Composition of Forces WS
advertisement

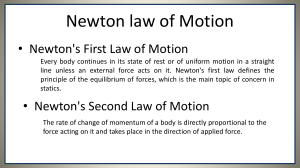
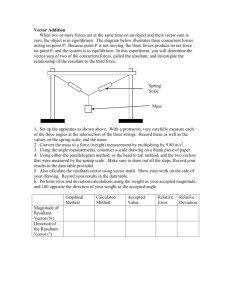
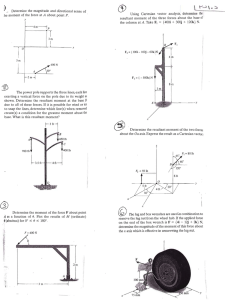
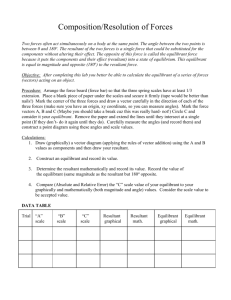
Physics --- Composition of Forces WS Name ___________________________ Conceptual Questions: 1. Concurrent forces are two or more forces that act on the same ____________________ at the same ____________________________. 2. Concurrent forces can be treated as vector ( components , resultants ). Finding the resultant of these forces is called ___________________________________ of forces. Why is this a better term than addition of forces? 3. When a parallelogram is constructed in order to combine forces, the resultant is the ___________________________________ of the parallelogram. 4. What is the resultant of a pair of forces, 100.0 N North and 70.0 N South? What is the resultant of the pair of forces if they both act North? 5. The state of a body in which there is no change in its motion is called _____________________. 6. When no unbalanced forces act on an object, the object can have no _____________________ ______ ______________________. 7. What is the net force that acts on an object in equilibrium? ____________________. 8. A(n) ______________________________ force is the force required to put an object in a state of equilibrium. This force has the same ______________________________ but opposite ___________________________ to the resultant of the concurrent forces acting on the object. 9. Understanding the Law of Acceleration (Newton’s 2nd Law), the equilibrant force causes the net force = _____, the acceleration will be ________, and the velocity is ______________________. SP1d. Measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces and Newton’s three Laws of Motion. SP1h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium. Physics --- Composition of Forces WS Name ___________________________ Mathematical Problems: 10. What is the resultant of these concurrent forces? 5 N North, 12 N South, 7 N South, 6 N North What is the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant force for this situation? 11. A) On force acts westward on an object with a magnitude of 24.0 N, the other force acts southward with a magnitude of 18.0 N. Compose these two concurrent forces into their resultant. (Remember to give magnitude and direction!) B) As long as these forces act on the object it will ( move uniformly , accelerate ) in what direction? ____________________________________ C) What would be the magnitude and direction of an equilibrant force for this situation? ___________________________________________________________________ D) As soon as this force is applied, the object will ( stop , slow down, move uniformly ). 12. Find the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant force for these two concurrent forces: 13.5 N West and 32.0 N North SP1d. Measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces and Newton’s three Laws of Motion. SP1h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium.