Forces Notes PPT
advertisement

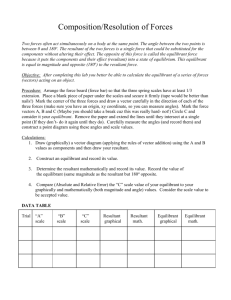
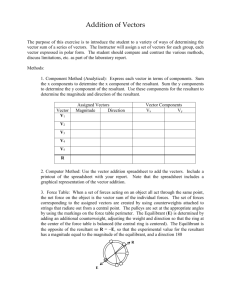
FORCES SP1d. Measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces and Newton’s three Laws of Motion. SP1h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium. Anything that affects the motion of an object A PUSH or a PULL Tension is a type of internal force when strings, ropes, etc. are used to transmit forces. Forces Force vectors are always drawn from the point of application. Always draw the vector pointing away from this point. Pushes are drawn as pulls from the other side. Forces are VECTORS • Concurrent Forces – two or more forces acting on the same point at the same time. • Resultant Force – a single force that has the same effect as two or more Combining Force Vectors • A state of a body in which there is no change in its motion. • At rest or constant velocity • Must have no net (unbalanced) forces acting on a body Equilibrium Equilibrant Force – a single force that would produce equilibrium. The equilibrant force is equal to and in the opposite direction of the Resultant force. Equilibrant Force To find the equilibrant force… 1) Find the resultant of the 2 concurrent forces 2) The equilibrant force must have the same magnitude, but act in opposite direction. To Find… • 2 components to 1 resultants • Concurrent forces can be composed • Finding the resultant • 2C’s 1R Composition of Forces • 1 resultant to 2 components • Finding the components when the resultant is known. • Resolving the resultant vector into its component vectors • 1 R 2 C’s Resolution of Forces