n - PEER
advertisement

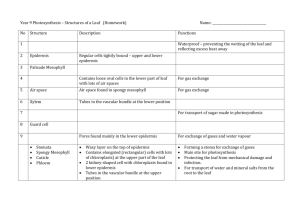
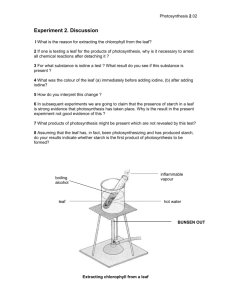
Photosynthesis What is photosynthesis? • Photosynthesis may look like a large, intimidating word. Let’s break it down in order to get a general idea of what it means: • "Photo" means light. Synthesis means to put together • During photosynthesis, plants use the energy contained in this sunlight to turn carbon dioxide and water into energy in the form of a carbohydrate (sugar) called glucose. electromagnetic energy becomes ________ chemical So _____________ energy. Photosynthesis 1. Radiant Energy from the sun is turned into chemical energy. 2. The chemical energy is used to “put together” glucose from carbon dioxide “building blocks” Photosynthesis Equation 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + Energy from Sunlight C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O http://www.xtec.cat/~mherna23/summer03/amspot/picture/photosynthesis.jpg 6 molecules of carbon dioxide combine with 12 molecules of water in the presence of sunlight energy to form one molecule of sugar plus 6 molecules of oxygen and 6 molecules of water. Where does photosynthesis take place? http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/Leaf_anatomy.svg/769px-Leaf_anatomy.svg.png Roots “The Warehouse” The three major functions of roots are 1. Absorption of water and inorganic nutrients 2. Anchoring the plant body to the ground 3. Storage of foods http://www.livingwilderness.com/southwest/pine-root-rock.jpg Transport Tissues “The Conveyor Belts” • Xylem – Transports water from the root to the plant • Phloem – Transports organic nutrients from the plant to the root http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/Leaf_anatomy.svg/769pxLeaf_anatomy.svg.png Epidermis “The Outer Wall’ • The epidermis is the outer single-layered group of cells covering a plant. • The epidermis forms the boundary between the plant and the external world. The epidermis serves several functions: protection against water loss, regulation of gas exchange, and absorption of water and mineral nutrients. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/Leaf_anatomy.svg/769px-Leaf_anatomy.svg.png Palisade Cells “The Assembly Lines” • Palisade cells are a type of leaf tissues that contain chloroplasts. • Palisade cells are placed all over the top of a leaf, maximizing the extent of light absorption. As a result, the top of a leaf is often darker than the bottom. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/Leaf_anatomy.svg/769px-Leaf_anatomy.svg.png Chloroplasts “The Workers” Leaves of plants have chloroplasts that are filled with chlorophyll, which capture the energy from the sunlight). Water and carbon dioxide move to the chloroplasts and chemical reactions there produce oxygen and sugars. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/chloroplasts/images/chloroplastsfigure1.jpg Chloroplasts Continued “The Workers” Cells can contain 50 or more chloroplasts! The thylakoids look like coins. These contain chlorophyll and are responsible for collecting light. In the stoma, enzymes assemble sugar fragments from the CO2 and H2O. http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/chloroplasts/images/chloroplastsfigure1.jpg Stoma “The Smoke Stack” • The stoma is the opening that connects the outside to the inside. Air flows into the leaf through the stoma. • The air brings carbon dioxide (CO2), needed for photosynthesis, with it. Oxygen (O2), a byproduct of photosynthesis, flows out through the stoma. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9 0/Leaf_anatomy.svg/769px-Leaf_anatomy.svg.png Virtual Lab http://i.treehugger.com/images/2007/10/24/Stomata.jpg http://i.treehugger.com/images/2007/10/24/chloroplast-jj-001.jpg http://www.vcbio.science.ru.nl/images/fesem_epidermis_zoom_zlabel.jpg