Durable Competitive Advantages: Using
Economic Moats to Improve Investment Returns
×
Pat Dorsey, CFA
Director of Equity Research
© 2008 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved.
<#>
Agenda
×Our
Approach to Competitive Analysis
× What is an Economic Moat
× What’s Not
×Where
×Why
Morningstar Finds Moats
Moats Matter
×Using
Economic Moats in the Investment Process
2
What’s A Moat?
× Capital
seeks the areas of highest potential return, so all firms face
competition that seeks to force down high returns on capital.
× But some firms generate high returns for a very long time.
× How? By creating economic moats around their businesses.
× An
economic moat is a structural business characteristic that allows
a firm to generate excess economic returns for an extended period.
× Note that “structural” means “inherent to the business.”
× Smart managers and great execution are important, but
they’re not structural attributes.
3
What’s a Moat?
The
key to having an economic moat is the sustainability of excess
returns, rather than the absolute level of return on capital.
A company with 40% returns on invested capital (ROIC) due
to a hot product has no moat. The returns cannot be
forecasted with any level of confidence.
Fashion stocks (Crocs, Heelys), Motorola Razr
A company with 12% ROIC – and a low cost of capital – that
is structurally protected from the competition may have a
wide economic moat, because we can forecast those returns
with a high degree of confidence.
Pipelines, Railroads
4
Sources of Economic Moats
× Intangible
Assets
× Brands
× Patents
× Approvals & Licenses
× Customer
× The
Switching Costs
Network Effect
× Cost
Advantages
× Process
× Location
× Unique Assets
× Scale
5
Sources of Economic Moats
× Intangible
assets
× Brands: Does it increase the consumer’s willingness to pay,
or reduce search costs?
× Sony
vs. Tiffany
× Doublemint & Juicy Fruit
× Patents: Valuable, but subject to expiration & challenge.
× Big
pharma vs specialty pharma
× Licenses & Government Approvals.
× Waste haulers, aggregate companies
6
Sources of Economic Moats
×Switching Costs: Do the costs – in time or money – of switching to
a competing product/service outweigh the benefits?
× Monetary/Labor Costs
-Oracle
-Autodesk
-Data processors
× Low or uncertain benefits from switching
-Amazon
-Asset managers
7
Sources of Economic Moats
× The
Network Effect – One of the most powerful types of competitive
advantage, which occurs when the value of a good or service
increases with the number of users.
× Examples
×
×
×
×
×
of the Network Effect
eBay
Western Union
MasterCard, American Express, Discover, Visa
Microsoft
Financial Exchanges
8
Sources of Economic Moats
× Cost
Advantages – Not necessarily tied to size
× Process – Invent a cheaper way of delivering a good or service
that rivals cannot (or will not) replicate. Dell, Nucor, Steel
Dynamics, Southwest/other LCCs.
× Low-cost resource base – Ultra Petroleum, Compass Minerals.
× Scale
-Distribution – Stericycle, Cintas, Sysco, UPS
-Manufacturing – Intel
-Niche Markets/Single-Scale Efficiency – Graco, Blackbaud
9
What’s Not An Economic Moat
× Size
/ Dominant Market Share: High market share does not give a
firm a moat. (Ask Compaq – or GM.) In fact, market share may be
irrelevant – bigger is not necessarily better.
× Technology:
What one smart engineer can invent, another can
improve upon. (Exception: Creating a standard that’s widely adopted.)
× Easily-replicable
× Hot
cost advantages (lean manufacturing, outsourcing.)
Products: Krispy Kreme, Tommy Hilfiger, Crocs, Iomega, etc.
× Can generate high returns on capital for a short period of
time, but sustainable returns are what make a moat.
10
What’s Not An Economic Moat
× Management:
Smart managers may create a moat over time, but
great management is not a moat by itself.
× "Go
for a business that any idiot can run – because sooner or
later, any idiot probably is going to run it." – Peter Lynch
× “When
management with a reputation for brilliance tackles a
business with a reputation for poor economics, it is the
reputation of the business that remains intact.” – Buffett
× Management
matters, but moats matter more.
11
Where Morningstar Finds Economic Moats
× Three
groups: Wide, Narrow, and None.
× Wide
moats are tough to find. Less than 10% of the 2100 companies
that we follow have wide economic moats. (169, to be precise.)
× Moats
vary by sector & industry.
× Fewer moats in highly commoditized or competitive sectors
like computer hardware, consumer services
(retail/restaurants), or industrial materials. Only 1/3 of the
companies in these three sectors are wide/narrow moat.
× More moats in areas with high switching costs (data
processors) and durable brands (consumer products),
12
Why Moats Matter
× Moats
add intrinsic value!
×A
company that is likely to compound cash flow internally for many
years is worth more today than a company which isn’t.
Time Horizon
No Economic Moat
ROIC
Narrow Economic Moat
ROIC
ROIC
Wide Economic Moat
Time Horizon
Time Horizon
13
Why Moats Matter
× When
comparing two companies with similar growth rates, returns
on capital, and reinvestment needs, the company with the moat has a
higher intrinsic value.
× Underestimating
a moat results in opportunity cost, while
overestimating a moat can cause you to pay for value creation which
never materializes.
× Some
fast-growing companies are worth the premium, because the
excess returns are more likely to persist. If a firm has a wide moat
that will allow it to reinvest cash flow at a high rate of return for many
years, what looks expensive may actually be quite a bargain.
14
Why Moats Matter
“Time is the friend of the wonderful business, affording it the
opportunity to reinvest incremental capital at favorable rates and increase
the value of the enterprise. Over time, the price you paid for a terrific
company looks cheaper and cheaper. For the inferior business at the cheap
price, time may turn out to be the fell destroyer.“
– Bob Goldfarb, Sequoia Fund
15
Why Moats Matter
×Moats
enforce investment discipline.
× High returns on capital will always be competed away –
eventually.
× For most companies (and their investors), the regression to
the mean is fast and painful.
× But a few generate excess returns for many years, and moats
give us an analytical framework for selecting them.
16
Why Moats Matter
×Companies
with moats have greater resilience.
× If a firm can fall back on a structural competitive advantage,
it’s more likely to recover from temporary troubles.
× This is a great psychological backstop for the investor who’s
buying when everyone else is screaming “sell!”
× If you’re confident in the moat, it’s easier to average down if
you initiate a position too early.
17
Isn’t the Moat Already Priced In?
×Short
answer: Sometimes, but less frequently than you might think.
×Long
answer:
× Most market participants own securities for short time
periods, and moats matter much more in the long run than
over the short term. (Time-horizon arbitrage.)
× Recency bias causes most investors to assume that the
current state of the world (good or bad) persists for longer
than it usually does.
× Our performance record suggests that waiting for wide
moats to become cheap is a compelling strategy.
18
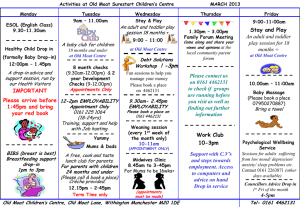
Wide + Cheap
×The
Wide Moat Focus is an index of our 20 most undervalued widemoat stocks. Holdings are equally-weighted and rebalanced quarterly.
YTD
Trailing
1-Year
Trailing
3-Year*
Trailing
5-Year*
Morningstar Wide Moat Focus
Index (ETN Ticker: WMW)
41.6%
9.3%
6.0%
9.0%
S&P 500 Index
20.5%
-9.1%
-4.8%
1.0%
Returns through 9/18/2009
* Annualized returns
Source: Morningstar
More on Moats
× Competitive
× The
Strategy, by Michael Porter (Free Press, 1998)
Essays of Warren Buffett, compiled by Lawrence Cunningham (John
Wiley, 2002) .
× Berkshire letters are also free at www.berkshirehathaway.com
× Competition
× Annual
× The
Demystified, by Bruce Greenwald (Penguin, 2005)
Reports – The more, the better. Build that mental database!
Halo Effect, by Phil Rosenzweig (Free Press, 2007)
20
More on Moats
× The
Little Book that Builds Wealth, by Pat Dorsey (John Wiley, 2008)
21
Contact Information
×Patrick
Dorsey
Director of Research
Morningstar, Inc.
+1 312.696.6560
patrick.dorsey@morningstar.com
© 2008 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved.
<#>
Durable Competitive Advantages: Using
Economic Moats to Improve Investment Returns
×
Pat Dorsey, CFA
Director of Equity Research
© 2008 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved.
<#>