Growing degree days (GDD)

Temperature & Respiration
A/H 100G
J.G. Mexal
HORT Humor
Take Home Quiz (due Monday 2/27/06)
What will be the impact of global climate change to:
• Natural ecosystems
• Agriculture in the southwest
• Urban landscapes, esp. golf courses
– Discuss these in terms of near-term consequences (10-20 years) and long-term (>
30 years)
What is ‘Respiration’?
• The conversion of stored energy (sugar) into metabolic energy (ATP)
• Occurs in mitochondria
• Requires sugar
• Generates ATP + CO
2
The parts of a cell
Ps & Rs Comparison
Photosynthesis
• Occurs only in green cells
• Occurs in chloroplasts
• Occurs only in light
• Requires light, CO
2
, H
2
O
• Produces O
2 and sugar
• ATP produced by photophosphorylation
(used to make sugar)
• Results in biomass gain
Respiration
• Occurs in all living cells
• Occurs in mitochondria
• Occurs 24/7
• Requires O
2 and sugar
• Produces CO
2
, H
2
O
• ATP produced by oxidative phosphorylation
(‘burning’ sugar to make other products)
• Results in biomass loss
Temperature Effects on Ps & Rs
Relative Response (%)
100
80
Photosynthsis
Respiration
60
40
20
0
0 10 20 30
Temperature (C)
40 50
Temperature Effects on Ps & Rs
Relative Response (%)
100
80
Photosynthsis
Respiration
60
Net Ps
40
20
0
0 10 20 30
Temperature (C)
40 50
Terms
•Cool season crops
•Warm season crops
•Cold-hardiness
•Dormancy
•Endo-
•Eco-
•Para-
•Chilling requirement
•Growing degree day GDD)
•Stratification
•Scarification
•Vernalization
•Heat-zone map
•Hardiness zone map
Cool season crops
• Prefers air temperatures: 20-25 o C
– Soil temperatures: 15-22 o C
• Crops:
– Lettuce
– Cole crops
– Carrots
– Spinach
− Kentucky bluegrass
− Christmas trees
− Wheat
− Barley
Warm season crops
• Prefers air temperatures: 25-35 o C
– Soil temperatures: 20-28 o C
• Crops:
– Tomato
– Sorghum
– Soybean
– Afghan pine
− Bermuda grass
− Corn
− Chile
− Pineapple
Cold-hardiness
• Definition : ability to survive temperatures below 0 o C.
• Function of tissue, season, growth stage
– Shoots <-40 o C − Roots ~ -10 o C
• N.B. Chilling injury is injury to tropical fruits caused by temperatures between 0-5 o C
Basic Plant Biology
Factors Affecting Acclimation-Size
Winter
• Buds = -25 o
• Cambium = -50 o
• Roots = -10 o
Spring
• Buds = -3 o
• Cambium = -4 o
• Roots = -4 o
• Seedling = -30 o • Seedling = -3 o
• Germinant = -2 o
Basic Plant Biology
Factors Affecting Acclimation- Genetics
Intolerant
• Eucalyptus camaldulensis
– Shoots = -10 o C
– Roots = -3 o C
Tolerant
• Pinus pinea
– Shoots = -40 o C
– Roots = -10 o C
Basic Plant Biology
Mesquite/ April 2003
-8
-10
-12
-14
-16
-18
-4
-6
Dormancy & Cold-hardiness
Cold - Hardiness of Apple Blooms
LT
50
0
( o C)
-2
LT50
LT10
LT90
1-O ct
15
-O ct
1-N ov
15
-N ov
30
-N ov
15
-D ec
30
-D ec
15
-J an
30
-J an
15
-F eb
28
-F eb
15
-M ar
30
-M ar
15
-A pr
15
-M ay
30
-M ay
Approximate Calendar Date
Basic Plant Biology
Cold - Hardiness of Apple Blooms
-6
-8
-10
-12
-14
0
1000
-2
-4
Dormant
2000 3000
12mm Green
Green Tip
Silver Tip
4000
Tight Cluster
5000
Full Pink
Growing Degree Hours ( o C)
6000 7000
Full Bloom
Photos by:
Basic Plant Biology
How a Tree Grows
• Dormancy-lack of visible growth
– Ecodormancy- environmental stress induced-
• Growth resumes when stress removed
– Endodormancy- requires chilling
• Growth resumes after chilling requirement met
(h between 0-10 o C), and sufficient GDD accumulate
– Paradormancy- regulated by other buds
• Remove the controlling bud and ‘whalaa’
Dormancy & Cold-hardiness
Dormancy of Apple Blooms
Chilling Units
1.0
Growth Units
20
0.5
15
0
-0.5
-1.0
0 5
10
10 15 20
Temperature ( o C)
25
5
30
0
Growing degree days (GDD)
• Growing degree days (GDD) is a measure of temperature requirements for plants and can be used to estimate growth and development.
• The basic concept of growing degree days is that plant development will occur when temperatures exceed a base temperature.
Growing degree days (GDD)
• Corn: the maximum temperature plus the minimum temperature in a day divided by 2 minus 50.
• Fifty is selected as the constant because corn grows little at 50 °F or below.
• 86°F is the maximum temperature
Growing degree days (GDD)
• Example: If a low temperature was
60 °F and the high was 90°F, the GDD would be 60 + 86 = 146 divided by 2
= 73 – 50 = 23 GDD.
National Climate Zone Map
E Gregory McPherson <egmcpherson@ucdavis.edu>
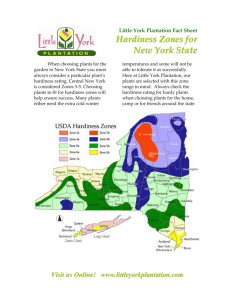
Plant Hardiness Zone Map
USDA Hardiness Zone Map
Plant Heat Zone Map
Nursery Industry
Heat-Zone Map/
AmHortSoc
Zone 9
Days/yr> 86F
7-14
14-30
30-45
45-60
60-90
90-120
120-150
New Mexico Maps
Days/yr> 86F
7-14
14-30
30-45
45-60
60-90
90-120
120-150
Zone 9
Seed Dormancy
• Stratification
– Overcoming physiological dormancy by exposure to cold temperatures (wet or dry)
• Scarification
– Overcoming physical dormancy by mechanical abrasion
• Mechanical
• Chemical (acid)
• Thermal (hot water)
• Percussion (certain species)
Vernalization
• Chilling to induce transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth
• Examples:
– Winter wheat
– Onions (biennial)
– Bulbs (daffodil, tulip)
Things to know:
•Cool season crops (T & e.g.)
•Warm season crops (T & e.g.)
•Cold-hardiness (definition, LT
50
•Dormancy
)
•Endo-
•Eco-
•Para-
•Chilling requirement
•Growing degree day GDD)
Things to know:
• Stratification (e.g.)
• Scarification (e.g.)
• Vernalization (e.g.)
• Heat-zone map (what it means)
• Hardiness zone map (what it means)
Infrared Surface Temperature Influenced by Surface Cover
Temperature ( o F)
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
6 8 10
Turf
Asphalt
Artificial Turf
12 14 16 18
Military Time (hr)
20 22 24