Respiratory System
advertisement

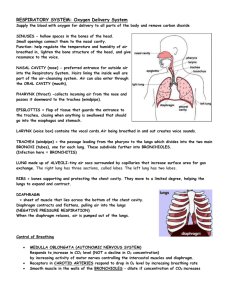
Respiratory System What is the respiratory system? • The respiratory system is the system of the body that deals with breathing. • When we breathe, the body takes in the oxygen that it needs and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesn't need. • • Major Organs Upper respiratory: nose, phaynx Lower respiratory: larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Parts of the respiratory system • • • • Lungs The lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. In the lungs oxygen is taken into the body and carbon dioxide is breathed out. The red blood cells are responsible for picking up the oxygen in the lungs and carrying the oxygen to all the body cells that need it. The red blood cells drop off the oxygen to the body cells, then pick up the carbon dioxide which is a waste gas product produced by our cells. The red blood cells transport the carbon dioxide back to the lungs and we breathe it out when we exhale. Trachea The trachea (TRAY-kee-uh} is sometimes called the windpipe. The trachea filters the air we breathe and branches into the bronchi. Bronchi The bronchi (BRAHN-ky) are two air tubes that branch off of the trachea and carry air directly Diaphragm Breathing starts with a dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of the lungs called the diaphragm (DYuh-fram). When you breathe in, the diaphragm contracts. When it contracts it flattens out and pulls downward. This movement enlarges the space that the lungs are in. This larger space pulls air into the lungs. When you breathe out, the diaphragm expands reducing the amount of space for the lungs and forcing air out. The diaphragm is the main muscle used in breathing. Within the lungs, the trachea branches into a left and right bronchus, which divide into increasingly smaller branches called bronchioles. The smallest bronchioles end in a cluster of air sacs, collectively called an acinus. The acinus comprises individual air sacs called alveoli. Alveoli are like small balloons that inflate and deflate with air during respiration. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs between the alveoli and a capillary network within the alveolar wall. Capillaries are microscopic blood vessels that exchange material between the blood and body tissues. In the lung capillaries, blood from tissues where cellular metabolism is occurring is called deoxygenated blood because it contains many carbon dioxide molecules and few oxygen molecules. • The respiration process has two parts: inspiration (inhaling) and expiration (exhaling). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts, moves downward, and causes the thoracic cavity volume to increase. Because the lungs are closely associated with the interior chest wall, they expand as the thoracic cavity expands. When the diaphragm relaxes (upward position), the thoracic volume decreases and the lungs partially deflate. This process is called expiration. The elastic recoil of the expanded thoracic wall and lungs also helps expiration. • After inhalation, the alveoli contain many oxygen molecules. The alveoli are in close contact with the capillary network. This proximity enables the minuscule oxygen molecules to diffuse (pass freely) from the alveolus to the bloodstream, flowing from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. In the bloodstream, the oxygen attaches to red blood cells and is transported to the rest of the body. Likewise, carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveolus where it is transported out of the body during exhalation. During respiration, the pleurae (pleural membranes) help the lungs to expand and contract. These membranes are sacs that tightly cover the lungs and the chest inside wall. Between these two linings is a space called the pleural cavity that contains a thin layer of fluid. This fluid allows the lungs to move freely against the thoracic cavity inside. Interesting knowledge The average person breathes in the equivalent of 13 pints of air each minute. People yawn because the brain detects low levels of oxygen in the lungs and triggers the response so the body will intake a large amount of oxygen. Hiccups are caused by several things, and are the product of spasms, or sudden movements, in the diaphragm. Eating too fast is one common cause of hiccups. Hiccups are sudden, involuntary contractions of the diaphragm muscle. As the muscle contracts repeatedly, the opening between your vocal cords snaps shut to check the inflow of air and makes the hiccup sound. Irritation of the nerves that extend from the neck to the chest can cause hiccups. ?Bourgeois Questions? • What does the respiratory system control? The respiratory system controls breathing. It also exchanges gases in your lungs and tissue. What is the main purpose of the respiratory system? The main purpose of the respiratory is supplies oxygen and carbon dioxide. What are the tiny hairs in your nose that warm and filter air called? the tiny hairs in your nose are called Cilia. What kind of respiratory diseases are there that are caused by smoking tobacco products? Lung cancer, and emphysema What is the process that brings oxygen into your body? Breathing is the process that brings oxygen into your body. What contains the vocal cords in your body? Your Larynx Where does air pass through to go to your lungs? It goes past the epiglottis. Wha t does the resp irato ry syst em cont rol? The resp irato ry syst em cont rols brea thing .It also exch ange s gase s in your lung s and tissu e. Wha t is the mai n purp ose of the resp irato ry syst em? The mai n purp ose of the resp irato ry is supp lies oxyg en and carb on dioxi de. Wha t are the tiny hair s in your nose that war m and filter air calle d? the tiny hair s in your nose are calle d Cilia . Wha t kind of resp irato ry dise ases Lung are canc ther er, e and that emp are hyse caus ma ed by smo king toba cco prod ucts ? Wha t is the proc ess that brin gs oxyg en into your body ? Brea thing is the proc ess that brin gs oxyg en into your body . Wha t cont ains the Your voca Lary l nx cord s in your body ? Whe re does air It pass goes thro past ugh the to go epigl to ottis. your lung s? In the diag ram belo w, Diagram of lung alveoli below. . Your everyday Respiratory Diseases • Asthma - constriction of hypersensitive airways; • Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) - lung disease causing shortness of breath; • Chronic Bronchitis - inflammation and permanent scarring of the bronchial tubes • Emphysema - damage to air sacs walls causing loss of elasticity; • Pleurisy - inflammation of the pleural membrane lining lungs and the chest cavity; • Lung Cancer - malignant tumors that develop in lung tissue • Acute Bronchitis-inflammation of the bronchial tubes; • Influenza - serious infection cause by the influenza virus; • Pneumonia - infection of the lungs caused by a virus or bacteria; • Sinusitis - inflammation of the sinus cavities; • Common Cold - infection caused by a virus; • Why Do I Yawn? When you are sleepy or drowsy the lungs do not take enough oxygen from the air. This causes a shortage of oxygen in our bodies. The brain senses this shortage of oxygen and sends a message that causes you to take a deep long breath---a YAWN. • Why Do I Sneeze? Sneezing is like a cough in the upper breathing passages. It is the body's way of removing an irritant from the sensitive mucous membranes of the nose. Many things can irritate the mucous membranes. Dust, pollen, pepper or even a cold blast of air are just some of the many things that may cause you to sneeze. • What Causes Hiccups? Hiccups are the sudden movements of the diaphragm. It is involuntary --- you have no control over hiccups, as you well know. There are many causes of hiccups. The diaphragm may get irritated, you may have eaten to fast, or maybe some substance in the blood could even have brought on the hiccups.