Cells
advertisement
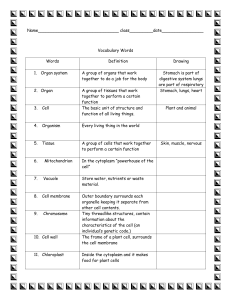
Chapter 8 Pretest 1. Which cells surround and consume harmful organisms that invade the body? A. antibodies B. phagocytes C. epithelial cells D. Hormones 2. Which system carries oxygen in the body? A. endocrine system B. skeletal system C. circulatory system D. nervous system 3. ____________ is a gel-like material that surrounds the internal parts of a cell. A. chloroplast B. nucleus C. cytoplasm D. Mitochondria 4. The system that fights disease and other foreign agents. A. circulatory B. immune C. endocrine D. urinary 5. Mucus, skin, tears, saliva, and ____________ are all part of your first line of defense. A. earwax B. eyeball C. finger nail D. tongue 6. __________ are chemical message made by endocrine glands. A. hormones B. cells C. tissues D. glucose * Chapter 8 Lesson 1 Big Idea: All living things are made of cells. To stay alive and healthy, cells need food, water, and a way to eliminate waste. A single cell is the smallest structure that carries out the activities necessary for life. *Animals and plant cells have 3 features in common: 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. cytoplasm cell membrane: outer covering of the cell; water & food enter through it; wastes move out of the membrane nucleus: part of cell that directs all cell activities & carries info for cell reproduction cytoplasm: gel-like material that spreads around the internal parts of the cell Organelle: structure that has a specific task within the cell *for example: mitochondria (energy), vacuoles (stores materials), golgi bodies (transports), endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus cell control center; reproduction Cell Membrane structure and transport Only plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts. cell walls: adds support to a plant cell chloroplast: organelle that makes food from sunlight, water & carbon dioxide Cell Transportation • A cell membrane allows water, gases, and wastes to pass in and out of the cell. • Cell membranes use both passive & active transport. passive transport no energy needed active transport requires energy passive transport Diffusion: process that spreads substances through a gas or liquid from a HIGHER to a LOWER concentration Active transport requires energy & goes from LOWER to HIGHER. Special Type of Diffusion: Osmosis: a type of diffusion that allows water to pass, but not the solutes in the water; keeps water inside the cells Using Energy Photosynthesis: process that plants use to make food by using the energy of sunlight chloroplasts Photosynthesis takes place in the ___________ and depends on a green pigment called chlorophyll. Sugar that plants produce in photosynthesis is glucose called _________. Mitochondria breaks down these sugars into energy. The energy is stored in an ATP molecule. Did you know? Your body is made up of trillions of cells. Yet you began as just a single cell! How did you grow? Cell division * Chapter 8 Lesson 2 Main Idea: Complex organisms have many types of cells. Each cell has special structures that allow it to carry out specific tasks. Different Cells for Different Jobs Tissues: group of cells that has a common structure and function Organs: 2 or more types of tissues that work together Example: brain, heart, kidneys Organ systems: group of organs that work together to perform complex tasks Organ Systems The more complex the organism, the greater the number of organ systems it needs to survive. Humans have 11 organ systems. Each system plays a particular role in the body. Systems influence each other. Some organs work for more than one system. ORGAN SYSTEM FUNCTION Circulatory System carries oxygen and removes CO2 via blood Musculoskeletal System Nervous System supports body and allows you to move Endocrine System works like a chemical communication system; has glands that produces hormones Respiratory System exchanges oxygen and CO2 between the organism and the environment (breathing) controls movements and other organ systems; brain-controlled Hormone: chemical message that travels through the blood and carries special info. Humans have about 50 hormones. They do things such as regulate growth and energy use, control blood sugar, and cause specific body changes Organ Systems (7 of the 11 systems) Circulatory System Digestive System Endocrine System Musculoskeletal System Nervous System Respiratory System Urinary System Organization of Living Things cells tissues organs organ systems organisms * Chapter 8 Lesson 3 infectious disease: contagious; disease caused by organisms or viruses noninfectious disease: disease caused by malfunction of an organ system immune system: organ system that fights disease & foreign agents 1st line of defense Includes ways your body stops disease agents from entering the body Examples: skin, tears, saliva, ear wax, mucus 2nd line of defense Starts if harmful agents enter your body inflammation: blood reacts to fight infection phagocytes: cells surround & consume harmful disease agents 3rd Line of Defense Immune System - this system fights harmful agents of disease *produces antibodies to fight invading agents A vaccination puts a small amount of a live or dead virus into the body. The vaccine causes the immune system to develop antibodies. In summary, The Human Body’s Defenses Against Disease tears, saliva, mucus, skin, ear wax inflammation phagocytes immune system Let’s see what you have learned! Diffusion is ________ passive transport that allows water to pass through the membrane from an high to ____ low concentration. area of _______ We start as a single cell. We grow as a result cell division of ________________. Cytoplasm ____________ is a gel-like material that surrounds the internal parts of a cell. A sugar that plants produce through glucose photosynthesis is _______________. Phagocytes ______________ are cells that surround and consume harmful organisms that invade the body. circulatory The _____________ system carries blood (which contains oxygen) to all parts of the body. immune system fights disease. The __________ Hormones _____________ are chemical message made by endocrine glands. (hint: efgh) ORGAN SYSTEMS brain is the center; controls other parts of the body carries blood & oxygen all over the body circulatory system nervous system has glands that produces chemical messages called hormones supports the body and allows for movement musculoskeletal system word bank: musculoskeletal endocrine endocrine system circulatory nervous Study Guide 3 things cells have in common: cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm 2 things plants cells have that animal cells don’t: cell wall, chloroplasts organ systems 1st, 2nd, 3rd defense systems Vocabulary diffusion glucose cell division hormones phagocytes