VECTORS Example 15: Two force vectors with magnitude 30
advertisement

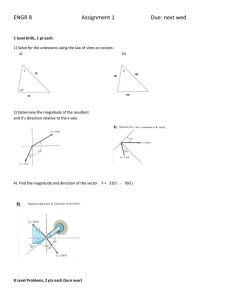
VECTORS Example 15: Two force vectors with magnitude 30 pounds and 70 pounds act on an object. If the angle between the force vectors is 40º, what is the magnitude of the resultant force vector R? Round your answer to a whole number. We will use the Parallelogram Rule for vector addition as follows: We can now find the magnitude of the resultant vector R by applying the Law of Cosines to the triangle ABC. From geometry we know that adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary, that is, their sum equals 180o. Therefore, the measure of angle ACB is 180o - 40o = 140o. The magnitude of the resultant force vector is approximately 95 pounds. Example 16: Find the magnitude of the equilibrant force between the forces of 48 and 60 newtons acting on a point A. The angle between the forces is 50o. Round your answer to whole numbers! The equilibrant force is the force necessary to counterbalance the joint action of two forces. If the resultant of two forces is R, then - R is called the equilibrant of the two forces. A newton is a unit of force used in physics. NOTE: ||R|| = ||-R|| We will find the magnitude of the resultant vector R by applying the Law of Cosines to the triangle ABC. From geometry we know that adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary, that is, their sum equals 180o. Therefore, the measure of angle ACB is 180o - 50o = 130o. The magnitude of the equilibrant force is also approximately 98 newtons.