Chapter 5 Notes: The Structure of Matter
advertisement

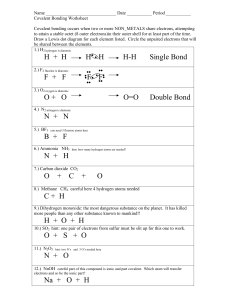
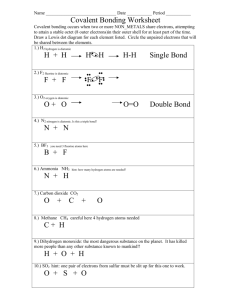
Integrated Science I When elements combine, new properties are formed! Ex) Sodium is a shiny, soft, slivery metal that reacts violently with water Ex) Chlorine is a poisonous greenish-yellow gas Together, they combine to make ordinary table salt Shows what elements are in a compound Shows the exact number of atoms of each element Subscripts (written below) = how many atoms of the element 0 has two hydrogen atoms for every 1 oxygen Ex) H2 atom Elements form compounds when the compound is more stable than the individual atom(s) Ex) Nobel Gases remain individual elements because they are already stable with full outer electron levels Ex) Other elements combine to fill their outer energy levels Atoms are chemically stable when their outer energy level is filled Atoms gain, lose, or share for a total of eight electrons in the outer energy level, this is called the octet rule. Two types of compounds: Ionic Covalent Ionic compounds are formed from the attraction of positive and negative ions. Positive ions are metals on the left side of periodic table Negative ions are gasses on the right side of periodic table Electrons are taken from another element to fill outer energy level (8 electrons needed) Ex) What does it look like when magnesium and chlorine bond? Mg +2 Step 1: Identify metal (with charge): ______________________ Cl -1 Step 2: Identify nonmetal (with charge): __________________ Use the crisscross method to balance charges. 2+ 1- Mg Cl Step 3: Write symbols & charges: ______________________ MgCl2 Step 4: Crisscross and change to subscript: ______________ ****always remember to reduce Ex) What does it look like when calcium and oxygen bond? Ca +2 Step 1: Identify metal (with charge): ______________________ O -2 Step 2: Identify nonmetal (with charge): __________________ Use the crisscross method to balance charges. 2+ O2Ca Step 3: Write symbols & charges: ______________________ CaO Step 4: Crisscross and change to subscript: ______________ ****always remember to reduce Formed between a metal and nonmetal Step 1: Write the full name of positive ion Step 2: Write the root name of negative ion Step 3: Add ending –ide to the end of negative ion Subscripts are not part of the name! Ex) Use your periodic table to write the name for the following binary ionic bonds: 1. NaCl Sodium Chloride ____________________________________ 2. BeO Beryllium Oxide ____________________________________ REMEMBER: Pure elements have equal numbers of protons and electrons Ex) Sodium has 11 protons (+) and 11 electrons (-) This makes its charge zero because the + and – balance In an ionic bond, an element loses or gains electrons from its outer energy level, which makes their charge unbalanced Ex) Sodium has 1 electron its outer energy level, which is lost when it bonds with chlorine. Now Sodium has 11 protons (+) and 10 electrons (-) This makes its charge 1+ because there are more + charges Ionic numbers follow trends/patterns like group numbers Metals lose electrons and become positive ions Gasses gain electrons and become negative ions Crystal lattice structure: alternating positive and negative ions in ionic compounds make a crystal lattice structure. These compounds are brittle solids. The smallest ratio of positive and negative ions make up the formula of the compound Covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons Formed between 2 nonmetals A molecule is formed from the sharing of electrons in a covalent bond Some can form more than one compound with each other Example: nitrogen and oxygen can form N2O NO NO2 N2O5 Use Greek prefixes for the first and second element Do NOT use prefix for first element if it is mono Ex) CO2 Carbon dioxide Ex) N2O4 Dinitrogen Tetraoxide Total Atoms 1 2 Prefix monodi- 3 4 5 tritetrapenta- 6 7 8 hexaheptaocta- N2O = Dinitrogen Monoxide __________________________ NO = Nitrogen Monoxide __________________________ NO2 = __________________________ Nitrogen Dioxide Dinitrogen Pentoxide N2O5 = __________________________ Ionic Covalent Electrons Gain/Lose to become neutral Share to become neutral State of Matter Solid Mostly Liquid Freezing Point High Low Boiling Point High Low Texture Sometimes brittle Often rubbery Solubility Most will dissolve in liquids Very few dissolve Conductivity High Low Composition Made from metal and nonmetal Made from two nonmetals (gasses) The Law of Conservation of mass and energy states that matter can never disappear! It simply changes forms If elements bond together, they do not disappear, they simply combine together to form a new substance! Balancing Chemical Equations Chemical Equations – A representative of a chemical reaction that uses symbols and formulas to show reactants and products Reactants = left side Products = right side Law of Conservation of Mass means amounts of products and reactants must be equal! Parts of a Chemical Equation Use coefficients to represent the number of units of each substance in a reaction (kind of like the number of ingredients in a recipe) Use subscripts to represent the number of atoms in a molecule of a particular element How to Balance Chemical Equations Choosing coefficients becomes easier with practice At first it is trial and error A four-step process: 1. Describe the reaction in words in your head 2. Write the equation using formulas and symbols if it is not already written that way 3. Check for balance with numbers under 4. Add coefficients where needed for balance Chemical Equation Practice #1 P + O2 P4O10 (Step 1: Find total atoms of P and O on each side) 4 ___ 1 P ___ ___ 2 O ___ 10 Now use coefficients to balance 5 2 ___P 4 + ___O 1 4O10 ___P 4 P ___ 4 ___ 10 O ___ ___ 10 Chemical Equation practice #2 Al2O3 Al + O2 Answer: 2Al2O3 4Al + 3O2 Chemical Equation Practice #3 BaCl2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + HCl Answer: BaCl2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + 2HCl How Can a Chemical Reaction Speed Up? Factors that cause chemical reactions to happen faster: High temperatures (think about mold) Large surface area because there are more particles that can react Concentration level High pressure Catalysts