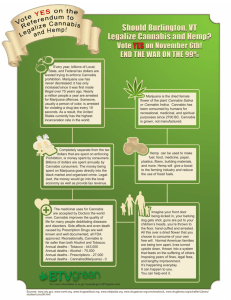
Cannabis Fact Sheet LP10
Physiological Complications
550-106
Jamie M. Floeter
12/08/2012
Marijuana
A hemp plant that is gray, green, or a brown mixture of shredded
dried leaves, flowers, seeds, and stems.
“Cannabis Sativa” Classification in 1753 by a Swedish botanist named
Carolus Linnaeus. Cannabis Sativa is a dioecious plant (male and female
plant) that is readily grown in many parts of the world.
Cannabis can be considered a sedative and a mind altering drug that
contains over 421 different chemicals. Many of these chemicals have not
been identified. One of these identified chemicals in THC. (Delta-9
Tetrahydrocannbinal)
Botanists have never been able to trace its original origin. The first
known record was in a book written by a Chinese Emperor Shen Nung in
2737 BC, who prescribed marijuana for treating gout, malaria, gas pains,
and absentmindedness. In history you will find that it’s uses where medical
use and its woody like fibers to make cloths and rope.
Trends in the United States
According to the 2008 National Survey on Drug use and Health that
there were about 15.2 million past-month users. Making marijuana the most
commonly used illicit drug in the United States.
Marijuana is used widely among young adults and teenagers. In 2009,
11.8 percent of 8th graders reported to using marijuana, and 6.5 percent
were current users. 10th graders were at 26.7 that had used marijuana in
the past year, and 15.9 were current users. In 12th graders they were at
32.8 that had used in the last years while 20.6 were still currents users.
I do hope that by the time my son gets to be in late middle school and
early high school things will have changed. I hope the teachers better
educate their students about this drug. Even though I don’t completely
oppose to the drug, I feel that children are to under educated and have not
matured enough to use the drug. I also feel that marijuana has a bad effect
on a teenager’s attitudes and their outlook on life. I also believe that THC
doesn’t mix well with the rush of hormones that teens produce while going
through puberty.
Cannabis Fact Sheet LP10
Physiological Complications
550-106
Jamie M. Floeter
12/08/2012
Therapeutic use
Marijuana has been used in therapy for centuries. Marijuana has been
used to treat many types of illnesses such as depression, migraines, chronic
pain, anorexia, asthma, glaucoma, and muscles spasms.
The Food and Drug Administration feel that there are other medicines
that are at least as effective and do not have abuse potential.
Street Names
Mary Jane
Green
Bud
Devils lettuce
Nuggets
Nuggies
Dank
Ganj
Ganja
Smoke
Reefer
Killer
Effects on the brain
The chemical in marijuana “THC” stimulates the brain cells to release
dopamine. THC also affects the nerve cells in the part of the brain where our
memories are formed. This is why people who use have troubles learning or
remembering certain things and events. Like what they had for breakfast.
What’s going on that causes the High?
THC stimulates our cannabinoid receptors, disrupting the
functions of natural cannabinoids. The overstimulation of these receptors in
certain brain areas. Over time and chronic use can alter the functions of the
CBR’S system along with other brain changes that can lead to abuse and
withdrawal.
Cannabis Fact Sheet LP10
Physiological Complications
550-106
Jamie M. Floeter
12/08/2012
Physiological Effects
In the Cardiovascular System depending on dose, Cannabis can
increase a person’s heart pulse rate, but it can also reduce the typical heart
rate to inhalation when breathing or coughing. It also produces hemoglobin
that limits the amount of air that gets to the tissues that is around the heart.
Cannabis can cause swelling in blood vessels around the eyes, causing them
to go blood shot.
In the Respiratory system cannabis is dangerous. Cannabis contains
more carbon monoxide that a cigarette and the smoke for cannabis is
inhaled much deeper and held longer thus causing more of a tar build up.
Cannabis can also weaken the white blood cells in the living lung tissue.
These cells remove debris from the lungs.
Cannabis plays its toll on the CNS such as altered perceptions, delayed
reaction time and an increase in appetite. In some cases, those who smoke
in a bad setting or under extreme amounts of stress, they can feel high
anxiety. Those chronic users can lose motivation and self-interest.
Signs of Dependence
Daily use
Tolerance
Withdrawal
Lack of motivations
Lack in personal self
Social difficulties
Failed to attempts to quit
Cannabis Fact Sheet LP10
Physiological Complications
550-106
Jamie M. Floeter
12/08/2012
References
http://www.drugscience.org/Archive/bcr5/Marijuana_Use_in_the_United_Sta
tes.pdf
A special report from the bulletin of Cannabis Reform
By Jon Guttman, Ph.D.
Sept 22, 2008
http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuanaabuse/what-scope-marijuana-use-in-united-states
NIDA, The Science of Drug Abuse and Addiction
What is the scope of marijuana use in the U.S.
Updated Sept. 2010
http://intraspec.ca/medical-marijuana.php
Medical Marijuana
Medicianl and Therapeutic uses of Cannabis Sativa
Updated Sept 29, 2011
http://bigheadshop.com/marijuana-streetnames.htm
Marijuana Street Names Drug Info
http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/exchange/node/1808
How marijuana affect the brain?
Akudo Ejelonu
2004 First Web Paper
http://druglibrary.org/schaffer/Library/studies/ledain/physiological_effects.h
tm
Cannabis
The Report of the Canadian Government Commission of Inquiry into the NonMedical Use of Drugs – 1972
Cannabis Fact Sheet LP10
Physiological Complications
550-106
Jamie M. Floeter
12/08/2012
http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/c/cannabis_dependence/intro.htm
Copyright © 2011 Health Grades Inc. All rights reserved. Last Update: 6 November,
2012
Drugs and Society
By, Hanson, Venturelli, Fleckenstein
Jones and Bartlett Learning, LLC © 2012
Criteria
Fact Sheet defines/describes cannabis.
Fact Sheet identifies trends in cannabis
consumption in the U.S.
Fact Sheet describes the therapeutic uses of
cannabis and controversy regarding medical
marijuana.
Fact Sheet provides a list of street names for
cannabis.
Fact Sheet describes the effects of cannabis
abuse on the brain.
Fact Sheet identifies the physiological effects
from cannabis abuse.
Fact Sheet identifies the health risks of the
cannabis abuse.
Fact Sheet identifies the signs and symptoms
of cannabis abuse/dependence.
Fact Sheet is organized, professionally
appearing, and free of errors.
Fact Sheet synthesizes information from a
variety of sources.
Fact Sheet is submitted by the due date.
Fact Sheet includes “References” to sources of
information used.
Values
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 8 4 0
10 0
10 8 4 0