Exploring Green Careers
advertisement

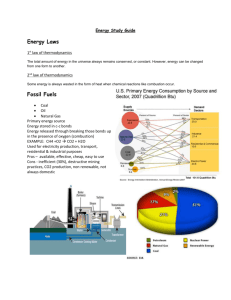
Exploring Green Careers Presentation Developed by: Ms. Maribel Morales & Dr. Emma Garcia-Salas HYDROPOWER Hydropower is energy extracted from moving water. More than 200 years ago, Greeks used falling water to power grinding wheels and in the 1700’s it was used extensively in the industrial revolution to power mills and pumps. Nowadays, power is normally produced by using falling water to power electrical turbines. HYDROPOWER Generating electricity using water has several advantages. The major advantage is that water is a source of cheap power and requires no imported fuel. Also, because there is no fuel combustion, there is little air pollution in comparison with fossil fuel plants. GEOTHERMAL Geothermal heat is the heat that comes from the earth’s core; which is always trying to radiate outward. This clean and sustainable form of energy is a result of been brewing for over 4 billion years. Temperatures may reach over 9, 000 degrees Fahrenheit. GEOTHERMAL In order to harness geothermal energy, geothermal energy technology is used to conduct this radiated heat through various layers to serve our energy consumption. Heat is conducted through the various layers of the Geothermal energy technology that is based upon our ability to utilize this radiating heat to serve our energy consumption. GEOTHERMAL Geothermal energy technologies rely on tapping the heat within the earth itself. Geothermal technologies capture solar energy directly or indirectly so that the heat energy taken from the earth is not apparently replenished. DEVELOPMENT OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY First Geothermal Electricity commercialization conversion of highgrade hydrothermal resources to electricity began in Italy in the early 1900s. The first commercial-scale development tools were placed at the Geysers in California, in 1960. A 10-megawaatt unit owned by Pacific Gas & Electric. ARE YOU READY FOR THE JOBS OF THE FUTURE? There are so many ways to join the green economy. One way is to switch over your current knowledge to an industry that is in demand. Geothermal Installer Geothermal installers are in demand. Even in a down economy, companies are making big profits and looking for more installers all the time. Geothermal installers do quite a bit. Many times installers are the small business owners. They have to deal with all that is involved in keeping the business running. Geothermal Operations Engineer Choosing to be a Geothermal Operations Engineer may provide great opportunity in the near future. While the renewable energy field is experiencing massive growth, geothermal plants may experience even faster growth than other renewable energy plants. This would create a demand for workers in the geothermal field, engineers included. SOLAR Solar energy provides a sustainable, renewable and clean source of energy. It conserves natural resources by considerably reducing fossil fuel dependence, greenhouse gas emissions and peak time grid constraints. Sustainable Solutions Solar has grown rapidly, achieving an average annual growth of 25% or more over the past couple decades. First: Solar produces sustainable solar energy solutions that protect our environment and conserve our natural resources Residential Solutions Solar modules will be available for residential solutions beginning in 2009 through SolarCity, a leading residential and small commercial solar power and solar leasing company in the United States. Commercial Power Solutions Solar solutions are sold to system integrators, independent power project developers, and utility companies for commercial, grid-connected solar power plant applications. SOLAR JOBS Solar Operations Engineer A Solar Operations Engineer is essentially an architect of new solar energy facilities. They design new solar systems, supervise and inspect the structures during construction, then test and monitor the new facilities. Solar Operations Engineers are generally considered to be experts on solar energy technology. They help develop new technologies, and adapt existing solar technologies to new, different circumstances. Solar & PV Installer-Roofer These are the people who install electricityproducing photovoltaic (PV) solar panels into the roofs of residential and commercial homes and buildings. Qualified, experienced Solar & PV InstallerRoofers are hard to find, even in today's growing "green" technology economy. This is because, in addition to having the skills and construction experience of a roof, Solar & PV Installer-Roofers must also have a working knowledge of solar electronics. Get Into the Solar Sales Career Solar sales agents are responsible in selling and marketing PV systems to residents everywhere. PV, which stands for Photovoltaic, is one of the industries in the green collar jobs market. When planning to step into the solar sales career, however, certain requirements and credentials should be met. Get Into the Solar Sales Career A person with knowledge and skills in sales would be perfect for this job. Mainly, because sales talking is not that simple - you have to know what you are selling and how to convince people that these products are of a new wave industry that is changing a global perspective. A person with the gift of gab and a nice personality and of course, well grounded on the science of solar power can easily cinch a sale. HYDROGEN Hydrogen is the most plentiful element not only on Earth but also in the universe, accounting for 90 % of the universe by weight. HYDROGEN The great attraction of hydrogen is that, once isolated, it is a clean burning fuel that produces neither carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) nor toxic emissions and can be used for electricity production, transportation and other energy needs. Hydrogen Jobs hydrogen plant is a type of gas plant. Gas plants take gasses and turn them into a useable form. Many of these plants liquefy gasses such as hydrogen and oxygen and also purify them so that they can be used as fuels. The career outlook for a hydrogen plant operator & operations manager is good. They make on average $17-$21 an hour Operations Manager To become an Operations Manager at a hydrogen plant, you will need to have at least a Bachelor's degree in Engineering. Thankfully, engineering degrees are offered at most colleges, so it shouldn't be difficult to get one. While you are in college, some recommended coursework includes chemistry and alternative energies. Operations Manager Working in a hydrogen plant as an operations manager is a job that requires great attention to detail. There are a great many systems to be monitored, valves that need to be opened and closed in the proper sequence, and forms and charts that need to be filled out daily. Pressure and moisture content of the hydrogen will also need to be checked at certain stages. Being reliable and able to work without supervision is critical to this line of work. An Operations Manager has many things that they have to do on time every day to keep problems from developing.