Digestive system
advertisement

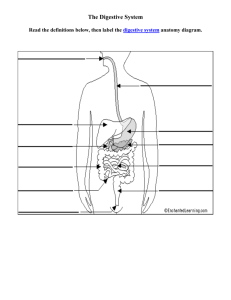
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Mechanical & Chemical breakdown of food Converts food into energy & nutrients to feed body Consists of the alimentary canal & the accessory organs ALIMENTARY CANAL Muscular tube about 8 meters long Passes through thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities ALIMENTARY CANAL Consists of : Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus ALIMENTARY CANAL WALL STRUCTURE 4 Layers Mucosa 1. Protects tissue beneath Submucosa 1. Nourishes surrounding tissues Muscular Layer 1.Provides movement of the tube Serosa 1. Outer covering of tube ACCESSORY ORGANS Includes Salivary glands Liver Gallbladder Pancreas MOUTH Begins digestion Mechanical digestion Receives food CHEEKS & LIPS Cheeks •associates with chewing and expression •Lateral walls of the mouth Lips •Skeletal muscle •Sensory receptors TONGUE Skeletal muscle Mixes food Taste buds to detect sensation Papillae provides friction Lingual tonsils Lingual frenulum PALATE Roof of oral cavity Hard palate Soft palate Uvula Palatine tonsils Pharyngeal tonsils TEETH Breakdown food mechanically Unique two structures -primary -secondary Types of teeth: -incisors -canines - pre molars - molars Enamel as protection SALIVARY GLANDS Secrete saliva Bicarbonate breaks down acid concentration 3 major glands - Parotid - submandibular - sublingual Salivary amylase Mucus PHARYNX Divided into 3 parts -Nasopharynx -Oropharynx -Laryngopharynx Important passageway Part of swallowing mechanism Move food to esophagus SWALLOWING MECHANISM ESOPHAGUS About 25 meters long Propels food from pharynx to stomach Descends from thorax to trachea Mucus glands moisten & lubricate Closes stomach entrance Prevents regurgitation STOMACH STOMACH Regions 1.Cardiac region 2.Fundus (Fundic) region 3.Body region 4.Pyloric (Antrum) region •Function: churn/mix food with gastric juices (segmentation), send chyme to small intestine GASTRIC ENZYMES Function of enzymes: Speed up breakdown of food molecules into their ‘building block’ components Reactions occur outside of cell lining the gut • Pepsin: degrades food proteins into peptides • Hydrochloric acid: break down foods and release enzymes to continue break down • Intrisic factor: important for absorption of vitamin B12 • Mucin: lubrication and signaling for cell barriers • Gastrin: aids in gastric motility • Rugae: Thick folds in the inner wall of the stomach that disappear when the stomach is destended REGULATION OF HORMONES IN THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM *Hormones reach target cells by the circulatory system Stimulating hormones of digestive process • Cholecystokinin (CCK) • Gastrin • Ghrelin • Secretin Inhibiting hormones of digestive process • Cholecystokinin (CCK) • Gastric inhibitory polypeptide • Enterogastrin • Secretin • Somatostatin STIMULATING HORMONES 1.Cholecystokinin: Site of production: Small intestine Mucosa Target Organ: Pancreas, Gallbladder, Hepatopancreatic Sphincter 2.Gastrin: Site of production: Stomach Mucosa Target Organ: Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine 3.Ghrelin: Site of production: Stomach Target Organ: Brain 4.Secretin: Site of production: Small Intestine Mucosa Target Organs: Pancreas, Liver INHIBITING HORMONES Cholecystokinin: Site of production: Small Intestine Mucosa Target Organ: Brain 2. Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide: Site of production: Small Intestine Mucosa Target Organ: Stomach 3. Enterogastrin: Site of production: Small Intestine Target Organ: Stomach 4. Secretin: Site of production: Small Intestine Mucosa Target Organ: Stomach 5. Somatostatin: Site of production: Stomach Mucosa, Small Intestine Mucosa Target Organ: Stomach, Pancreas, Small Intestine, Gall bladder 1. PANCREAS • Function: Secretes digestive juice, or pancreatic juice • Associated with small intestine • Located posterior to parietal peritoneum PANCREATIC DUCT Function: •Transports pancreatic juice to small intestine •Hepatopancreatic Ampulla •Hepatopancreatic Sphincter PANCREATIC JUICE •After food enters the duodenum the pancreas secretes pancreatic juice •Contains enzymes that break down foods •These enzymes digest carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids PANCREATIC ENZYMES Carbohydrate- digesting enzyme: Pancreatic Amylase: Splits molecules of starch or glycogen disaccharides Fat-digesting Enzyme: Pancreatic Lipase: Breaks triglyceride molecules into fatty acids & monoglycerides Protein-Splitting (Proteolytic) Enzymes: Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidase: Each split bonds between particular combinations of amino acids in proteins, Secreted in inactive forms, Must be activated by other enzymes REGULATION OF SECRETION • Nervous and endocrine systems regulate secretion of pancreatic juice • Stimulation of hormones: • Secretin • Cholecystokinin LIVER Functions: •Carbohydrate Metabolism •Produces bile which breaks down fats •Takes glucose and turns it into glycogen •Storage •Blood filtering •Detoxification GALLBLADDER Function: •Stores bile •Bile exits gallbladder and enters small intestine through the bile duct they share SMALL INTESTINE Tubular organ that extends from pyloric sphincter to large intestine Fills up most of abdominal cavity 5.5-6 meters long PARTS OF SMALL INTESTINE Duodenum -shortest & most fixed portion of small intestine -follows a C shaped path as it passes anterior to R kidney & 3 upper lumbar vertebrae Jejunum -Proximal two fifths of small intestine -diameter of the wall is thicker than ileum Ileum -remainder of small intestine -more lymph nodules -higher bacterial population WALLS OF SMALL INTESTINE WALL Inner wall has a velvety appearance Intestinal villi, most numerous in duodenum and proximal parts of the jejunum Increase surface area of the intestinal linin, aiding absorption of digestive product Villi absorbs the fluid that intestinal gland secrete ENZYMES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE peptidases- which breaks down peptides into amino acids Sucrose, Maltase & Lactase – breaks down disaccharides into monosaccharides glucose, fructose and glactose Intestinal lipase – breaks down fat into fatty acids & glycerol Enterokinase shortens trypsin Secretion is stimulated by gastric juice, chyre, and reflexes stimulated by expansion od the small intestine LARGE INTESTINE Diameter is greater than small intestine Begins in lower right side of the abdominal cavity the ileum joins cecum Function: absorbs water & electrolytes -forms and stores feces -secretes mucus PARTS OF LARGE INTESTINE Consists of cecum, colon, rectum & anal canal Cecum: - beginning, pouch like -vermiform appendix is the worm like narrow tube that closes the end (unknown digestion function) Colon: - Ascending colon – begins at cecum & extends to posterior abdominal wall to piny inferior to the liver - Transverse colon – longest and most moveable - sags un the middle below stomach CONTINUED - Descending Colon: - Passes to left abdominal cavity to the brim of the pelivis -Sigmoid Colon: - S shaped part, descends from colon to rectum -walls lack villi & plicae circularis - longitudeinal muscle fibers don’t cover the wall -small collections of fat in serosa on outer surface - movements are similar to small intestine but slower - peristaltic waves occur only 2 or 3 times a day - waves produce mass movements which large secretion of wall constricts inside to move toward rectum RECTUM Firmly attached to sacrum by peritoneum Ends about 5 cm inferior to tip of coccyx Regulates elimination of feces ANAL CANAL Formed by last 2.5 – 4 cm of large intestine Mucus membrane in canal folded in series of 6-8 longitudinal canals Distal ends of canal opens to the outside as the anus 2 sphincter muscles guard the anus Internal anal sphinter muscles, involuntary control, smooth muscle External anal sphinter muscle, skeletal muscle voluntary control DIGESTION VIDEO WORKS CITED • bioserv. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <http://bioserv.fiu.edu/~walterm/FallSpring/digest_nutrition/digestlect.htm>. • Blue Study. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <https://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/an2-16-perineum/deck/11438928>. • "Digestive System: Physiology." kctc.edu. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <http://legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat2/notes/APIINotes8%20Digestive% 20Physiology.htm>. • Dreams time. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <http://www.dreamstime.com/royaltyfree-stock-image-large-intestine-3d-image22102016>. • "Human Digestive System." Youtube. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b20VRR9C37Q>. • Johns Hopkins. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <http://www.hopkinscf.org/what-iscf/basic-science/gastrointestinal-tract-problems/what-enzymes-do/>. • Boundless. “Hormones of the Digestive System.” Boundless Anatomy and Physiology. Boundless, 06 Feb. 2015. Retrieved 12 Feb. 2015 from <https://www.boundless.com/physiology/textbooks/boundless-anatomy-andphysiology-textbook/the-digestive-system-23/phases-of-digestion-226/hormones-ofthe-digestive-system-1110-6772/> • Sutter Health. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015. <http://www.cpmc.org/advanced/lapsurg/surgery/procedures/gallbladder.html>. Wiki Books. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Feb. 2015.