cells
advertisement

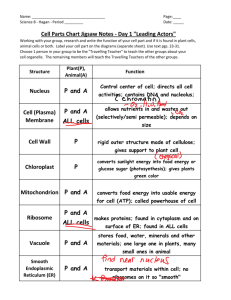
Cells Chapter 5 Organelles With Their Structure and Function Organelles •Tiny structures inside of eukaryotic cells that perform specialized jobs •Similar to organs in the human body 1. Cell Membrane • Separates the cell from its environment • Regulates what enters and leaves the cell • “Selectively permeable” – Only leaves certain substances into or out of the cell Structure of a cell • Found in all cells – Bacteria – Plants – Animals – Fungi – protists membrane: 1. Phospholipid bilayer 2. Proteins which can be: 1. embedded (on surface) 2. Integral (all the way through) Fluid Mosaic Model 2. Cell Wall • Found outside of the cell membrane on – – – – Algae Plants Fungi And some bacteria • Support structure • Non-living • Parts – Primary cell wall • Made first and found on the very outside – Secondary cell wall • Made second and found between the primary cell wall and the cell membrane – Middle Lamella • Gluey pectin that holds the cells together Cell Wall 3. Nucleus • Dark structure found inside all eukaryotic cells • Contains all genetic material for the cell (DNA) • Controls all cellular function with the DNA, therefore • • controls all function in the organism Usually the largest organelle in the cell Parts – Nuclear membrane • • • • Boundary between the cell and the nucleus Double phospholipid bilayer Regulates what enters and leaves the nucleus Contains pores – Nucleolus • Made of RNA and protein • Makes ribosomes – Chromosomes • Genetic material (DNA) Nucleus Structure 4. Mitochondria • Inner and outer membrane • Inner membrane is folded into “cristae” • Takes food (sugar) and converts it into usable energy for the cell (ATP) • Process is called cellular respiration • ATP – Adenosine triphosphate – Cellular energy – Found in all cells 5. Chloroplast • 2 membranes • • • – Inner and outer Found only in plants, algae and some protists Captures light energy and makes food for the plant Contains chlorophyll (green pigment) 6. Cytoplasm • Fluid between nucleus and cell membrane • Contains the rest of the organelles • Mostly water with the following materials dissolved in it – Food – Wastes – Pigments – Electrolytes cytoplasm 7. Ribosomes • Make protein for the cell and the rest of the • • • • organism Can be free floating in the cytoplasm Can be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum Made of 2 parts – RNA – Protein Made in the nucleolus of the nucleus 8. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Large complex network of canals that begins with the nucleus and meanders through out the cell to the cell membrane • Rough ER • Smooth ER – Has no ribosomes on the surface – Move and store • Chemicals • lipids – Has ribosomes attached to the surface – Proteins made on the ribosomes travel through the rough er – Highway system of the cell 9. Golgi Apparatus (Body) • Named after Camillo Golgi (discovered it) • Looks like a stack of flattened pancakes • Modify proteins that are made on the ribosomes • • on the rough ER Modify carbohydrates and lipids being attached to the proteins Collects, packages and distributes proteins to other cells 10. Lysosomes • Contain digestive enzymes • Digestion centers – Food vacuoles join with lysosomes to digest the food inside of them • Clean up crews – Break down old and broken organelles Lysosome 11. Vacuoles • Storage tanks for – Water – Proteins – Salts – Carbohydrates – Wastes – Simple membrane bound organelles – Very large in plants – Very small in animals 12. Plastids • Store food and pigment • Many varieties all found in plants – Chloroplasts – Leukoplasts- store starch granules – Chromoplasts- store pigment molecules 13. Cytoskeleton • Framework of the cell • Filaments and fibers that give the cell shape – Microfilaments •Long thin solid strands of protein – Microtubules •Long thicker hollow tubes of protein 14. Centrioles • Found in animals only • Used in cellular division to separate chromosomes 15. Cilia • Tiny hair-like projections that are in the surface • • • • of the cell membrane Help cells to move Made of microtubules Many on one cell May be found on tissues to move substances along ex. mucus 16. Flagella • Long- thread-like projection on the surface of a cell • Few on one cell • Made of microtubules • Helps cells move 17. Central Vacuole • • • • Large vacuole found in the center of most plant cells Contains water Keeps plant from wilting Pushes against cell walls and helps give the cell its shape