Group #1 Alkali Metals
advertisement

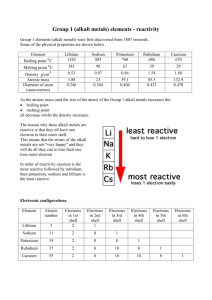
Group #1 Alkali Metals By: Gene, Tori, Sammi, Tom Origin of the group ★ The word alkali comes from the Arabic word for ashes. ★ Alkali is now used as another word for base. ★ Alkali metals react with water. General Characteristics of group ★ All of the elements are solids at room temperature except Caesium. ★ All of the elements have a silverish tint to them except Caesium which is a metallic gold. ★ The melting points decrease as you go down the group. ★ These elements have low densities compared to other elements. Lithium (Li) ★ Element: Lithium ★ What: 1st element in group one. ★ Density: 0.534 g/cm3 ★ Phase at Room Temperature: Solid ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ Melting Point: 180.5 degrees celsius Characteristics: Silvery, lightest of all metals, moist air causes corrosion. Origin of Name: Lithium derived from ‘lithos’, the Greek word for stone. Who/When: 1817 by Johan August Arfwedson Use of Element: Lithium is used for mental illnesses, for eating disorders, and for blood disorders. Sodium (Na) ★ Element: Sodium ★ What: 2nd element in group one. ★ Density: 0.97 g/cm3 ★ Phase at Room Temperature: Solid ★ Melting Point: 97.794 degrees celsius ★ Characteristics: Silvery-White so soft a room temperature you can cut it with a butter knife ★ Origin of Name: from the English word "soda" the origin of symbol Na from the Latin word "natrium" ★ Who/When: Sir Humphry Davy discovered in England in 1807 ★ Use of Element: Sodium is used as a coolant in nuclear reactors, and as a reactant in organic chemistry Potassium (K) ★ Element: Potassium ★ What: 3rd element in group one. ★ Density: 0.89 g/cm3 ★ Phase at Room Temperature: Solid ★ Melting Point: 63.5 degrees celsius ★ Characteristics: Silvery- White and lustrous Origin of Name: from the English word "potash", the Arabic word "qali" meaning alkali, the origin the symbol K comes from the Latin word "kalium". ★ Who/When: Potassium metal was first isolated by Sir Humphery Davy in 1807 ★ Use of Element: Potassium is used in organic chemistry as a powerful Reducing Agent Rubidium (Rb) ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ Element: Rubidium What: 4th element from the top in group one. Density: 1.53 grams per centimeter cubed Phase at Room Temperature: Liquid Melting Point: 39.48°C Characteristics: Silvery-white, metallic Origin of Name: From the Latin word "rubidius" meaning "dark red" or "deepest red". Who/When: 1861 by Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchoff. Found in the mineral lepidolite by using a spectroscope. ★ Use of Element: It has been used as a component of photocells, andit is sometimes used in fireworks to give them a purple color. Caesium (Cs) ★ Element: Caesium ★ What: 6th element in group one. ★ Density: 1.873 g/cm3 ★ Phase at Room Temperature: Solid ★ Melting Point: 28.44 degrees celsius ★ Characteristics: soft, gold-coloured metal ★ Origin of Name: from the Latin word "caesius" meaning "sky blue" or "heavenly blue". ★ Who/When: Discovered by Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen in 1860 ★ Use of Element: Used as a drilling fluid, to make special optical glass, as a catalyst promoter, in vacuum tubes and in radiation monitoring equipment. Francium (Fr) ★ Who: Marguerite Perey discovered Francium in 1939 ★ What: Last alkali metal, atomic number 87 and atomic weight of 223 amu, it occurs naturally and is a solid at room temperature. ★ Where: Curie Institute in Paris, France ★ How: francium-223 is made naturally when actinium-227 emits an alphaparticle ★ Melting Point: 27oC (300 K) (Pretty low) ★ Density: 1.873 g/cm3 Francium (Fr) Characteristics: Francium is a heavy, unstable, radioactive metal with a maximum half-life of only 22 minutes. Fun Facts: ● Francium is the second rarest element in the Earth’s crust, next to astatine. Less than thirty grams of francium exists on Earth at any given time. ● The discovery of francium completed humankind’s discoveries of naturally occurring elements. ● Francium, like the other alkali metals, reacts in the present of water. Uses of Francium: Commercially, there are no uses for francium, due to its rarity and instability. It is used for research purposes only. Reactivity of Alkali Metals