Domains & Kingdoms Notes (17.3)
advertisement

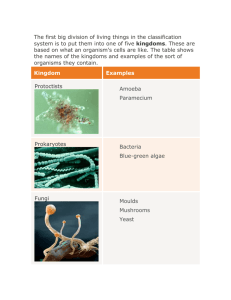
Domains & Kingdoms (17.3) State Standard SBCb: Compare how structures & function vary between the six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals. SBCd. Compare & contrast viruses with living organisms. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Grouping Species The ____________ category in the classification used by most biologists is the ____________. All organisms fit into one of 3 domains: Domain ____________ Domain ____________ Domain ____________ Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Grouping Species Cont’d Within the 3 domains, modern taxonomy defines _____ kingdoms. The six kingdoms are ____________, ____________, ____________, ____________, ____________, & ____________. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Prokaryotes ____________ prokaryotic organisms are either in Domain Bacteria or Domain Archaea. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Domain Bacteria only contains 1 Kingdom: ____________. Eubacteria (true bacteria) are prokaryotes whose cell walls contain ____________. They can be ____________ or cause ____________. Eubacteria are a diverse group that can survive in ____________ different environments. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Domain Archaea Domain Arachaea only contains 1 kingdom: ____________. Archaeabacteria are thought to be more ____________ than eubacteria. Archaea are diverse in shape and nutrition requirements. They are called ____________ because they can live in extreme environments (ex: ____________ or extremely ________ – deep oceans, hot springs, & swamps. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Domain Eukarya ________ ____________are classified in Domain ____________. Domain Eukarya includes ______ Kingdoms: ____________, ____________, ____________, & ____________. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Protista Protists are eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular. Protists are classified into three different groups— plantlike, animallike, and funguslike. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Protista Cont’d • ____________ complex organ systems & live in ____________environments • May or may not have a cell ____________. • May be ____________ or ____________ • ____________ set of organisms that don’t fit neatly into any other kingdom. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Fungi A ___________ is a unicellular or multicellular eukaryote that ____________ nutrients from organic materials in its environment. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Fungi Cont’d Absorptive ____________ Can’t ____________ Cell walls made of ____________ ____________ dead organisms & waste Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Plantae Members of Kingdom Plantae form the base of all terrestrial habitats. All plants are ____________and have cell walls composed of ____________. Most plants are ____________, but some are heterotrophic. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Animalia All animals are ____________, ____________ eukaryotes. Animal organs often are organized into ____________ organ systems. They live in the water, on land, and in the air. Animal cells __________ contain a ____________ ____________.