lab sheet
advertisement
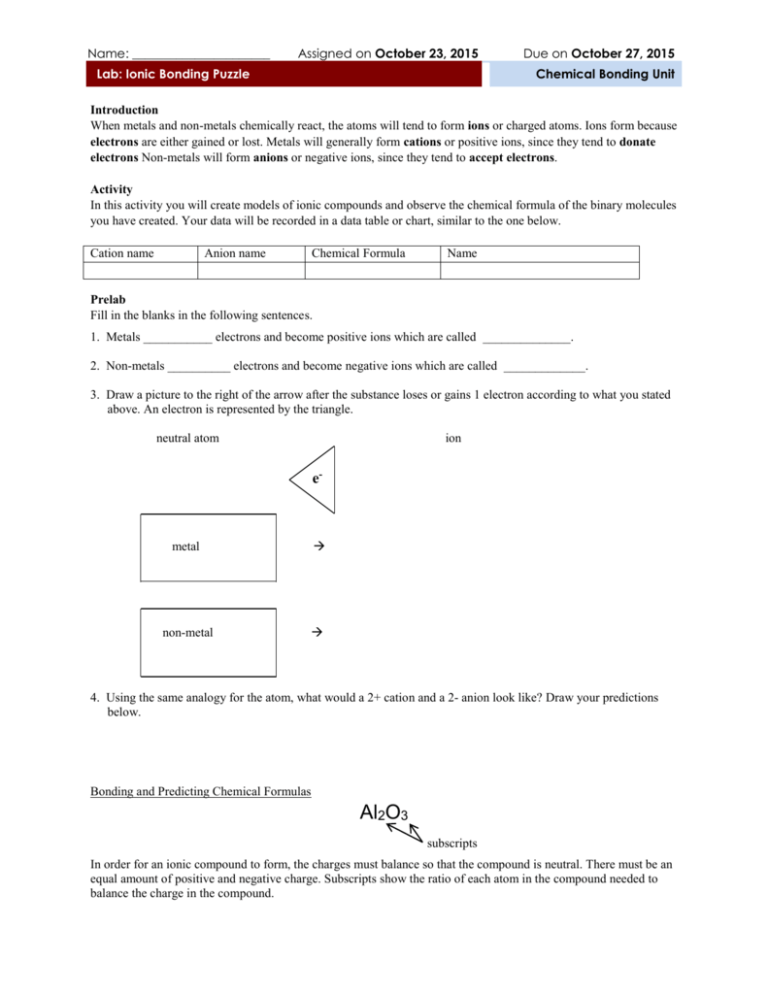
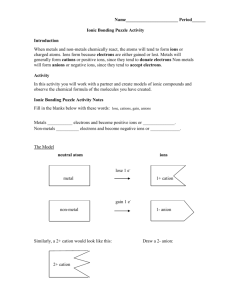
Name: ______________________ Assigned on October 23, 2015 Lab: Ionic Bonding Puzzle Due on October 27, 2015 Chemical Bonding Unit Introduction When metals and non-metals chemically react, the atoms will tend to form ions or charged atoms. Ions form because electrons are either gained or lost. Metals will generally form cations or positive ions, since they tend to donate electrons Non-metals will form anions or negative ions, since they tend to accept electrons. Activity In this activity you will create models of ionic compounds and observe the chemical formula of the binary molecules you have created. Your data will be recorded in a data table or chart, similar to the one below. Cation name Anion name Chemical Formula Name Prelab Fill in the blanks in the following sentences. 1. Metals ___________ electrons and become positive ions which are called ______________. 2. Non-metals __________ electrons and become negative ions which are called _____________. 3. Draw a picture to the right of the arrow after the substance loses or gains 1 electron according to what you stated above. An electron is represented by the triangle. neutral atom ion e- metal non-metal 4. Using the same analogy for the atom, what would a 2+ cation and a 2- anion look like? Draw your predictions below. Bonding and Predicting Chemical Formulas Al2O3 subscripts In order for an ionic compound to form, the charges must balance so that the compound is neutral. There must be an equal amount of positive and negative charge. Subscripts show the ratio of each atom in the compound needed to balance the charge in the compound. In what ratio will the 1+ and 1- ions combine to balance the charge? Draw the combination to the right of the arrow. 1+ + 1- What ratio do the +2 and -1 ions need to combine to balance the charge? Draw your result to the right of the arrow. 2+ + 1- Data Table Cation name Anion name Chemical Formula Name Conclusion Questions 1. Notice the shape and charge of each cation model. Why do you think there are slots in the metal atoms? (TIP: How do the atoms become ions?) _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Notice the shape and charge of the anion models. Why do you think there are tabs in the non-metal atoms? _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. If you were to make a neutral atom following the model, what would the shape be? Draw an example below. 4. Group the ion models by family. What do you notice about the number of tabs or slots? What do you notice about the tabs or slots and charge of all ions? Is there a pattern? Why do you think the model is made that way? _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What do you notice about the names of the cations and anions on the cards? How do they compare with the name of the neutral atom or element? Specifically, do the non-metals have anything in common about their name? _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ F1fluoride Na1+ sodium Mg2+ magnesium Al3+ aluminum F1fluoride K1+ potassium Cl1chloride K1+ potassium N3nitride Mg2+ magnesium Cl1chloride Al3+ aluminum K1+ potassium P3phosphide Br-1bromide Ca2+ calcium Br1bromide Cs1+ cesium 1+ cation wildcard 1- anion wildcard Ba2+ barium Li1+ lithium 2+ cation wildcard 3- anion wildcard S2sulfide Ca2+ calcium 1+ cation wildcard O2oxide Ca2+ calcium Li1+ lithium I1iodide Pb4+ lead Ba2+ barium O2Oxide 2- anion wildcard Na1+ sodium I1Iodide Al3+ aluminum