CH 11
advertisement

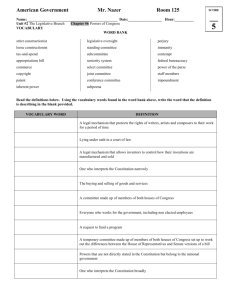
CH 11 Lawmakers and legislators Vocab! • • • • Constituent Pork Appropriations Casework Constituent • A person who lives in an electoral district and is represented by an elected official Pork • Publicly funded projects secured by legislators to benefit their home states or districts Appropriations • Funds allocated by a legislature for a stated purpose as part of a budget or spending bill Casework • Personal services provided by members of Congress to their constituents, often to help their constituents with problems they are having with the federal bureaucracy According to Article I of the Constitution, what are the specific, or enumerated, powers of Congress? • The enumerated powers of Congress are to levy and collect taxes, borrow money, regulate interstate and foreign commerce, coin money, and declare war. How does Congress check the other two branches of government? • Oversight of executive agencies; Senate confirmation of key officials appointed by the president; impeachment and trial of federal officials, including the president; Senate ratification of treaties negotiated by the president; override of a president’s veto of legislation; proposal of constitutional amendments How do you qualify to serve in Congress? • Formal qualifications: resident of the state in which elected, U.S. citizen for at least 7 years (House) or 9 years (Senate), at least 25 (House) or 30 (Senate) years old • Informal qualifications: college degree; background in business or law How does the government decide the number of representatives per state? • Every 10 years, a national census is conducted, and results are used to calculate the distribution of House seats. • States with a large increase in population may gain seats; states whose population drops lose seats. • Each state is guaranteed at least one seat in the House. Explain the difference between a delegate and a trustee. • Delegates seek to represent their districts by responding directly to the wishes and needs of their constituents. • Trustees try to represent their districts by exercising their best judgment and assuming that their constituents trust them to do the right thing. Which leadership position in Congress has the most power? List some specific powers of that position. • The House speaker has the most power in Congress. The speaker assigns bills to committees, appoints members to special committees and commissions, and decides what bills will be debated by the full House and when. What is a standing committee? • Standing committees: Permanent committees (such as the House Committee on Agriculture) that handle most legislative business and gather information from hearings and investigations. What is a subcommittee? • Subcommittees: Formed within standing communities, these do most of the work of reviewing proposed legislation. What is a special committee? • Select or special committees: Temporary committees formed to investigate a specific problem. • They do not review legislation but may make recommendations to Congress. What is a joint committee? • Joint committees: Permanent committees (such as the Joint Committee on the Library) made up of House and Senate members that are formed around issues of importance to both chambers. What is a conference committee? • Temporary joint committees formed to iron out differences between two versions of a bill passed by the House and Senate. How does a bill become a law? How does a bill become a law? How does a bill become a law? CH 11 Review T/F • The government uses the census to redistribute seats in Congress. T/F • True • The government uses the census to redistribute seats in Congress. Fill in the blank. • The ________________ committee handles the most detailed work of lawmaking in Congress. Fill in the blank. • The _standing__ committee handles the most detailed work of lawmaking in Congress. T/F • The power to ratify treaties belongs only to the Senate. T/F • True • The power to ratify treaties belongs only to the Senate. T/F • Term limits limit the number of years a legislator can serve in Congress. T/F • True • Term limits limit the number of years a legislator can serve in Congress. T/F • Term limits can apply to state lawmakers but not to members of Congress T/F • True • Term limits can apply to state lawmakers but not to members of Congress T/F • The number of seats in the Senate depends on the population of each state. T/F • False • The number of seats depends on the number of states. • Each state has 2 senators. Fill in the blank • ______________are residents of an electoral district represented by an elected official Fill in the blank • __Constituents__are residents of an electoral district represented by an elected official T/F • The “power of scheduling” refers to the Speaker’s ability to control the meeting dates of committees. T/F • False • The “power of scheduling” refers to the Speaker’s ability to decide which bills will be debated and when T/F • Most members of Congress begin their political careers in local politics T/F • True • Most members of Congress begin their political careers in local politics T/F • A conference committee is made up of members from both the legislative and executive branches. T/F • False • A conference committee is made up of members from both the House and Senate Final Question • Select your representative • Place your wager Short answer • How does Congress check the Executive Branch? • How does Congress check the Judicial Branch? How does Congress check the other two branches of government? • Oversight of executive agencies; Senate confirmation of key officials appointed by the president; impeachment and trial of federal officials, including the president; Senate ratification of treaties negotiated by the president; override of a president’s veto of legislation; proposal of constitutional amendments