Study of Networks and Services A Vision for the Portuguese
advertisement

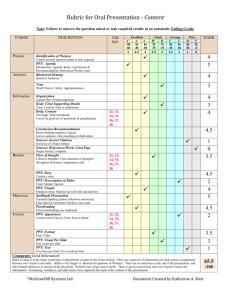
Study of Networks and Services A Vision for the Portuguese Telecommunications Industry in the 21st Century Summary of Conclusions Presentation to: APDC Arthur D. Little International, Inc. Av. Liberdade 200 4° Andar 1250 Lisboa March 16, 1999 Reference MPrSF01449 Study of Networks and Services 1 - Current Situation 2 - Future Directions 3 - Implications SUMAPDC.PPT 2 Current Situation Main Lines Evolution Telecommunications networks in Portugal have expanded significantly in recent years... Main Lines per 100 Inhabitants 70 Rest of Europe* Average of Western Europe 60 France Germany 50 U.K. Italy 40 30 Portugal Spain 20 10 0 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 *Rest of Europe includes Benelux, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Greece, and Ireland. Source: ITU Indicators Database, August 1998. SUMAPDC.PPT 3 Current Situation Cellular Penetration vs. Growth … although following distinct patterns for fixed, mobile and cable. Example: Cellular Penetration vs. Growth 25 1997 Cellular Subscribers per 100 Inhabitants Rest of Europe Italy 20 Average of WE Portugal UK 15 Spain 10 France Germany 5 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 1990-1997 Cellular Subscribers CAGR *Rest of Europe includes Benelux, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Greece, and Ireland. Source: ITU Indicators Database, August 1998, Arthur D. Little analysis SUMAPDC.PPT 4 Current Situation PC Penetration Evolution Portugal has traditionally spent less than the average of Western Europe on Information Technologies. Personal Computers per 100 Inhabitants Evolution 30 U.K. 25 Rest of Europe* 20 Average of Western Europe 15 France Germany Spain 10 5 Italy Portugal 0 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 *Rest of Europe includes Benelux, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Greece, and Ireland. Source: ITU Indicators Database, August 1998. SUMAPDC.PPT 5 Current Situation PC and Internet Penetration Constrained by low PC penetration, Internet penetration in Portugal remains low. 1997 Personal Computers and Internet Users Penetration per 100 Inhabitants 26% Germany 5% 24% United Kingdom France 7% 17% 2% 11% Italy Spain Portugal Personal Computer 2% 12% 2% 7% 2% 26% Rest of Europe* Average of Western Europe Internet users 8% 22% 6% *Rest of Europe includes Benelux, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Greece, and Ireland. Source: ITU Indicators Database, August 1998; IDC - The European Internet Access Market 1998 SUMAPDC.PPT 6 Current Situation Software Market Software development is an important piece of the content industry, yet to be further developed in Portugal. Software Market Growth Software Market as % of GDP 21000 0.9% Germany 7100 0.6% 12700 1.1% United Kingdom 6300 14100 0.9% 0.9% France 6500 0.7% 1995 7400 1987 3700 2800 1300 Italy 0.5% 0.4% 0.3% 0.3% Portugal 1800 698 10000 0.9% Average of Western Europe 8600 5000 0.6% Rest of Europe* 3700 15000 20000 Million dollars 1987 0.5% Spain 300 100 0 1995 0.7% 0.9% 0.7% 0 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 1.5 Percentage *Rest of Europe includes Benelux, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Greece, and Ireland. Source: OECD, The Software Sector: A statistical profile for selected OECD countries, January 1998. SUMAPDC.PPT 7 Current Situation Telecom and IT Expenditures Balance There is an unbalanced distribution of IT versus telecom investments in Portugal, resulting in the deployment of networks that have not fully realized their potential. 4 Greece Portugal 3 Preponderance of Telecom Telecom Expenditures 2 IT Expenditures Spain Ireland Italy Equilibrium IT = Telecom Germany U.K. 1 France Belgium Netherlands Preponderance of IT Luxembourg Denmark U.S. • Increased penetration of Telecom cannot compensate for lower IT investments • Balanced Telecom and IT penetration is pathway to development of information society 0 3 4 5 6 Telecom and IT Expenditures (% GDP) Sources: EITO, 1997, ITU Indicators Database, August 1998, Arthur D. Little analysis. SUMAPDC.PPT 8 Study of Networks and Services 1 - Current Situation 2 - Future Directions 3 - Implications SUMAPDC.PPT 9 Future Directions Complexity With the advent of convergence, the telecom environment has become highly complex. Internet Backbone NSPs/NAPs AT&T Network Controls WorldCom (ISP) @Home (high-speed Internet) Controls Twisted pair Coax TCI America Online (cable operator) Regional Bell Co. (phone operator) TV PC Example: AT&T - TCI buyout SUMAPDC.PPT 10 Current Situation Local Loop Technologies A rich local loop environment will prevail in the future, and no single technology will prevail. Local Loop Technologies LMDS Wideband WLL D: downstream U: upstream Source: Contactica SUMAPDC.PPT 11 Future Directions Industry Opportunities Digitization has enabled vertical disintegration of hardware, software and services industry layers and created opportunities for new and unexpected players to participate in these markets. New Player Strategies (examples) A Satellite Cable Terrestrial Terminal Consumer Transport Hardware and Software Vendors Advertising and Transactions Back-End Services Traditional broadcasters and new entrants Production Multimedia Industry Value Chain Aggregation and branding Content Provision A • Repositioning (e.g. ISP) A A • Straddling (e.g. Cable MSO) A B C • Alliance (e.g.: BIB BSkyB, Matsushita, BT) SUMAPDC.PPT 12 Future Directions New Application Services Arthur D. Little used its vision of the future to articulate over 90 new applications and associated tangible products and services. Conceptual The Global Information Society 2010 VISION Digital Economy THEMES APPLICATION CONCEPTS E-Commerce Online Banking Cyber Collaboration APPLICATIONS Online Grocery Shopping ... ... ... ... PRODUCTS Concrete Data Mining Delivery Service Cyber Community Smart Home Multimedia Entertainment Telegovernment Virtual Hospital Remote Education Infomated Individual Home Automation Information Appliances Life Management Integrated Communications Personal Safety ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Home Terminal Electronic Bodyguard Sensors Alarm ... SUMAPDC.PPT 13 Base Station Future Directions Promising New Applications Also in Portugal, market forces will tend to promote applications such as e-commerce and online gaming first. Exercise Results - Application Ranking 4 Applications A Online shopping mall Application Attractiveness (Value to Stakeholders) B Online financial advisor C Online interactive game-play 3 2 E Online grocer –Remote Education Health care-at-home 1 2 3 4 •Other H Entertainment planning –Online Interactive Game Play I Home control system –Online Financial Advisor J Personal information management –Telework K Contact assistance 0 •Public Interest –Telemedicine G Virtual classes 0 •Electronic Commerce D Universal mailbox F 1 Selected Applications L Electronic guardian angel Application Feasibility (Infrastructure, regulatory and socio-economic condition) Other application services such as remote education and telemedicine may bring significant value to society, but not necessarily be commercially attractive, thus requiring Government action. SUMAPDC.PPT 14 Future Directions Application Roadmaps The birth of new applications depends on advancements of content, transport, back-end services and terminal industries, and also on regulatory, socio-economic and value to stakeholder conditions. Milestone 1 Milestone 2 Content 2000 2004 Transport 2005 2001 2010 Application X 2003 2008 2001 2005 ... 2004 Regulatory and socioeconomic Milestone N Milestone N Milestone N Technology Roadmap for Each Application It is very important to recognize that all value chain elements must now be analyzed together as a whole. SUMAPDC.PPT 15 Study of Networks and Services 1 - Current Situation 2 - Future Directions 3 - Implications SUMAPDC.PPT 16 Implications Supply and Demand Drivers Focus should be maintained on providing the conditions to promoting the best environment for application development in Portugal. Demand Drivers Supply Drivers Competitiveness Macro Economic Environment Established Industry Understanding and Acceptance of Society Compelling Applications at Competitive Prices Strong Application Demand Strong Application Supply Willingness and Ability to Invest Access to Skills Access to Skills Access to advanced infrastructure Role of Government Effective Regulatory and Legislative Environment Effective Government Initiatives Source: Spectrum, adapted. SUMAPDC.PPT 17 Implications Infrastructure Investment The cumulative investment between 1998 and 2010 for narrowband and broadband infrastructure development will probably exceed U.S. $12.7 billion(1). Total Cumulative Infrastructure Investment $ 14 Total $12.7 billion 12 Narrowband $11.6 billion U.S. $ Billions 10 8 6 4 2 Broadband $1.1 billion 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 1 According to the assumptions of the Gradual Evolution scenario SUMAPDC.PPT 18 Implications Job Creation As a consequence of telecoms liberalization, new jobs will be created. Effects on Portuguese Employment of the Liberalization of the Telecom Sector Number of Jobs (thousands) 50,000 40,000 Breakdown of Total Jobs Created 50,000 Rapid liberalization, rapid introduction of new technologies 30,000 41,900 41,900 40,000 Total Jobs Created 35,100 35,100 30,000 28,300 28,300 27,930 20,000 23,639 25,900 23,870 20,000 Slow liberalization, slow introduction of new technologies 21,200 Within the Telecom Sector 10,000 10,000 0 0 1993 2000 2005 25,000 23,639 2010 7,100 23,100 16,900 12,000 Outside the Telecom Sector 0 1993 2000 2005 2010 Sources: Effects on Employment of the Liberalization of the Telecommunications Sector; EC; BIPE Counseil, January 1997; Arthur D. Little analysis. SUMAPDC.PPT 19 Implications Reinforcing Circle The goal is to promote in Portugal a reinforcing circle that links new investments, the development of skills and infrastructure, increased adoption rates for new services and the achievement of practical results. Skills generates promotes Infrastructure Adoption of new services Investment Reinforcing Circle promotes Results generates Promoting consistent Government programs and fostering smaller, entrepreneurial experiences is key to promote the reinforcing circle. SUMAPDC.PPT 20