CEA - Wayzata Public Schools

Unit 2 Terms & Definitions
Building Code
Legal requirements designed to protect the public by providing guidelines for structural, electrical, plumbing, and mechanical areas of a structure.
Compression Strength
The maximum compressive stress a material can withstand without failure.
Foundation
The lower part of a building, which transfers structural loads from the building to the soil.
Grading
The moving of soil to affect the elevation of land at a construction site.
Heat Loss
The energy needed to warm outside air leaking into a building through cracks around doors, windows, and other areas.
Insulation
Material used to restrict the flow of heat, cold, or sound from one surface to another.
Main
The principal pipe artery to which branches are connected.
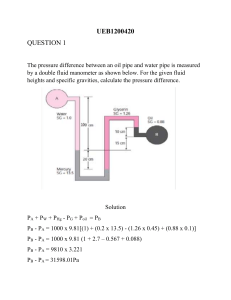
Pressure Head
The pressure of water at a given point in a pipe arising from the pressure in it.
R-Value
The numerical value used to indicate the resistance to the flow of heat.
Setback
Minimum distance that the zoning ordinance requires must be maintained between a structure and property lines or between two structures.
Solar Orientation
Consideration of the solar orientation of a building based on the relative position of the sun in order to purposely increase or decrease the amount of light or heat transferred to the building.
Static Head
Pressure of a fluid due to the head of fluid above some reference point.
Tensile Strength
The maximum stress a material subjected to a stretching load can withstand without tearing.
Thermal Conduction
The process of heat transfer through a solid by transmitting kinetic energy from one molecule to the next.
Thermal Convection
Heat transmission by the circulation of a liquid or a heated gas or air.
Truss
An assembly of structural members joined to form a rigid framework, usually connected to form triangles.
U-Factor
A measure of the heat transmission through a building part (as a wall or window) or a given thickness of a material (as insulation) with lower numbers indicating better insulating properties.
Valve
A fitting that is used to control the flow of fluid or gas.
Water Service
The pipe from the water main or other supply to the water-distributing pipes.