Population Dynamics
advertisement

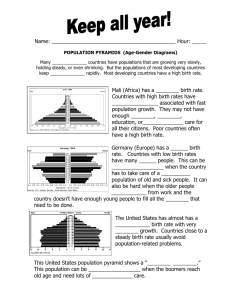
Population Dynamics EQ: How do populations interact with the environment? What is a population and how can it affect the ecosystem? What is a population? Populations are defined as • A group of individuals of the same species that live in the same geographic area at the same time. Characteristics of Populations • • • • Density Birth and death rates Growth rates Age structure Population density is defined as: • Number of individuals of a species within a given area • Usually referred to in terms of human populations – For example, Canada's population of 33 million, divided by the land area of 3,559,294 square miles • Can you do the math?? 9.17 people per square mile in Canada • However, population density also defines all species!!! Population Density How might population growth affect the density of a population? As population size increases, so does the population density. • As population size decreases, so does the population density. Biodiversity and Populations… • The variety of life on Earth, its biological diversity is commonly referred to as biodiversity. – The number of species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, the enormous diversity of genes in these species, the different ecosystems on the planet, such as deserts, rainforests and coral reefs are all part of a biologically diverse Earth. We will get more into Biodiversity and resources in the next unit… Why Is Biodiversity Important? • Biodiversity boosts ecosystem productivity where each species, no matter how small, all have an important role to play. • For example, – A larger number of plant species means a greater variety of crops – Greater species diversity ensures natural sustainability for all life forms – Healthy ecosystems can better withstand and recover from a variety of disasters, such as hurricanes. What is carrying capacity? • Carrying capacity refers to the largest population size a given environment can sustain/support. • What happened to the deer population between 1960 – 1966? What is growth rate? • Growth rate refers to how the population changes in size during a specific period of time. • Why might this graph show a decline in overall world growth rate by 2050? Types of Growth • Exponential Growth – when a population grows by a fixed percentage each year. Changes in the population size are noted by population growth curves. Types of Growth, cont • Fluctuating growth in Nature • Rise and crash growth ratepopulations grow rapidly and – fluctuates around carrying resources are used quickly, thus capacity. their populations crash. Or there is a sudden negative influence upon the population. Life history Patterns • Are developed when scientists study the factor that determines population growth – the reproductive pattern is called a life history pattern Rapid vs. Slow Life Histories Rapid • Are common among organisms from changeable or unpredictable envrionments Slow • Common among organisms that live in a more stable environment • Generally organims have a smaller body size, mature rapidly, reproduce early, and have a short life span • Larger body size, reproduce and mature slowly, and are long lived. Limiting factors to populations • A limiting factor is a biotic or abiotic factor that influences the survival rate (biotic potential) of populations. There are two types: – Density dependent – Density independent Density Dependent • Resources are dependent on how large the population is. In the graph to the left, moose and wolves are dependent on each other. As moose increase, so do wolves. However, if wolves decrease, what happens to moose? What other density dependent factors can you think of? Density Independent factors • Limiting factor whose influence is not affected by populations • If you look at the graph to the left, what caused the sudden decline in Aphid populations? When did this decline happen? • What other density independent factors can you think of? Book Work • P.99 Q’s 1-5 • Worksheet on Biomes Demography: the study of human population size, density, distribution, movement and growth rates EQ: How do humans affect the ecosystems? WARM UP: How do we study human populations and their affect on an ecosystem? A very brief activity… Human Population circle Population Circle Discussion • What did you observe about how our population changed over time? • How long did it take before the first person moved into the circle? • Towards the end of the simulation how long did it take to add 250 million people onto Earth? • What will happen if we continue to grow at this rate? Population Growth and The Distribution of Humans. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_9SutNmfFk • After watching the video – answer the questions. • 1. Around what year did you begin to notice an increase in population growth? • 2. What historical events, scientific advances or other changes may have contributed to a population increase? • 3. What historical events may have contributed to a population decrease? • 4. How might historical references help to explain changes and trends in population? Besides limiting factors, what else influences populations? • Birth rates • Death rates • Immigration or Emigration. (Do you know the difference?) • Migrations Birth Rates • Rate at which individuals are born is called natality. Death rates • Death rate is the rate at which individuals die which is called mortality. Immigration • Arrival of individuals from outside a given area. Emigration • A departure of individuals from a given area. The population of Ireland 1700-2000 numbers in millions Migrations • Seasonal movement into and out of an area. Paperclip Creatures. • You will get a container of 50 paperclips and a stop watch. • You will need to decide on the following: – You need two storks – You need two grim reapers • Count the total number of unconnected paperclips (if they are connected, unconnect them.) This number should be 0! • You will have 30 sec to connect as many paperclips as possible if you are a stork. However, the grim reaper will be unconnecting the paperclips as they are assembled. • Count the number of “living” paperclips (those that are together). Count the number of unconnected paper clips as well. • Repeat until you have completed 5 years total. Record your data. Paperclip Creatures. • We will tell you who is a stork and who is a grim reaper. Repeat the activity until you have completed 5 years total. Be sure to record all of your data. Paperclip Creatures. • Analysis Questions : 1. Make a graph of the total number of paperclip creatures versus the year for both runs. Put time on the x-axis. 2. Write a paragraph (3-5 sentences) that describes the relationship between time and population size. 3. What would your graph look like if there were more storks? Grim reapers? Explain your thinking. 4. How do births and deaths affect the size of a population? How do we calculate Population Growth? • Population growth is measured by Birthrate-deathrate= population growth. • A more complete growth model would include immigration and emigration, but these numbers are not always accurate. How do we calculate population growth rate? • Population growth is calculated using the following equation: • (Current year population-Previous year population)/previous year population x100 • For example the current deer population is 36, 10 years ago it was only 5. • 36-5= 31/5=6.2 x 100=620% Year National Population 2010 308,000,000 2000 281,000,000 1990 249,000,000 1980 227,000,000 1970 205,000,000 1960 181,000,000 1950 152,000,000 TRY IT! • (Current year populationPrevious year population)/previous year population x100 • Find the population growth rate between 1990 and 2000. 13% PGR • Then find the population growth rate between 2000 and 2010. 9.6% PGR Why might the population growth rate be lower between 2000-2010 than between 1990-2000? Warm UP: What are the characteristics that affect populations? Doubling Time • Is the time needed for a population to double in size. • Complete p. 102 Minilab Procedure and Q’s 1-2 from the book. Mini Lab Answers Data Graph Geographic Region Annual Percent of Growth Rate Doubling Time A B C D 2.4 1.7 1.4 0.5 29.2 41.2 50 140 E -0.1 Is decreasing and will not double 1. A; D 2. High potential for disease, problem with waste disposal, lack of space and/or water Age structures: refers to the proportions of the population that are in different age levels. Rapid Growth Age Structure • Rapidly growing countries have age structures with a wide base because a large percentage of the population is made up of children and teenagers. Slow Growth Age Structures • This age structure diagram predicts a slow but steady growth rate for the near future. Decline in Growth • This graph shows that the population is on the decline because there will be less people reproducing than people who have already reproduced. Age Structure Diagrams explained… • http://legacy.hopkinsville.kctcs.edu/Sitecore/instruc tors/JasonArnold/New%20VLI/Module%204/Mod4PartA/age_ structure_v2.swf WORK! • Be sure to turn in the paperclip creatures graph and analysis questions! • P. 103 Q’s 2-5 • Human Population worksheet