BIOTECHNOLOGY L.C. Syllabus
advertisement

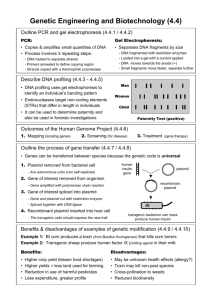
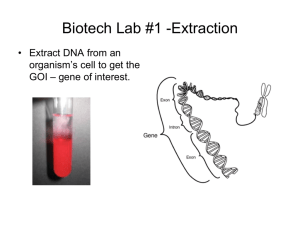
BIOTECHNOLOGY A. Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. B. Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: 1.inserting a foreign gene from one species into another, forming a transgenic organism 2.altering an existing gene so that its product is changed 3.changing gene expression so that it is translated more often or not at all. Humans are made up of trillions of cells Each cell: •46 human chromosomes •2 metres of DNA •3 billion DNA subunits (A,T,G,C) •Approximately 22,000 genes replication DNA genotype transcript RNA translation Protein phenotype A. It allows genes from one organism to be inserted into a cell of a different organism of a different species. • Examples: – Human genes can be inserted into a bacterium – Human genes can be inserted into cells from other animals – Bacterium genes can be inserted into plant cells 1. 2. 3. 4. Isolation-Isolate the gene Restriction- Cutting Transformation - Insert it in a host using a vector and produce as many copies of the host as possible Expression-Separate and purify the product of the gene E. coli bacterium Plasmid Bacterial chromosome 1 A cell with DNA containing the gene of interest 2 A plasmid is isolated. The cell’s DNA is isolated. Gene of interest 3 DNA The plasmid is cut with an enzyme. Examples of gene use 4 The cell’s DNA is cut with the same enzyme. Gene of interest 5 6 The targeted fragment and plasmid DNA are combined. DNA ligase is added, which joins the two DNA molecules. Examples of protein use Recombinant DNA plasmid Gene of interest 7 The recombinant plasmid is taken up by a bacterium through transformation. Recombinant bacterium 8 Clone of cells Genes may be inserted into other organisms. The bacterium reproduces. 9 Harvested proteins may be used directly. E. coli bacterium Bacterial chromosome A cell with DNA containing the gene of interest Plasmid 1 2 A plasmid is isolated. Gene of interest The cell’s DNA is isolated. DNA E. coli bacterium Bacterial chromosome A cell with DNA containing the gene of interest Plasmid 1 2 A plasmid is isolated. The cell’s DNA is isolated. Gene of interest 3 DNA The plasmid is cut with an enzyme. 4 The cell’s DNA is cut with the same enzyme. Gene of interest E. coli bacterium Bacterial chromosome A cell with DNA containing the gene of interest Plasmid 1 2 A plasmid is isolated. The cell’s DNA is isolated. Gene of interest 3 DNA The plasmid is cut with an enzyme. 4 The cell’s DNA is cut with the same enzyme. Gene of interest 5 The targeted fragment and plasmid DNA are combined. E. coli bacterium Bacterial chromosome A cell with DNA containing the gene of interest Plasmid 1 2 A plasmid is isolated. The cell’s DNA is isolated. Gene of interest 3 DNA The plasmid is cut with an enzyme. 4 The cell’s DNA is cut with the same enzyme. Gene of interest 5 6 Recombinant DNA plasmid The targeted fragment and plasmid DNA are combined. DNA ligase is added, which joins the two DNA molecules. Gene of interest Recombinant DNA plasmid Gene of interest 7 Recombinant bacterium The recombinant plasmid is taken up by a bacterium through transformation. Recombinant DNA plasmid Gene of interest 7 The recombinant plasmid is taken up by a bacterium through transformation. 8 The bacterium reproduces. Recombinant bacterium Clone of cells Genes may be inserted into other organisms. Recombinant DNA plasmid Gene of interest 7 The recombinant plasmid is taken up by a bacterium through transformation. Recombinant bacterium 8 Clone of cells The bacterium reproduces. 9 Harvested proteins may be used directly. (a) Isolation of a specific gene from donor e.g. human • Cells broken open • Genetic probe added • Reveals position of the gene of interest Genetic probe Position of gene of interest Donor DNA (b) Isolation of plasmid from a bacterial cell Bacterial cell Plasmid www.sci.sdsu.edu Restriction enzymes (also called endonuclease) act as molecular scissors and cut DNA at specific sites called restriction sites This makes a staggered cut with sticky ends ex: EcoRI Restri ction site Clipartguide.com Restriction site Restriction ezymes Restriction site Restriction site Donor DNA Restriction sites Restriction enzymes Plasmid Donor DNA Plasmid Sticky Ends Plasmid DNA with sticky ends Enzyme DNA ligase bonds sticky ends together A. Vector – molecule of DNA which is used to carry a foreign gene into a host cell ◦ Most common vectors are bacteria and viruses B. A vector has to have certain properties: 1. It is big enough to hold the gene we want 2. It is circular (or more accurately a closed loop), so that it is less likely to be broken down 3. It contains control sequences, such as a transcription promoter, so that the gene will be replicated or expressed. 4. It contain marker genes, so that cells containing the vector can be identified Enzyme DNA Ligase bonds sticky ends together Plasmid DNA Recombinant DNA Donor DNA Next slide for animation www.gch.ulaval.ca D. Recombinant DNA introduced into bacterial cell Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome Recombinant DNA Bacterial cell reproduces by Binary Fisson • Bacterial cell produces the polypeptide • Coded for by the donor DNA Donor DNA Plasmid 1. Cut with restriction enzymes Donor DNA Sticky Ends 2. Ligase bonds sticky ends together Recombinant DNA www.encarta.msn.com Genetically Engineered Products Insulin regulates the blood sugar level. The gene for human insulin is inserted into yeast or bacteria, from which large quantities of the human insulin are manufactured Production of humulin https://www2.vaxserve.com/ index.cfm?event=get... Undernourished people in poorer countries may have blindness caused by a lack of vitamin A Contains beta-carotene, which forms Vitamin A rBGH is a genetically engineered version of a hormone, which is found in the pituitary gland of cows and controls milk production http://www.healingdaily.com/detoxification-diet/rBGH. rBGH can increase cows’ milk production by as much as 20-30% http://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Milk_glass.jpg Elastic, light weight fiber 5 times stronger than steel One method involves inserting the gene from a weaving spider into a fertilized goat egg. The resultant “spider-goat” produces milk that can be manufactured into strong fibers. http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/spider/goat.jpg To make flak jackets, rope, textiles, sutures, artificial tendons, and bandages for burn victims Genes that make jellyfish glow are inserted into other organisms The organism glows under UV light Bt is a bacterial toxin that is toxic to some insects. In the lab, the gene that produces the toxic effect is inserted into the DNA of plants Bt crops produce an insecticide protein thousands of times more powerful than the chemical spray insecticides Genetically modified corn www.farmbureaulaporteco.org Can resist infection by an insect European corn borer Transgenic plants and farm animals pest-resistant (reduce use of pesticides), increase yield Increase storage time e.g. green tomato tomato with beef genes Clonal propagation: a source of tissue or organ for transplantation avoid all problems of immunoincompatibility. Gene therapy: Artificially replace the disease-causing gene with a normal allele. The normal allele can be carried by a virus vector to the target tissues. e.g. treatment of cystic fibrosis Production of pharmaceuticals for treatment of diseases e.g. human insulin, interferons Production of pharmaceuticals for disease prevention e.g. vaccine (hepatitis B vaccine) Use of GM microorganisms to make stonewash jeans Use of GM microorganisms to produce enzymes e.g. detergents GM E. coli possesses gene to break down cellulose, speeding up recycling of the most abundant biomass on earth GM microorganisms with enhanced ability to break down environmental pollutants Dangerous pathogens formed in the course New tools for militarists and terrorists Triggering of catastrophic ecological imbalance Moral problems in the use of GM techniques in man e.g. germ cell gene therapy Unknown effect of GM food on men Main concerns are in Genetically Modified Foods. Effects on Food Chains of genetically modified plants and animals. Also conflicts in relation to human cloning and stem cell research.