Body/Building the Sale
advertisement

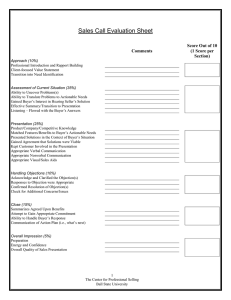
The Selling Process - 3 Stages Source Potential Customers Prospecting Opening The Sale Building The Sale Closing The Sale The Sales Presentation Follow Up Sale After Sales Service Rules of Selling • • • • • • • • • Adopt a Win – Win approach Know your product – features, benefits & USPs Sell the benefits, not the features Research prospect Know your customers’ needs/wants Listen to the buyer Relate what you are selling to the buyer’s wants and needs Plan your sales and be prepared Have clear and well prepared sales presentations, demonstrations and telephone calls • Make sure you know who the decision maker is Sourcing Customers/Prospecting • Internal Sources: • Personal Contact: • • • Money Authority Need – Enquiries to advertising – Phone/mail enquiries – Internet enquiries – Customer records • External Sources: – – – – – – – Following leads Referrals/introductions Community contact Other organisations Networks Newspaper Directories – – – – – – – – – – Business contacts Social networks Formal networks Networking Word of mouth Personal observation Cold canvassing Trade shows Conferences Sales seminars Contacting Prospects – Planning your Approach Objective • • • Make an appointment Create an interest Immediate sale How • • • • • Telephone Person to person E-mail Letter Visit Resources required What to say • • • • • • • Set an agenda Opening statement Sales pitch Qualifying questions Answers to objections Reponses to questions Build confidence & rapport • • • • • • Business cards Customer testimonials Brochures Portfolios Diary Writing materials Next steps • • • Obtain an appointment Send information Follow up Sales Presentation Structure • Opening the sale • Body/building the sale • Closing the sale Opening the Sale • Make an opening statement • Introduce yourself/your business • State the purpose of the presentation quickly (within 15 seconds) • Ask qualifying questions Body/Building the Sale • Provide information on you/your business and your product/service • Relate to the buyer’s needs/wants • Highlight unique selling points (USPs) • Focus on the benefits to the customer • Follow a logical sequence FAB Features Advantage Benefit High speed processor Can compute twice as fast Provides customer with more productive time Focus of sales pitch Why Objections Occur • • • • • • Disbelief/not convinced Budget/money issues Satisfaction with a competitive product Previous negative experience Fear of making the wrong decision Misunderstanding Handling Objections • Prepare responses in advance • Listen to the objection • Check you have understood the objection • Answer the objection • Advance the sale Buying Signals • Requesting a sample • Requesting names of other customers • Commenting positively • Indicating problems with previous vendors • Asking specific questions re: price, features, availability, options • Negotiating Closing Methods • • • • • • • • Assumptive close Alternative choice close Immediate gain close Fear close Direct request close Summary close Negotiation close Small decision close Follow Up • • • • • • Explain level of service at the time of the sale Make a courtesy call after the sale Give customer contact numbers etc Stay in touch Use a database Send customers information on offers etc Benefits of Customer Care • • • • • Satisfied customers will recommend you to others Encourages repeat sales Dissatisfied customers will complain on average to 10 other people Demonstrates professionalism Poor customer care will damage your image and reduce your profits