Islam - KCSD Connect

Islam
Green Textbook Questions/Answers
Page 231-234
• Arabia
What is the birthplace of Islam?
Foundations of Islam
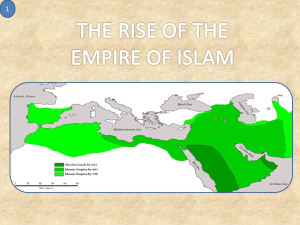
• Islam began in the 7 th century (600 CE)
• 600s: Conquered Persia, weakened Byzantine Empire, and converted most of the Middle East
• 700s: Muslims controlled Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Egypt, much of
North Africa, Spain, parts of Italy, Central Asia, and modern Pakistan
How did Muhammad become Allah’s prophet?
• Troubled by violence and treachery
• Often prayed in desert
• Angel Gabriel spoke to him, saying god had chosen him to be his prophet.
• Duty was to proclaim Allah as the 1 and only god.
• Eventually, Muhammad destroys idols in the Kaaba, but leaves the black stone.
What is the Significance of Mecca & the Kaaba?
• Muhammad was born in Mecca (holy city).
• Muslims go on hajj.
• Sacred Shrine
• Originally housed images of all the Arab gods
• Houses black stone (possibly a meteorite that
Arabs believe was sent from heaven to show
Adam and Eve where to build an alter.)
What does the inside of the Kaaba look like?
• For years many have wondered what it looks like inside the Kaaba.
Relying on second or third hand accounts from those who were lucky enough to enter just wasn't satisfying enough. Then one lucky person who went inside took his camera phone in with him and Millions have seen the shaky footage online.
• The interior of the Kaaba is now lined with marble and a green cloth covering the upper walls. Fixed into the walls are plaques each commemorating the refurbishment or rebuilding of the House of Allah by the ruler of the day. Watch the video below of the only place on
Earth that you can pray in any direction you want, the House of Allah, the first place of worship for mankind – the Kaaba.
• Inside the Kaaba Video
Basic Beliefs of Islam?
• 5 Pillars of Islam:
• Allah is only god (Muhammad is a human prophet, but not god)
• Pray 5x day towards Mecca
• Concern for Poor
• Fast during Ramadan
• Pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj)
• Abraham, Moses, Jesus = Prophets
• Judgment day (punish/reward)
• Hell = Jahannaam
• Heaven = Jannah
• Imam
• Koran – words of god through
Muhammad
• Must submit to the will of god
• Mosque
Hajj Rituals
• Walk counter clockwise 7x around Kaaba.
• Run back and forth between hills of Al-Safa & Al-Marwah.
• Drink from Zamzam well.
• Go to plain of Mt. Arafat to stand vigil.
• Spend night in plain of Muzdalifa.
• Perform symbolic stoning of devil throwing stones at 3 pillars.
• Shave head, ritual animal sacrifice, celebrate 3 days of Eid al-Adha.
Student Questions
• Is Hajj all year long?
• Hajj is between the 8 th and 12 th days of the last month of the Islamic calendar. Dates change from year to year. However, you can visit Mecca all throughout the year for umrah,
“lesser pilgrimage.”
• Have people been killed on Hajj due to crowd control?
• Yes! Crowd control is a problem, so thousands of people have been killed over the years in stampedes, protests and violent outbreaks. The outbreak of disease can also be a problem.
• How many people make the Hajj?
• About 2 million people.
Student Questions
• Can a non-Muslim sneak in to the Kaaba?
• All people in Saudi Arabia, must carry government identification (resident permit, national ID, visa) and that identification identifies you as Muslim or not. (All Saudi’s are assumed Muslim.) Checkpoints along the highway to Mecca stop passengers to check their identification. If you are not Muslim, you will be sent back.
• If a non-Muslim is found in the holy city, they will be punished. Usually deportation or jail.
• Can Sunni & Shiites take the Hajj together?
• Yes! But they should travel in groups together and at times fights will break out between them.
What are Women’s Roles in Society?
• Koran gave them the right to inherit and control property.
• Men can Divorce, but have to return dowry.
• Forbid killing of unwanted baby girls.
• Excluded from public places.
• Secluded within the home.
• Protected by male relatives.
• Men have complete authority over women.
• Must obey husband/father, raise kids, and manage household.
Discuss Caliphs and Different Dynasties.
• Caliph = Religious and political leader, successor to Muhammad
• Theocratic – political and religious
• Umayyad Dynasty
• Made Damascus (Syria)
• Competing Branches: Sunni (90%)/Shiite (10%)
• Differ over who was the rightful successor to Muhammad.
• Shiite – loyal to religious leader who could be traced back to Muhammad’s family
•
• Sunni – Can be elected or picked
• Arabic is the official language of the Muslim world.
Abbasid Caliphate
• 750 – 1258 CE
• Golden Age of Classical Islamic Culture
• Strong, peaceful, stable Caliphs
• Economic unity, trade, skilled craftsmen
• Built Capital at Baghdad (Iraq)
• Began to splinter in the 900s, fell to Mongols
Spread of Islam to Africa
• Beginning in the 600s, spread all across North Africa, and gradually to sub-Saharan Africa.
• Some groups remained Christian: Kush, Axum,
Ethiopia, parts of Egypt.
• Brought by Arab traders overland through Sahara caravans or by Indian Ocean.
• Arab slave trade
• Berbers: nomadic desert herders
Rise of the Turks - Mali
• Most powerful Islamic state in western sub-Saharan Africa
• Niger River
• Important trade route
• Traded gold, salt, ivory, animal skins, slaves
• Timbuktu
• Mansa Musa
• Oral storytelling and song-making
• “Son-Jara” or Sundiata – epic poem telling the story of Sundiata, the founder of the Mali empire.
Who were the Turks?
• Nomadic tribes from the foothills of Central Asia.
• Mamluks – Turkish cavalry warriors brought to Middle East to serve in Arab armies. Convert to Islam.
• Seljuks – patrons of Persian art, literature, culture; weakened Byzantine
Empire, ushered in the Crusades.
Middle East & the Crusades
• Christian Europeans established
“kingdoms” in the Middle East after the 1 st Crusade.
• No group was able to organize an effective resistance.
• Saladin – recaptured Jerusalem, drove back the 3 rd Crusade.
• By the end of the 13 th century,
Europeans expelled
• Mongols destroyed Abbasid
Caliphate in 1258 CE
• Decentralization
The Ottoman Turks
• Rose to prominence in 1300s, lasted until early 20 th century.
• Served Seljuks as vassals, then founded independent state.
• Advanced fleet and armies
(gunpowder artillery)
• 1453 CE – Fall of Constantinople, fall of Byzantine Empire
• Struggle against Christian Europe
Sunni vs. Shiite
What’s the Difference?
• Sunni vs. Shiite on Youtube
Youtube
Authority in Islam
• Sunni (90%)/Shiite (10%)
• Differ over who was the rightful successor to Muhammad.
• Shiite – loyal to religious leader who could be traced back to Muhammad’s family
• Sunni – Can be elected or picked
• So, they don’t recognize the same authority in Islam – kind of like the way Catholics and Protestants are all Christians and have the same Bible, but only Catholics recognize the authority of the pope. And like Catholics and Protestants, both
Sunnis and Shiites have their own religious holidays, customs and shrines.
Where do they live?
Sunni (90%, 940 million)
• Syria (majority)
• Northern Iraq
• Saudi Arabia (majority)
Shiite (10%, 120 million)
• Iraq (majority)
• Iran (dominate)
• Yemen (minority)
• Bahrain (minority)
• Afghanistan (minority)
• Pakistan (minority)
• Lebanon (minority)
Why are they still fighting?
• Fighting in Iraq Highlights Age - Old Conflict
• In addition to who is successor, their interpretations of the Qu’ran vary. Sunni’s do not consider Shiites to be proper Muslims.
• Sunni’s are a minority in Iraq, but they controlled politics.
• 2003 – US invaded Iraq, Saddam Hussein over thrown, and Shiites took power and revenge.
• New Shiite Prime Minister cracked down on Sunni protests.
• Extremist rebels in Syria crossed the border and promoted extremism among Sunni’s.
(Islamic State of Iraq & Syria = ISIS)
• Iraq’s army has trouble stopping extremist rebels. Since the US withdrew in 2011, no one is there to help them.
• These extremist groups have ties to terrorist organizations.
What is a Jihad?
• “Holy War”
• Struggle against those who do not believe in the Islamic god and do not acknowledge submission to Muslims.
• Inter spiritual struggle.
Terrorist Organizations: What’s the Difference?
ISIS
• Used more conventional military tactics (rifles/grenades)
• More brutal –beheading, social media
• More appealing to young people
• Wants to attack US
• Funded by selling oil on black market
Al Qaeda
• Wants to carry out attacks that seize attention from international media (9/11)
• Brutal, but not as bad – doesn’t want to turn recruits off
• Less appealing to young people
• Has attacked the US
• Funded by donations/donors
All this is taking place on the other side of the world. Why should I care?
• Islam is a global religion.
• ~12 million Muslims live in the United States.
• America has significant strategic and military interests in the region.
• The number of Muslims is expected to rise by 35 percent in the next 20 years, to reach 2.2 billion people.
Islamic Culture
Why don’t Muslims eat pork?
• Some Jews and Christians also do not eat pork.
• Although the clip below is the answer spoken by a Christian minister, the answer to this question is the same.
• Why Muslims don't eat pork?
Women in Islam
• Hijab (Head scarf)
• Koran gave legal and economic status, right to inherit and control property
• Upon divorce, woman received dowry back.
• Excluded from public view, secluded from home
• Care of husbands/sons/family
• Obey husband, manage household
• Male authority
Islamic Marriages
• Purpose = preserve the religion through the creation of a family.
• Polygyny is allowed for men, not women. Men may have up to 4 wives if they can treat them equally. This practice is declining and illegal in some areas, but 150 countries in Africa,
Middle Eat, & 3 rd world countries still allow it.
• Most marriages are arranged, but arrangement is not required.
• Imam can help you find a match.
• Matchmaking websites can help you find a match.
• Homosexuality is forbidden and condemned by the Qu’ran.
• Men can marry a Christian or Jew, but no other nonbeliever. Women must marry a Muslim.
Islamic Divorce
• Khula = when a woman initiates a divorce.
• Can only have a divorce for 2 reasons:
• If she can prove her husband has not had intercourse with her in 2 months.
• If husband has not provided food and shelter
• Women have to repay dowry and forfeit child custody.
• Talaq = Man initiates the divorce
• He only has to say “I divorce you” 3 times, and it is official.
Muslim Civilization
• Very wealthy
• Blended with Greek, Roman, Byzantine, Persian, and Indian cultures
• Role of non-Muslims in empire
• Trade in the Mediterranean
• Abbasid Baghdad – libraries, hospitals, palaces public gardens, street lighting
Medicine, Math, Science
• Use of Arabic numbers, studied Euclid
• Physician Razi – Hawi (medical encyclopedia), symptoms of smallpox and measles
• Ibn Sina (Avicenna) – Cannon of Medicine
• Astronomy – earth round, circumference, compass, and astrolabe
• Gunpowder weaponry
Influence on Culture
• Madrasas – Religious Colleges
• Islamic Law – Sharia
• Sharia law can not be altered, but Imam’s have a little flexibility regarding interpretation.
• Most intrusive and strict legal system in the world, especially against women.
SOME Sharia Law
• • Theft is punishable by amputation of the right hand.
• Criticizing or denying any part of the Qu’ran is punishable by death.
• Criticizing or denying Muhammad is a prophet is punishable by death.
• A Muslim who becomes a non-Muslim is punishable by death.
• A non-Muslim who leads a Muslim away from Islam is punishable by death.
• A non-Muslim man who marries a Muslim woman is punishable by death.
• A man can marry an infant girl and consummate the marriage when she is 9 years old.
• A woman can have 1 husband, but a man can have up to 4 wives; Muhammad can have more.
• A man can unilaterally divorce his wife but a woman needs her husband's consent to divorce.
• A man can beat his wife for insubordination.
• Testimonies of four male witnesses are required to prove rape against a woman.
• A woman who has been raped cannot testify in court against her rapist(s).
• A woman's testimony in court, allowed only in property cases, carries half the weight of a man's.
• A female heir inherits half of what a male heir inherits.
• A woman cannot drive a car, as it leads to fitnah (upheaval).
• A woman cannot speak alone to a man who is not her husband or relative.
• Meat to be eaten must come from animals that have been sacrificed to Allah
• Muslims should engage in Taqiyya and lie to non-Muslims to advance Islam.
Arts & Literature
• Minarets
• Ibn Rushd (Averroes) – translated Aristotle, tried to reconcile with ideas of
Islam, reasoned no conflict between faith and reason.
• Omar Khayyam – “the Rubaiyat”
• The “Arbian Nights”
• Ibn Battuta – “Travels”
• Sufism