blog 1-2 Molecular Geometry
advertisement

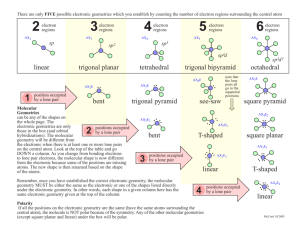
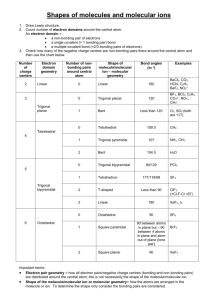
Molecular Geometry 2-2 Ch. 6 – Molecular shape • Molecules are three-dimensional objects that occupy a threedimensional world; In general, only the smallest molecules can be said to have a fixed geometrical shape; the icosahedral C60 “soccer ball” is a rare exception. VSEPR Theory • Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory - focuses on the bonding and nonbonding electron pairs present in the outermost (“valence”) shell of an atom to which are connected two or more other atoms. • Electron pairs orient themselves in order to minimize repulsive forces. VSEPR Theory • Types of e- Pairs – Bonding pairs - form bonds – Lone pairs - nonbonding e- Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs!!! Determining Molecular Shape • Draw the Lewis Diagram. • Shape is determined by the # of bonding pairs and lone pairs. Know the 5 common shapes ! 1. Common Molecular Shapes 2 bond 0 lone LINEAR AB2 180° Linear molecules: AB2 • Ex: BeCl2 and CO2. • -If you write out the electron dot formula for carbon dioxide, you will see that the CO bonds are double bonds. Double bonds are treated like single bonds when shape is determined!!!!!! Cl BeCl2 Be Cl TWO ELECTRON PAIRS AROUND BERYLLIUM ATOM 180° 270° Be Be 90° 180° The shape of BeCl2 is linear. THE MOLECULAR SHAPE IS BASED ON THE POSITION OF THE ATOMS! • CO2 2 bond 0 lone O C O LINEAR 180° 2. Common Molecular Shapes 3 bond 0 lone AB3 TRIGONAL PLANAR 120° Trigonal planar: AB3 • In the molecule BF3, there are three regions of electron density extending out from the central boron atom. The repulsion between these will be at a minimum when the angle between any two is 120°. This requires that all four atoms be in the same plane; the resulting shape is called trigonal planar. F BF3 F B NO OCTET ON B ! F THREE ELECTRON PAIRS AROUND THE BORON ATOM. MOLECULAR SHAPE ATTACH 120° 120° B FLOURINES TO EPG. F B 120° F F THE SHAPE OF BF3 IS TRIGONAL PLANAR. 3. Common Molecular Shapes 2 bond 1 lone AB2E AB2E2 BENT <120° Shape with lone pairs: AB2E2 2 bonding electrons and 2 lone pairs or AB2E , 2 bonding electrons and 1 lone pair • Bent: • The nonbonding electrons are also in orbitals that occupy space and repel the other orbitals. SeO2 O Se O VSEPR treats double bonds like a single bond Se O SeO2 IS V-SHAPED, OR BENT O RESONANCE! Se O Se O O O Common Molecular Shapes 2 bond 2 lone H2O BENT 104.5° 4. Common Molecular Shapes 4 bond 0 lone AB4 TETRAHEDRAL 109.5° Tetrahedral: AB4 • Methane, CH4, contains a carbon atom to which are connected four hydrogens. Consequently, the four equivalent bonds will point in four equivalent directions in three dimensions. H CH4 H C H There are four H electron pairs around the carbon atom. 90° 90° C 90° 90° BUT………. There is a better arrangement for four electron pairs: TETRAHEDRAL The angle is….. 109.5° C Put on the H-atoms……. There is a better arrangement for four electron pairs: TETRAHEDRAL H C H H H 4 electron pairs tetrahedral EPG The shape of CH4 is tetrahedral. 5. Common Molecular Shapes 3 bond 1 lone AB3E TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL 107° • PF3 3 bond 1 lone F P F F TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL 107° Polyatomic ions • The charge will dictate how many less or extra electrons will be added to the lewis dot diagrams. Polyatomic ions • NO3• the negative charge tells you that you need to add one more electron to the diagram. 5 + 3(6) + 1 = 24 Nitrate anion O N O O VSEPR treats multiple bonds as effective single electron pairs. Trigonal planar is the shape