start from “1”, not “0”. Matrix(ROW#,COLUMN#) m(1,3) %1st row 3rd column m(2,:) %access whole second row m(:,3) %access whole second column Operators Assignment = a = b (assign b to a) Addition + a + b Subtraction - a -b Multiplication * or .* a*b or a.*b Division / or ./ a/b or a./b Power ^ or .^ a^b or a.^b A “.” means element wise operation Conditional Structures for i=1:2:7 %Loop from 1 to 7, steps of 2 if(i==3) disp(‘i is 3’) %print output elseif(i==5) disp(‘i is 5’) end end Functions All functions are separate m-files. The first line in a function file must be of this form: function [outarg_1, ..., outarg_m] = myfunction(inarg_1, ..., inarg_n) The function name should be the same as that of the file. Function Example myfunction.m function y = myfunction(x) a = [-2 -1 0 1]; y = a + x; Function Example anotherfunction.m function [y, z] = anotherfunction(a, b) y = a + b; z = a - b; Plotting x=rand(1,100); y=rand(1,100); plot(x,y,’*’); Plotting To put a label on X-Axis xlabel(‘my x label’); To put a label on Y-Axis ylabel(‘my y label’); To put a Title of the Plot title(‘my title’); MATLAB Image Processing Image Processing Toolbox is needed. I=imread(‘cute_baby.jpg’); %read Image imshow(I) %show image MATLAB Image Processing I2=rgb2gray(I); % convert RGB to gray imwrite(I2, ‘cute.jpg’); % save gray image figure, imshow(I2) % image in new figure MATLAB Image Processing figure,imhist(I2) % show histogram MATLAB Image Processing From the histogram, we see that the image intensity is missing low values, only high values are present. MATLAB Image Processing I3 = histeq(I2); %Histogram Equalization figure, imhist(I3); MATLAB Image Processing figure, imshow(I2) %Original image figure, imshow(I3) % Equalized Image Help with MATLAB Type help at the MATLAB prompt or help followed by a function name for help on a specific function. Online documentation for MATLAB at the MathWorks website: www.mathworks.com There are also numerous tutorials online that are easily found with a web search.