Amphibians Review #1 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
advertisement

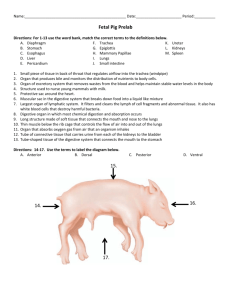
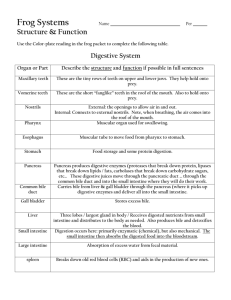
Amphibians Review #1 Membrane that blinks to keep amphibian eyes moist on land and closes to cover the eye when swimming under water. Nictitating membrane Deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from Right atrium the body enters the _________________ from the sinus venosus. These are located in the frog’s skin and help to keep it moist Mucous glands The multi-purpose cavity that receives waste from the digestive system, urinary bladder, and sperm and eggs from the reproductive system before exiting the body. cloaca Frogs belong to the Kingdom : Animalia Phylum: Chordata Sub Phylum: Vertebrata Class: Amphibia Order: Anura Cold blooded organisms with moist, thin skin, webbed feet, a 3-chambered heart, that undergo metamorphosis from a larval to adult stage are Amphibians called ____________________ Oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the Left atrium lungs enters the _________________ Respiratory organ found in the larval stage of amphibians gills Name the parts of the brain starting at the spinal cord and moving toward the nose. Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Optic lobes Cerebrum Olfactory lobes Thin fan-like membrane that holds the digestive organs in place. mesentery The upper portion of the small intestine closest to the stomach is called the ___________________ duodenum Cutaneous respiration involves exchanging skin gases through the ______________ Blood vessels that carry blood away from arteries the heart are called ____________________. Match the brain part to its function: Controls involuntary body organs ___________________ Medulla oblongata Higher thinking & learning _______________ cerebrum Processes info about vision Optic lobes (tectum) & hearing _______________ balance & motor coordination ____________ cerebellum Olfactory lobes Processes info about smell _______________ Pulmonary respiration uses this body organ. lungs The eardrum in a frog is called the __________________ Tympanic membrane Name the body system for each organ: oviducts Reproductive kidneys Excretory olfactory lobes Nervous lungs Respiratory Skin Integumentary/Respiratory Number of chambers in an amphibian heart 3 Tail-less amphibians like frogs and toads belong to the order _______________ Anura “An = without uro = tail” Hormone made by the thyroid gland that controls metamorphosis Thyroxin Digestive organ that produces bile for the small intestine. liver The digestive organ where nutrients are absorbed from digested food. Small intestine Frogs use positive pressure breathing. They move air in and out by raising and lowering the _______________________ Roof of their mouth Area of the brain for higher thinking that is responsible for learning, memory, and reasoning cerebrum Small bone that extends between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear Columella Match the part with its function: Make bile __________________ liver Gall bladder store bile __________________ intestine (duodenum) place where bile is used Small __________________ gills respiratory organ in tadpoles _______________ makes trypsin _________ pancreas Conus arteriosus A valve in the _________________ prevents mixing of the high oxygen and low oxygen carrying blood Blood leaving the heart travels through the pulmonary ______________ to the arteries lungs. Match the part with its function: Processes nitrogen waste for the kidneys liver __________________ removes nitrogen waste from blood and makes urine __________________ kidneys spleen removes worn out blood cells __________________ Skin & lungs respiratory organs in adult frogs _______________ kidneys excretory organ in adult frogs _____________ Type of circulatory system in a frog Closed Open closed stomach Acids in the _______________ helps to break down food. Match the part with its function: Regulates ion/water concentrations in blood __________________ kidneys urinary bladder stores urine __________________ Large intestine concentrates & collects digestive waste _____________ cloaca receives urine, feces, & sperm or eggs _____________ pancreas makes insulin and glucagon _________ Follow the path of blood in the frog circulatory system. Sinus venosus RIGHT LEFT Atrium Atrium Ventricle Body organs Lungs Conus arteriosus Name two respiratory organs in adult frogs Lungs and skin external Fertilization in frogs is _______________ External internal Tell where each mouth opening leads to: Eustachian tubes internal nares glottis gullet ears External nares Respiratory (lungs) Digestive (esophagus) Food stored in the _______________ fat bodies is used during hibernation and estivation. The teeth located on the roof of the frog’s mouth between the internal nares are called vomerine __________________ teeth. Small sac located on the under the right lobe of the liver that stores bile. Gall bladder TRUE or FALSE Blood traveling to the lungs in the pulmonary arteries is HIGH in oxygen. FALSE It’s going to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Main excretory organ in an ADULT frog Kidneys Process by which frogs lie dormant through the winter. hibernation Match the part with its function: Nictitating membrane Covers eye under water __________________ Fat bodies stores food for hibernation/estivation _______________ ileum Coiled portion of small intestine ________________ between duodenum and large intestine ventricle Pumps blood _______________ Tympanic membrane eardrum _____________ Largest artery leaving the heart Aorta Tell one way frog circulation is different from a fish Frogs: 3 chamber heart 2 loops Fish: 2 chamber heart 1 loop Gradual change in form which occurs during the life of an amphibian metamorphosis This organ makes, stores, and processes red blood cells spleen Openings in the roof of the mouth that connect to the external nares (nostrils) Internal nares Ribbon-like structure located in the mesentery between the stomach and the upper intestine pancreas Name the 2 parts of the frog circulatory system that carry BOTH oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Ventricle and Conus Arteriosus Process by which amphibians lie dormant through a hot, dry season. estivation Explain how AMPLEXUS helps reproduction in frogs. With amplexus, sperm and eggs are released at same time and in the same place so it increases chance of fertilization deuterostomes Frogs are _____________________ that deuterostomes protostomes means their blastopore becomes their _____________ anus mouth anus vertebrates Frogs are _________________. vertebrates invertebrates Thyroxin is made by the _________________. Thyroid gland Excretory organs in a TADPOLE Kidneys & gills Tell one way adult frog circulation is like a fish BOTH: Closed circulation have conus arteriosus & sinus venosus ventricle pumps blood have arteries, veins, & capillaries SUBSTANCE BILE TRYPSIN GLUCAGON INSULIN THYROXIN MADE BY? FUNCTION? LIVER Breaks down FATS PANCREAS Breaks down PROTEINS PANCREAS Causes cells to release stored glucose PANCREAS Causes cells to store glucose THYROID GLAND Controls metamorphosis The medulla oblongata controls Higher thinking internal organs muscle coordination smell Internal organs The part of the systemic circulation in which blood circulates from the heart to the lungs and back to PULMONARY the heart is called _________________ circulation. Region of the frog brain which receives info from the eyes is the _______________ lobe Optic Number of loops in the circulatory system of amphibians 2 loops; one to lungs and back one to body systems and back The blood vessel that carries blood from the Pulmonary artery heart to the lungs is the _______________ Hint: think about what circulation to the lungs is called and what blood vessels that leave the heart are called! Organ which produces eggs Ovary Opening to the digestive system in the back of the throat Gullet The circulatory system in which blood flows from the heart to the body systems and back to the heart is the ________________ circulation. Systemic Teeth located along the upper jaw Maxillary Blood returns to the left atrium from the lungs in the _______________ __________. Pulmonary veins Match the function with the body part Bone between eardrum and inner ear columella _____________________ Controls higher thinking, learning, reasoning, etc. ______________________ cerebrum Vessels that carry blood away from heart ________________ arteries nostrils _________________ External nares Teeth on roof of mouth _______________ vomerine Receives blood returning to heart from lungs ______________________ Left atrium Organ that produces sperm Testes Tube that carries eggs from the ovary to the cloaca. Oviduct LABEL THE PARTS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Carries blood from heart to lungs and back to heart Carries blood to liver Carries blood to kidneys Carries blood to heart itself Carries from heart to body organs and back to heart PULMONARY HEPATIC RENAL CORONARY SYSTEMIC The portion of the brain closest to the spinal cord in a frog. Medulla oblongata Eardrum in a frog Tympanic membrane Structure where eggs are stored before being laid is the ______________ Uterus Tube that carries eggs from the ovary to the cloaca. Oviduct These yellowish fingerlike structures store fat for hibernation and times with little food. Fat bodies This reproductive structure in females makes eggs ovary Match the function with the body part Controls motor coordination & balance _____________________ cerebellum glottis Opening to lungs ______________________ Medulla oblongata Controls body organs ________________ Tympanic membrane Eardrum _________________ Respiratory organ in tadpoles _______________ gills Receives blood returning to Sinus venosus heart from body ______________________ The thyroid gland belongs to the __________________ system. endocrine During periods of extreme cold amphibians undergo a dormant time called ________________. hibernation These structures located near the kidneys make sperm testes Name the 3 body systems that share the cloaca exit cavity. Digestive, excretory, reproductive During hot, dry periods amphibians can undergo a dormant time called _________________. estivation Match the function with the body part Makes bile _____________________ liver Gall bladder Stores bile ______________________ Makes trypsin pancreas & other digestive enzymes ________________ Protects the eye underwater ________________ Nictitating membrane Respiratory organ in tadpoles _______________ gills Receives sperm/eggs, cloaca urine, & digestive waste _________________ Match the function with the body part Place where bile Small intestine & trypsin are used _____________________ Upper part of small intestine duodenum ____________________ ileum Coiled part of small intestine ________________ Small intestine Absorbs nutrients ________________ Respiratory organ in adult frogs Lungs skin _____________ & __________ cutaneous ________________ respiration involves breathing through skin. Adult amphibians release their nitrogen waste in the form of _______ urea which is diluted with water to make urine. Tell 2 things that have to change INSIDE a tadpole as it becomes an adult. •Switch from breathing with gills to breathing with lungs & skin •switch from excreting ammonia to urea • add a chamber to heart •add a loop to circulatory system •Switch excreting nitrogen waste through gills & kidneys to just kidneys THE END